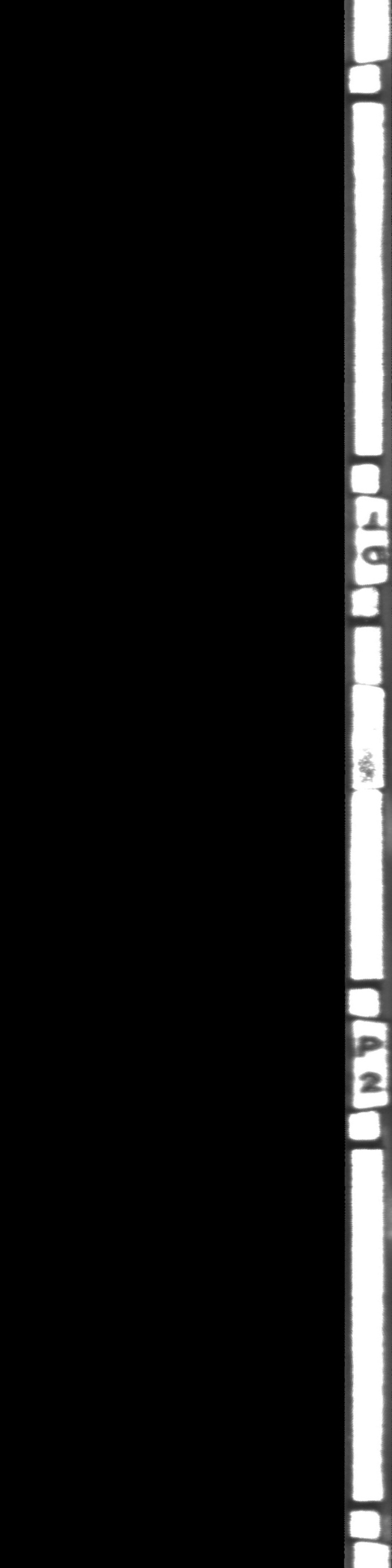
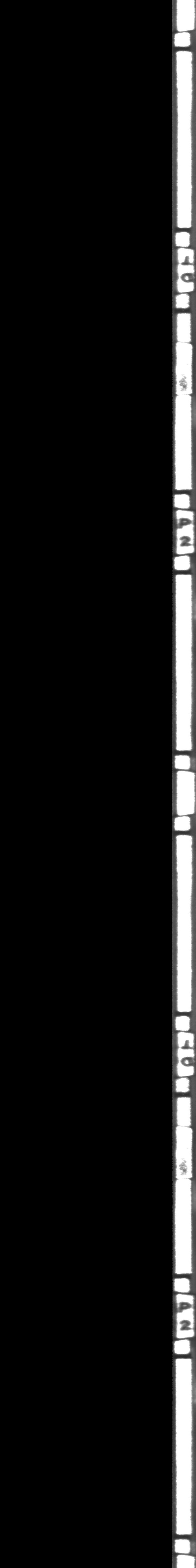
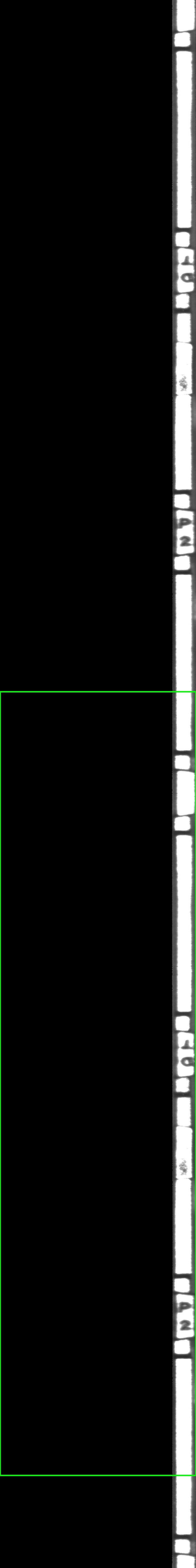
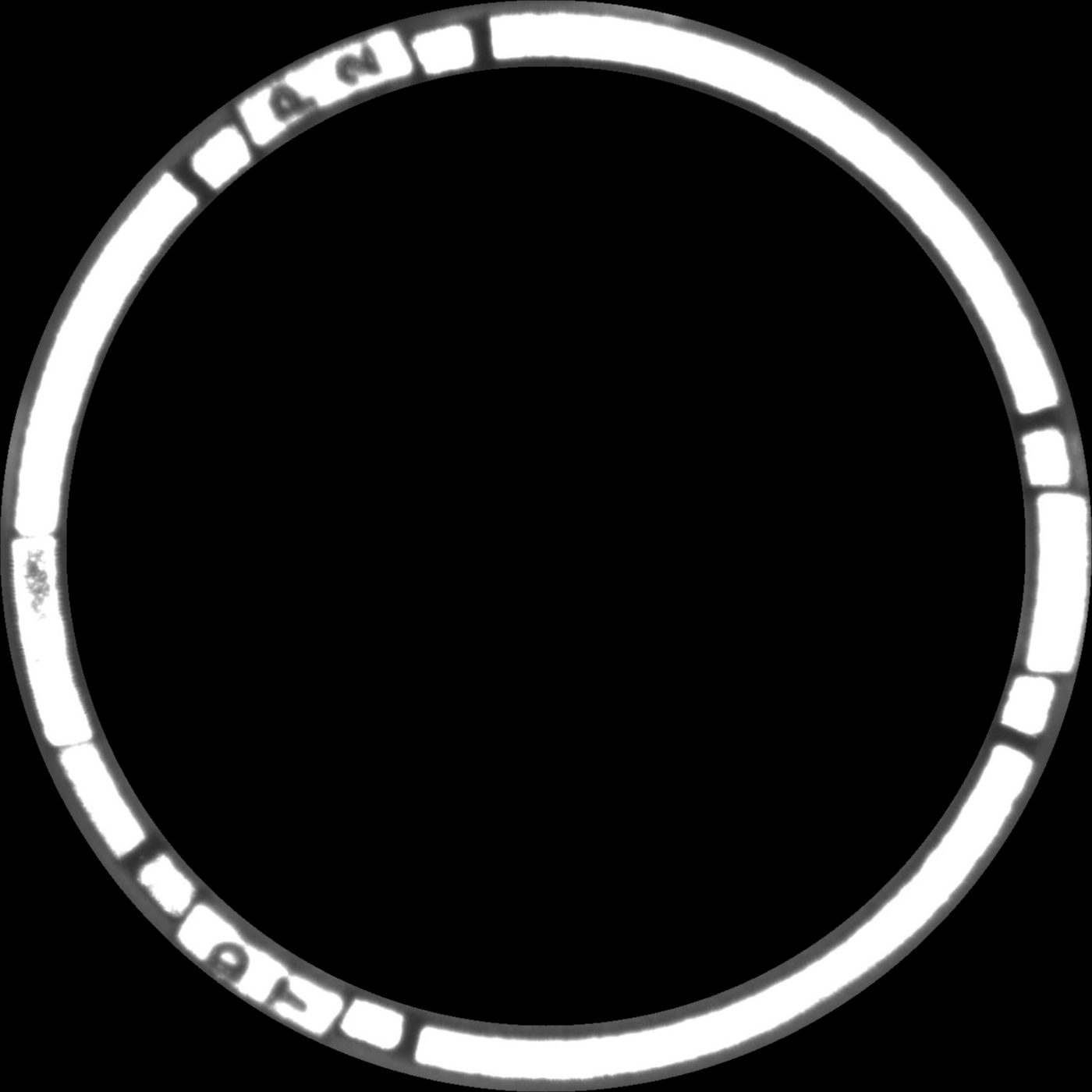
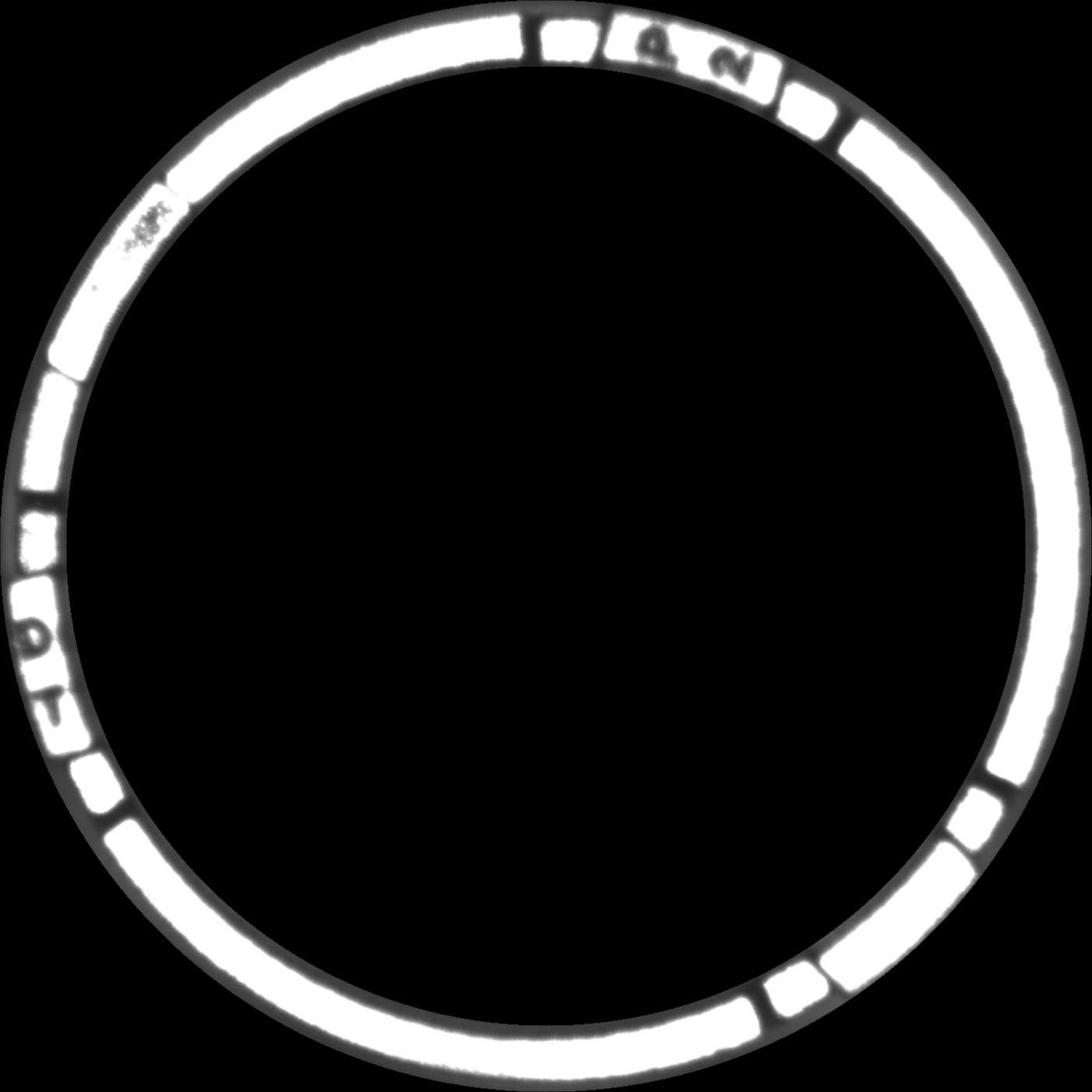
I'm trying to detect angle difference between two circular objects, which be shown as 2 image below.
I'm thinking about rotate one of image with some small angle. Every time one image rotated, SSIM between rotated image and the another image will be calculated. The angle with maximum SSIM will be the angle difference.
But, finding the extremes is never an easy problem. So my question is: Are there another algorithms (opencv) can be used is this case?
