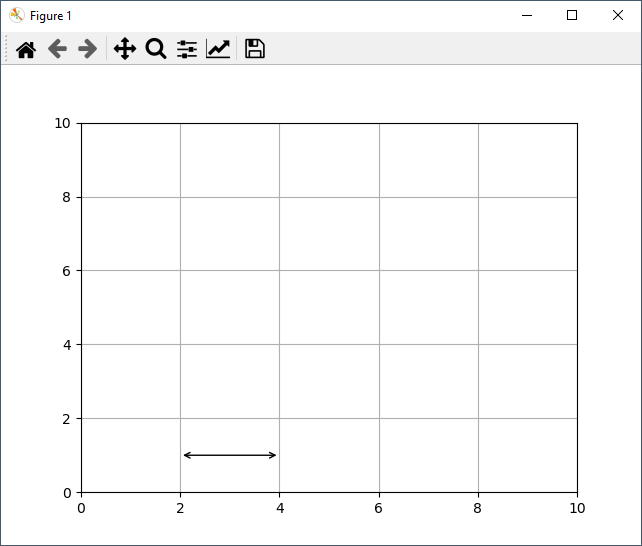
Consider the following simple example:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot()
ax.plot([0],[0])
ax.grid()
ax.set_xlim([0,10])
ax.set_ylim([0,10])
ax.annotate("", (2, 1), (4, 1), arrowprops={'arrowstyle':'<->'})
plt.show()
So, with the ax.annotate, I want to draw an arrow from point (x=2, y=1) to point (x=4, y=1); however the output is this:
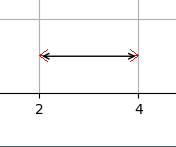
As visible on the screenshot, the arrowheads do not come to exactly the endpoints (x=2, y=1) and (x=4, y=1) - but instead, there is a small amount of whitespace "padding" or "margin".
How can I have the arrow endpoints (the tips of the arrowheads) to align exactly with the stated endpoints? To make it explicit, I tried editing the image above, and manually drawing the arrowheads (in read) where I'd want them to be:
Thanks to comment by @JodyKlymak, I looked into 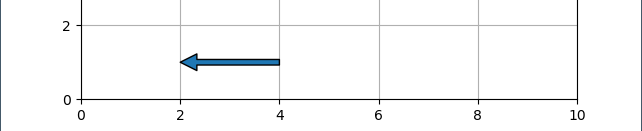
So, let me reformulate - is it possible to get "correct" full-length arrow, with the default left-right arrow from ax.annotate (the one that looks just like a line, and not as a thicker filled surface)?
CodePudding user response:
Ok, I finally got it; the piece of information I was missing from 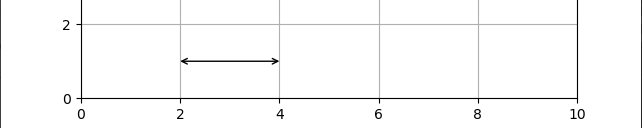
CodePudding user response:
It's not possible to use shrink with 'arrowstyle':'<->' as you mentioned. However, you can use duplicate of ax.annotate("", (2, 1), (4, 1), arrowprops={'shrink': 0}) as in:
ax.annotate("", (2, 1), (4, 1), arrowprops={'width': 0.01,'facecolor':'black','shrink': 0})
ax.annotate("", (4, 1), (2, 1), arrowprops={'width': 0.01,'facecolor':'black','shrink': 0})