I have:
- regular visitors
- merchants
- and of course our admins and internal team
Do I store all user accounts in the [regular visitors] database, then separate "sensitive" data into a [merchants] and an [internal] database to ensure at least some kind of security or is there a better alternative?
Also, I'm using Entity Framework to build the database - although I'm currently only working on the web interface, I eventually want to add a mobile app interface and possibly a windows app interface to the project - how do I ensure the models are shared so I don't have redundant code to duplicate?
Any help is sincerely appreciated.
Thanks.
*Currently storing all data in a singular database.
CodePudding user response:
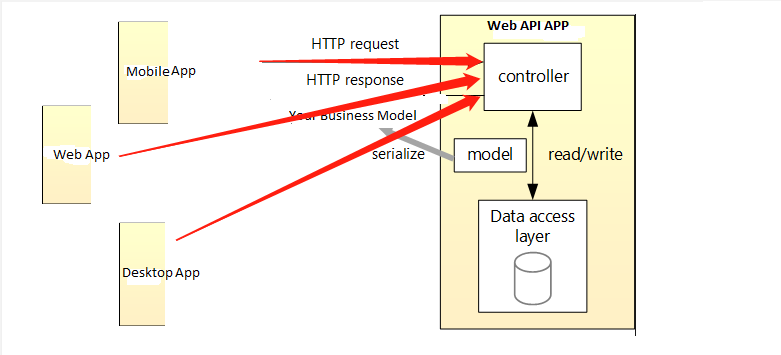
Let's clarify few things before starting, if you could observe now a days, all typical modern application handle request either from mobile device or web browser (all the platforms like Windows, Mac, Linux). and from the desktop platform. See the drawing below:
Application Architecture:
Therefore, the request are coming from different devices, which we call (cross platform) but we can make the endpoint universal. There are different technology out there. You could consider Asp.net Web API
Now come to your point.
"How do I ensure the models are shared so I don't have redundant code to duplicate?"
There are couple of way to restrict code redundancy. You can consider
SOLID principle. Within theSOLIDyou could specifically implementSingle Responsibilitymeansa class should only have one responsibilityadditionally you could implementInheritanceofOOPso that you can reuse of the base code in your derive class when yourproject/applicationwould continuously extended.
There are bundle of example you could found online for above terms.
So what I am trying to explain is make the your backend application universal so that it can handle all the request no matter where they are coming from. So that it would be easier for you to handle code reusability and eventually it would restrict the redundancy as well.
Now Consider Your Domain Model:
Into your
ApplicationDbContextyou can now define all of yourdomain modellike you can think of your business model as the domain model for example:RegularVisitors,Merchantsandadmins and internal teamasUsersdomain model, You can design yourApplicationDbContextas below:
public class ApplicationDbContext: DbContext
{
public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Merchants> Merchants{ get; set; }
public DbSet<RegularVisitors> RegularVisitors{ get; set; }
public DbSet<User> User { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Merchants>().ToTable("Merchants");
modelBuilder.Entity<RegularVisitors>().ToTable("RegularVisitors");
modelBuilder.Entity<User>().ToTable("User");
}
}
This is how you could move forward considering your requirement. For details implementation you could consider
this threadto implement your requirement accordingly
Hope above steps and implementations guided you accordingly.