EDIT:
Thanks @Micka, I just do the same way he suggest and remove black region like @Yves Daoust said to improve processing time. Here is my final result:
ORIGINAL IMAGE
 ROTATED SHIFTED IMAGE
ROTATED SHIFTED IMAGE
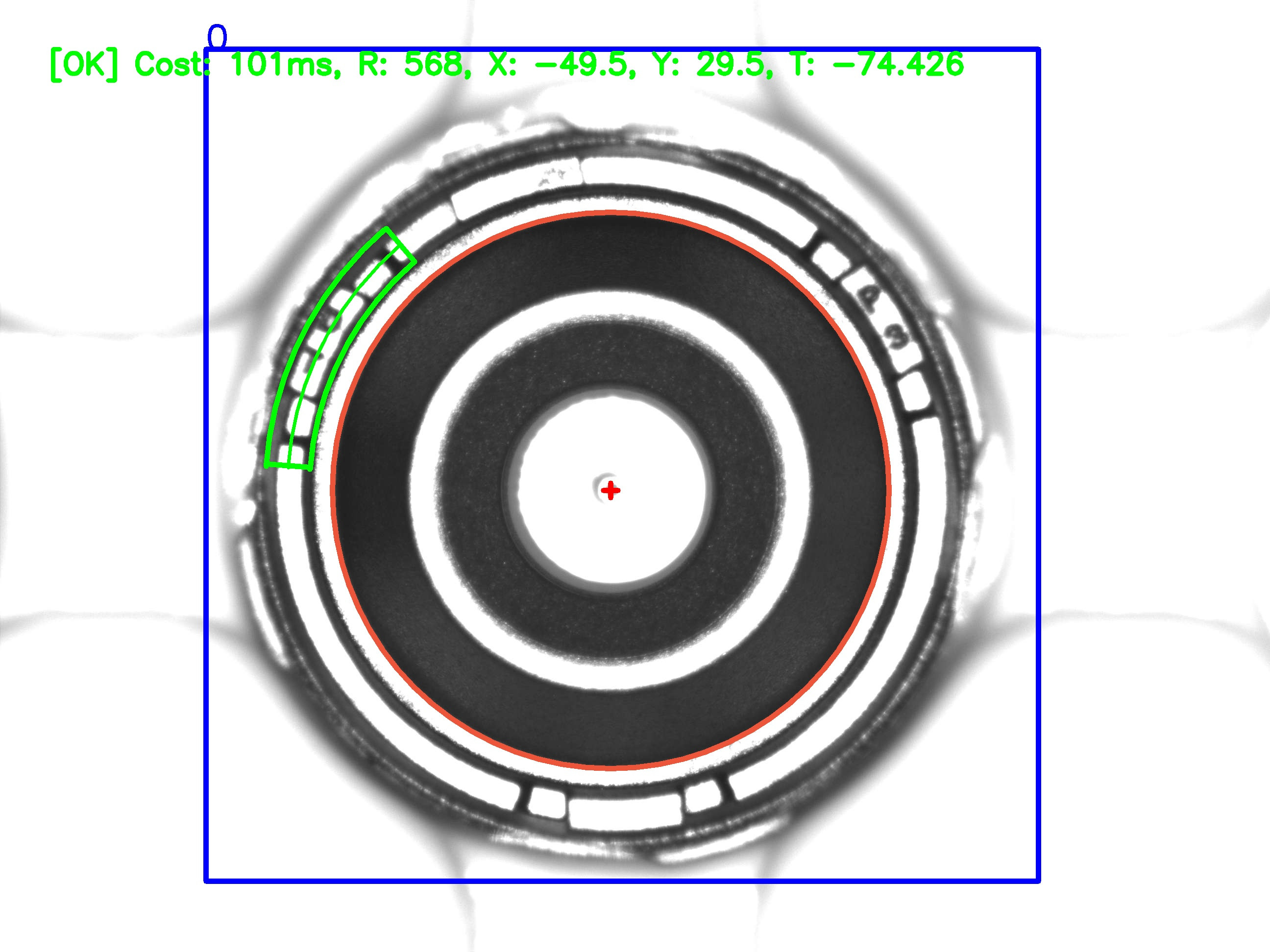
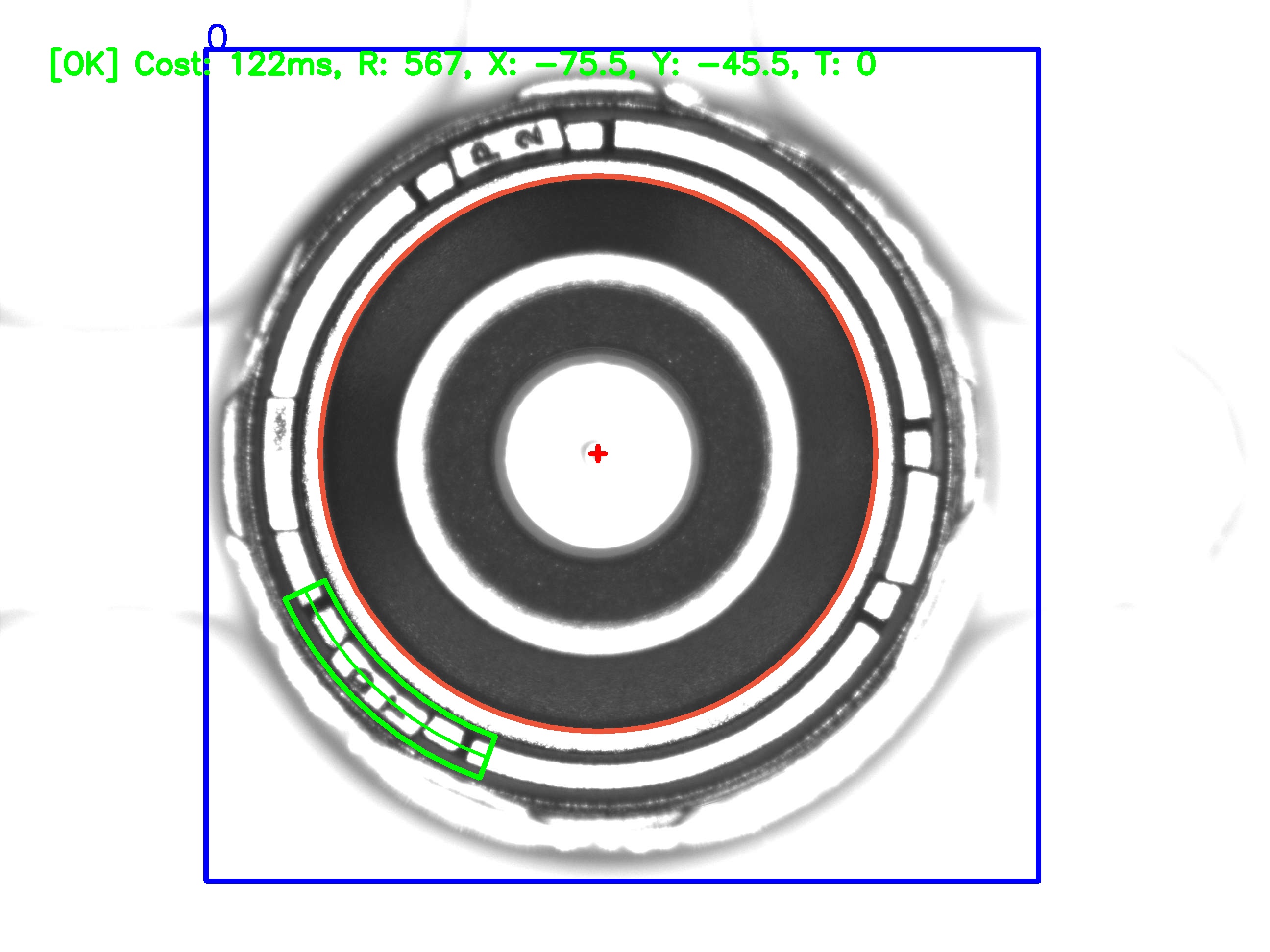
CodePudding user response:
Here's a way to do it:
- detect circles (for the example I assume circle is in the image center and radius is 50% of the image width)
- unroll circle images by polar coordinates
- make sure that the second image is fully visible in the first image, without a "circle end overflow"
- simple template matching
Result for the following code:
min: 9.54111e 07
pos: [0, 2470]
angle-right: 317.571
angle-left: -42.4286
I think this should work quite well in general.
