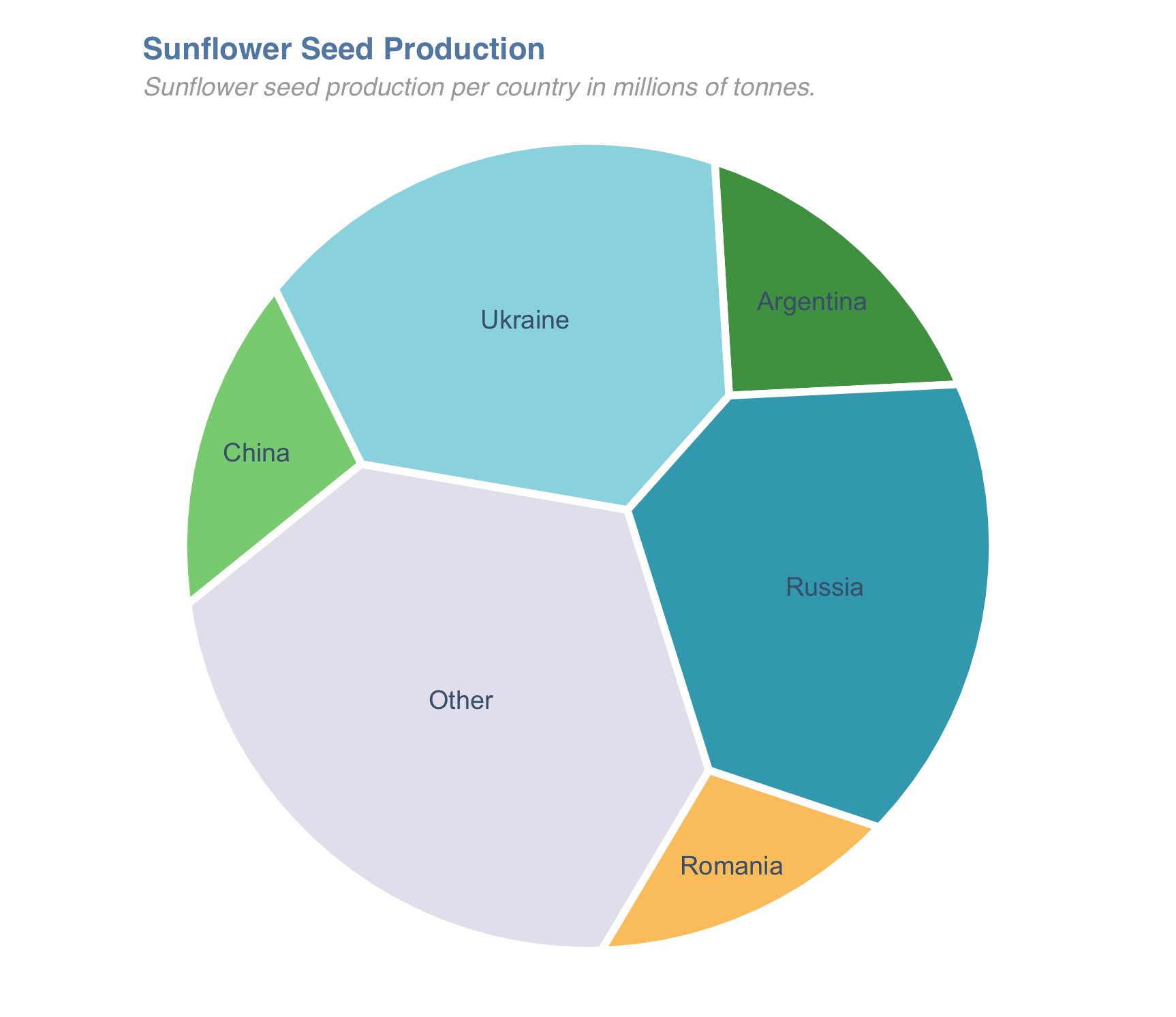
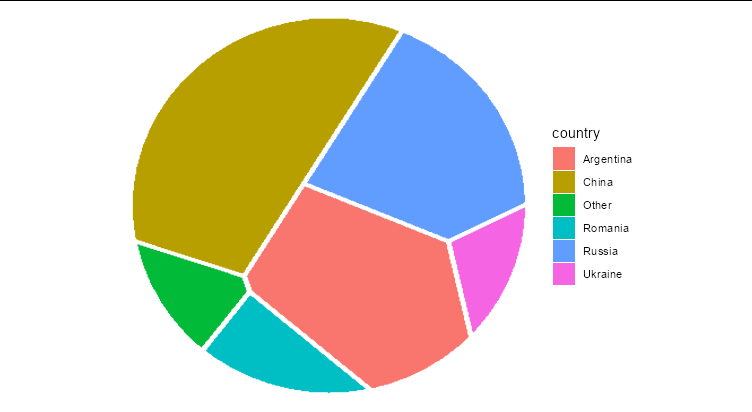
I have a data frame that looks like this. It contains the sunflower seed productivity of each country. I want to add next to this data polygon data so I can plot it with ggplot2.
