I'm trying to understand the appropriate settings for vs code so that I can import local .py files from different sub directories in my vs code project. I ended up solving my problem by adding sub directories I need to import from to PYTHONPATH in my .env file like so: PYTHONPATH = "dir_relative_path1;dir_relative_path2...". However I also tried fixing my problem by adding directories to extrapaths in my .env like so: extrapaths = ["dir_relative_path1", "dir_relative_path2", ...] but this didn't work.
On top of that I also tried changing python.analysis.extraPaths in my settings.json file like so python.analysis.extraPaths= ["dir_relative_path1", "dir_relative_path2", ...] but this also didn't work.
I was hoping someone could clarify the different usages of settings.json vs .env and PYTHONPATH vs extrapaths etc in the context of VS CODE knowing where to look for imports.
CodePudding user response:
First of all, it needs to be clear that vscode uses the opened folder as the workspace. In python, if you want to import modules in different folders, you have to add pythonpath to specify the path, otherwise an error will occur.
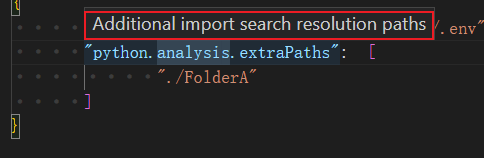
But in fact, even if you add pythonpath, sometimes importing in vscode will still display a yellow warning prompt error. This is because the python extension's intellisense has not detected the imported module, so you need to add "python.analysis.extraPaths" to eliminate the warning.
It can be simply understood that the pythonpath of .env really tells the interpreter that the path of the imported package is that the code can run normally without reporting an error. The "python.analysis.extraPaths" in settings.json only provides the path for the python extension's intellisense, but it does not work for the code to run. You can see that vscode's interpretation of this setting is Additional import search resolution paths.