int main()
{
// load images
cv::Mat image1 = cv::imread("C:/data/StackOverflow/circleAngle/circleAngle1.jpg");
cv::Mat image2 = cv::imread("C:/data/StackOverflow/circleAngle/circleAngle2.jpg");
// generate circle information. Here I assume image center and image is filled by the circles.
// use houghCircles or a RANSAC based circle detection instead, if necessary
cv::Point2f center1 = cv::Point2f(image1.cols/2.0f, image1.rows/2.0f);
cv::Point2f center2 = cv::Point2f(image2.cols / 2.0f, image2.rows / 2.0f);
float radius1 = image1.cols / 2.0f;
float radius2 = image2.cols / 2.0f;
cv::Mat unrolled1, unrolled2;
// define a size for the unrolling. Best might be to choose the arc-length of the circle. The smaller you choose this, the less resolution is available (the more pixel information of the circle is lost during warping)
cv::Size unrolledSize(radius1, image1.cols * 2);
// unroll the circles by warpPolar
cv::warpPolar(image1, unrolled1, unrolledSize, center1, radius1, cv::WARP_POLAR_LINEAR);
cv::warpPolar(image2, unrolled2, unrolledSize, center2, radius2, cv::WARP_POLAR_LINEAR);
// double the first image (720° of the circle), so that the second image is fully included without a "circle end overflow"
cv::Mat doubleImg1;
cv::vconcat(unrolled1, unrolled1, doubleImg1);
// the height of the unrolled image is exactly 360° of the circle
double degreesPerPixel = 360.0 / unrolledSize.height;
// template matching. Maybe correlation could be the better matching metric
cv::Mat matchingResult;
cv::matchTemplate(doubleImg1, unrolled2, matchingResult, cv::TemplateMatchModes::TM_SQDIFF);
double minVal; double maxVal; cv::Point minLoc; cv::Point maxLoc;
cv::Point matchLoc;
cv::minMaxLoc(matchingResult, &minVal, &maxVal, &minLoc, &maxLoc, cv::Mat());
std::cout << "min: " << minVal << std::endl;
std::cout << "pos: " << minLoc << std::endl;
// angles in clockwise direction:
std::cout << "angle-right: " << minLoc.y * degreesPerPixel << std::endl;
std::cout << "angle-left: " << minLoc.y * degreesPerPixel -360.0 << std::endl;
double foundAngle = minLoc.y * degreesPerPixel;
// visualizations:
// display the matched position
cv::Rect pos = cv::Rect(minLoc, cv::Size(unrolled2.cols, unrolled2.rows));
cv::rectangle(doubleImg1, pos, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4);
// resize because the images are too big
cv::Mat resizedResult;
cv::resize(doubleImg1, resizedResult, cv::Size(), 0.2, 0.2);
cv::resize(unrolled1, unrolled1, cv::Size(), 0.2, 0.2);
cv::resize(unrolled2, unrolled2, cv::Size(), 0.2, 0.2);
double startAngleUpright = 0;
cv::ellipse(image1, center1, cv::Size(100, 100), 0, startAngleUpright, startAngleUpright foundAngle, cv::Scalar::all(255), -1, 0);
cv::resize(image1, image1, cv::Size(), 0.5, 0.5);
cv::imshow("image1", image1);
cv::imshow("unrolled1", unrolled1);
cv::imshow("unrolled2", unrolled2);
cv::imshow("resized", resizedResult);
cv::waitKey(0);
}
This is how the intermediate images and results look like:
unrolled image 1 / unrolled 2 / unrolled 1 (720°) / best match of unrolled 2 in unrolled 1 (720°):