CodePudding user response:
It's relatively easy to make a Voronoi tasselation in R, but it's harder to make a Voronoi treemap. The linked Q&A does it by using the voronoiTreemap package, which is essentially just a wrapper round a JavaScript library. As far as I can tell, this is the only published R package that generates Voronoi treemaps.
Our two options are to calculate the polygons ourselves from scratch, or somehow extract the polygons from the SVG output of voronoiTreemap.
With regards to the first option, this is not a trivial problem. To see just how complex it is, and also to get a fully worked solution in R, you can check out 
Now click on Export -> Save as image and save your plot as Rplot.png
Now we can do
polygons <- rast('Rplot02.png')[[2]] %>%
app(fun = function(x) ifelse(x > 220, 255, 0)) %>%
as.polygons() %>%
sf::st_as_sf() %>%
filter(lyr.1 == 0) %>%
sf::st_buffer(dist = -0.002) %>%
sf::st_coordinates() %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
mutate(country = df$country[L2], prod = df$prod[L2]) %>%
select(-(L1:L3))
Resulting in the following data frame with our polygons:
head(polygons)
#> X Y country prod
#> 1 0.6460000 0.3970068 Ukraine 11
#> 2 0.6460000 0.4054322 Ukraine 11
#> 3 0.6460501 0.4054499 Ukraine 11
#> 4 0.6461468 0.4054900 Ukraine 11
#> 5 0.6462413 0.4055351 Ukraine 11
And we can see that this is a data frame of polygons of the Voronoi treemap by doing:
ggplot(polygons, aes(X, Y, fill = country))
geom_polygon()
coord_fixed(0.52)
theme_void()
CodePudding user response:
There probably is a smart algorithm for this but here is how you could make such a diagram by brute force.
Your data
df <- data.frame(country = c("Ukraine", "Russia", "Argentina", "China", "Romania", "Other"),
prod = c(11.0, 10.6, 3.1, 2.4, 2.1, 15.3))
A function that finds a solution through optimization
library(terra)
vtreeMap <- function(d) {
p <- vect(cbind(0,0), crs=" proj=utm zone=1") |> buffer(1)
A <- expanse(p) * d / sum(d)
f <- function(xy) {
if (any(xy > 1) || any(xy < -1)) return(Inf)
xy <- vect(matrix(xy, ncol=2), crs=crs(p))
e <- extract(p, xy)
if (any(is.na(e[,2]))) return(Inf)
v <- crop(voronoi(xy, bnd=p), p)
mean( (A - expanse(v))^2 )
}
xy <- spatSample(p, length(A)) |> crds() |> as.vector()
opt <- optim(xy, f)
print(paste("MSE:", round(opt$value, 5)))
vp <- vect(matrix(opt$par, ncol=2))
crop(voronoi(vp, bnd=p), p)
}
Call the function
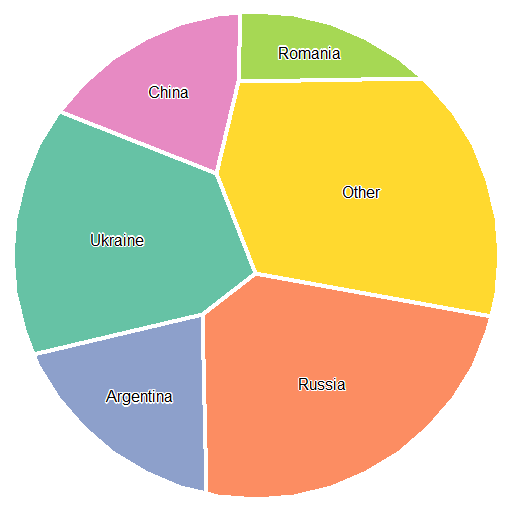
set.seed(3)
vp <- vtreeMap(df$prod)
[1] "MSE: 0.01187"
And plot it
library(RColorBrewer)
vp$country <- df$country
plot(vp, col=brewer.pal(6, "Set2"), axes=FALSE, lwd=4, border="white", mar=rep(0.1, 4))
text(vp, "country", halo=TRUE)
You may need to tweak the optimization procedure (different algorithm, additional options) a bit for the best result (low MSE).
For example, you may use
opt <- optim(xy, f, method="BFGS", control=list(abstol=0.001, maxit=500))
If you do not like this particular solution, change the seed and try again until you find one that pleases you.
If you want to use ggplot2 you can do
library(tidyterra)
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(vp) geom_spatvector(aes(fill = country)) theme_void()