I'm making a card game and want to use the Unicode playing cards which range from U 1F0A0 to U 1F0DE.
Is there a way to create a partial Unicode sequence such as "\U0001F0" and then concatenate the last two digits on the end, or some way to change the last two digits of a full sequence to the ones needed?
I have tried StringBuilder, ToCharArray, .Insert, .Remove, .Add, .Replace etc, to replace the last two digits.
I have tried,
string cardCode = "\U0001F0" suit value;
string cardCode = "@\U0001F0" suit value;
string cardCode = $"\U0001F0{suit}{value}";
but of course the last two only display the string as plaintext, and the first one is an invalid escape sequence.
CodePudding user response:
Write a case based on your needs.
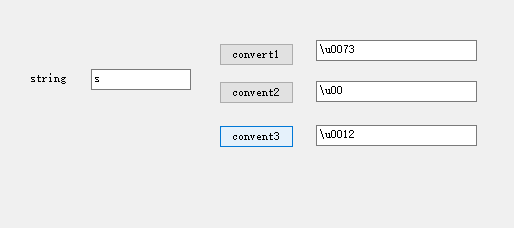
UI page:
Achieve effect:
Code logic: Variables are converted to Unicode strings, and then the last 2 digits are replaced.
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string s = textBox1.Text;
char[] charbuffers = s.ToCharArray();
byte[] buffer;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < charbuffers.Length; i )
{
buffer = System.Text.Encoding.Unicode.GetBytes(charbuffers[i].ToString());
sb.Append(String.Format("\\u{0:X2}{1:X2}", buffer[1], buffer[0]));
}
textBox2.Text = sb.ToString();
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string s = textBox1.Text;
char[] charbuffers = s.ToCharArray();
byte[] buffer;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < charbuffers.Length; i )
{
buffer = System.Text.Encoding.Unicode.GetBytes(charbuffers[i].ToString());
sb.Append(String.Format("\\u{0:X2}{1:X2}", buffer[1], buffer[0]));
}
s = sb.ToString().Substring(0, sb.ToString().Length - 2);
textBox3.Text = s;
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string s = textBox1.Text;
char[] charbuffers = s.ToCharArray();
byte[] buffer;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < charbuffers.Length; i )
{
buffer = System.Text.Encoding.Unicode.GetBytes(charbuffers[i].ToString());
sb.Append(String.Format("\\u{0:X2}{1:X2}", buffer[1], buffer[0]));
}
s = sb.ToString().Substring(0, sb.ToString().Length - 2);
s = s.Insert(4, "12");
textBox4.Text = s;
}
}
hope it helps you.
CodePudding user response:
There is a Unicode codepoint for each playing cards. The same value for different suits are multiples of 16 apart. And the values are nicely ordered from 1 for the ace to 14 for the king. So the effective codepoint can easily be calculated.
As proposed in the comments, Char.ConvertFromUtf32() will convert the integer codepoint into a string:
using System;
public class Card
{
public const int Spade = 0;
public const int Hearts = 1;
public const int Diamonds = 2;
public const int Clubs = 3;
public const int Ace = 1;
public const int Two = 2;
public const int Three = 3;
public const int Four = 4;
public const int Five = 5;
public const int Six = 6;
public const int Seven = 7;
public const int Eight = 8;
public const int Nine = 9;
public const int Ten = 10;
public const int Jack = 11;
public const int Knight = 12;
public const int Queen = 13;
public const int King = 14;
public static string CardString(int suit, int val) {
return Char.ConvertFromUtf32(0x1F0A0 suit * 16 val);
}
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(CardString(Spade, Eight));
Console.WriteLine(CardString(Diamonds, Ace));
Console.WriteLine(CardString(Hearts, Queen));
Console.WriteLine(CardString(Clubs, King));
}
}
The result is: