After converting to kotlin the following error occurs: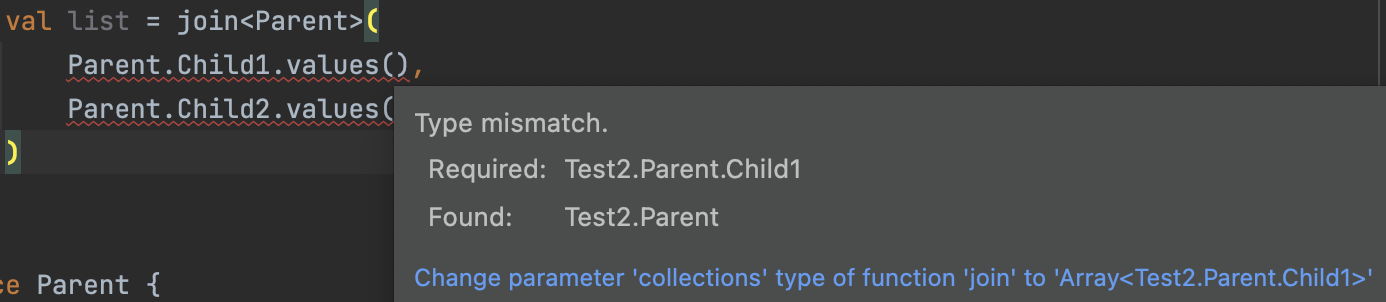
java code. no errors:
public class Test {
public void getList() {
List<Parent> list = join(
Parent.Child1.values(),
Parent.Child2.values()
);
}
public interface Parent {
enum Child1 implements Parent {}
enum Child2 implements Parent {}
}
public <T> List<T> join(T[]... collections) {
ArrayList<T> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (T[] collection : collections) {
result.addAll(Arrays.asList(collection));
}
return result;
}
}
kotlin code. type mismatch error
class Test2 {
val list: Unit
get() {
val list = join<Parent>(
Parent.Child1.values(),
Parent.Child2.values()
)
}
interface Parent {
enum class Child1 : Parent
enum class Child2 : Parent
}
fun <T> join(vararg collections: Array<T>): List<T> {
val result = ArrayList<T>()
for (collection in collections) {
result.addAll(collection.toList())
}
return result
}
}
Help me please, how i can fix this error?
No idea how to fix it
CodePudding user response:
I believe it is an error in the design of Java's generics implementation that allows you to do that. It leaves open the possibility of a T (Parent in this case) being put into an array that can only accept some subtype of T, which will throw an exception at runtime.
Kotlin is more strict with generics, preventing possible runtime crashes from any accidental assumptions like that you could make.
Change the type of the function parameter to Array<out T>. This means it's an Array that you can pull Parents out of, but the compiler will prevent you from putting any arbitrary subtype of Parent into it (it's a Parent producer, but not consumer). That means an array of Child1 or Child2 is a valid subtype of an array of Parents that only produces.
fun <T> join(vararg collections: Array<out T>): List<T> {
//...
