I have this code here:
But I get the error message:
The operator < is undefined for the argument type(s)LocalTime, int
Why is that? How can I fix the code?
Here is the code again as text:
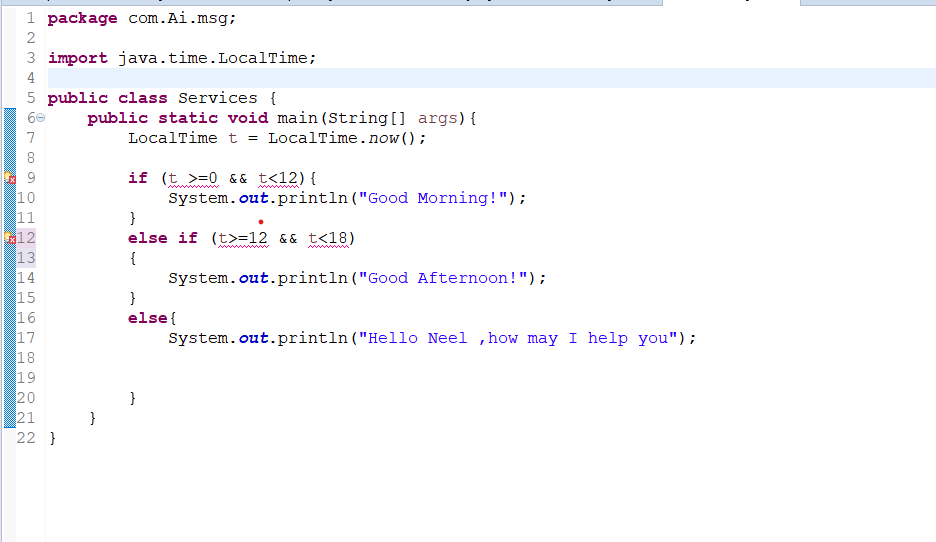
import java.time.LocalTime;
public class Services {
public static void main(String[] args){
LocalTime t = LocalTime.now();
if (t >=0 && t<12){
System.out.println("Good Morning!");
}
else if (t>=12 && t<18)
{
System.out.println("Good Afternoon!");
}
else{
System.out.println("Hello Neel ,how may I help you");
}
}
}
CodePudding user response:
Comparing objects
You can not use < on anything else than primitives like int. Use compareTo instead.
Like first.compareTo(second), the result is either
- negative (if smaller),
0(if equals) or- positive greater 0 (if greater).
So the equivalent of to first < second would be first.compareTo(second) < 0.
Comparing LocalTime in particular
For the java.time API, there are also special methods like isBefore and isAfter which make this comparison even simpler.
LocalTime vs int
Also, you can not compare a high level object such as LocalTime to a plain int. Have a look at
LocalTime.of(12, 0)
and similar methods instead.
There are also some special pre-created constants, such as LocalTime.MIDNIGHT and LocalTime.NOON.
Putting everything together
If you follow both advices, the fixed code could look like:
LocalTime t = LocalTime.now();
if (t.isAfter(LocalTime.MIDNIGHT) && t.isBefore(LocalTime.NOON)) {
System.out.println("Good Morning!");
} else if (t.isAfter(LocalTime.NOON) && t.isBefore(LocalTime.of(18, 0))) {
System.out.println("Good Afternoon!");
} else {
System.out.println("Hello Neel, how may I help you");
}
Ideally you could also introduce a quick helper method such as
private static boolean isBetween(LocalTime start, LocalTime time, LocalTime end) {
return time.isAfter(start) && time.isBefore(end);
}
to simplify the code further:
LocalTime t = LocalTime.now();
if (isBetween(LocalTime.MIDNIGHT, t, LocalTime.NOON)) {
System.out.println("Good Morning!");
} else if (isBetween(LocalTime.NOON, t, LocalTime.of(18, 0))) {
System.out.println("Good Afternoon!");
} else {
System.out.println("Hello Neel, how may I help you");
}
CodePudding user response:
The straightforward way to translate your code into something that works is
LocalTime t = LocalTime.now();
int h = t.getHour();
and then compare 'h'.
For more complicated cases, for example if you wanted to check whether it was before 12:30, look into constructions like
t.isBefore(LocalTime.of(12, 30))
or possibly
!LocalTime.of(12, 30).isAfter(t);
(The two differ in the decision of the exact time 12:30)
CodePudding user response:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalTime t = LocalTime.now();
int h = t.getHour();
if (h >= 0 && h < 12) {
System.out.println("Good Morning!");
} else if (h >= 12 && h < 20) {
System.out.println("Good Afternoon!");
} else {
System.out.println("Hello Neel ,how may I help you");
}
}
}This worked for me