I've been trying to do something like a numpy.array_split(), but to split it like this instead:
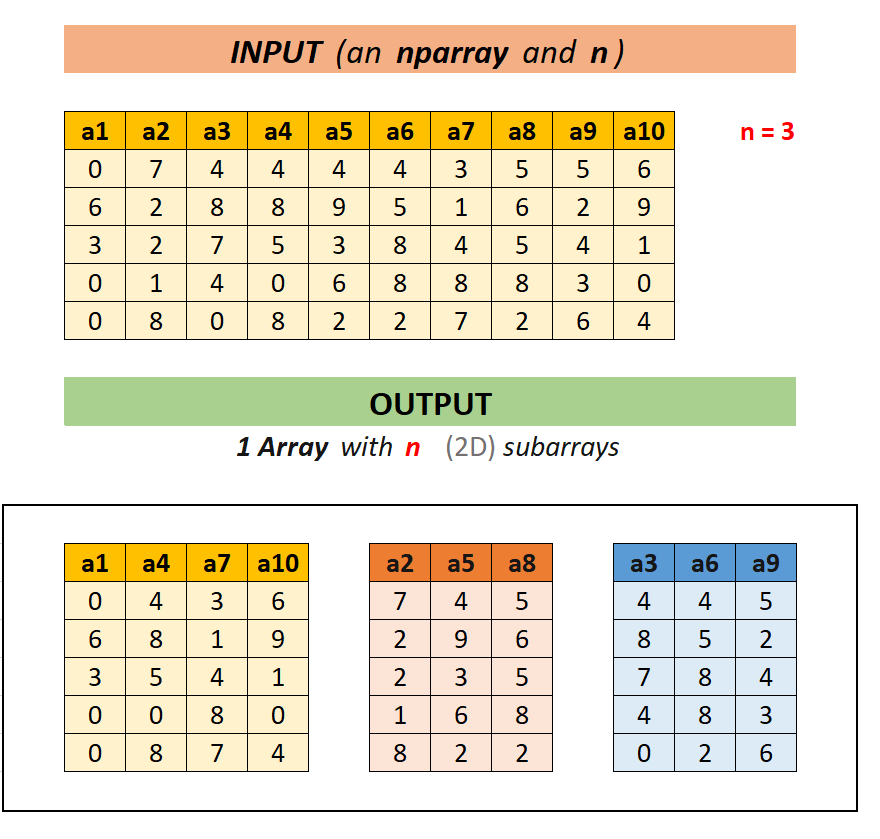 So It would return an array (for example let's call it output[] ) with n 2D subarrays inside of it.
So It would return an array (for example let's call it output[] ) with n 2D subarrays inside of it.
For example (for n = 3):
- output[0] would return the (yellow) subarray with columns a1, a4, a7, a10,
- output[1] would return the (red) subarray with columns a2, a5, a8,
- output[2] would return the (blue) subarray with columns a3, a6, a9.
def split(arr, n):
output= [[] for _ in range(n)]
for v, help in zip(arr, cycle(out)):
help.append(v)
return output
I don't know how to combine rows into one 2D array, so I have many 1D arrays instead of one 2D.
CodePudding user response:
Not sure if a native solution exists but you can use:
# get groups
group = np.arange(a.shape[1])%n
# groups sorting order
order = np.argsort(group)
# get counts of each group (in order as the output is sorted)
_, idx = np.unique(group, return_counts=True)
# split the reindexed array
out = np.split(a[:, order], np.cumsum(idx[:-1]), axis=1)
Output:
[array([[ 0, 3, 6, 9],
[10, 13, 16, 19],
[20, 23, 26, 29],
[30, 33, 36, 39],
[40, 43, 46, 49]]),
array([[ 1, 4, 7],
[11, 14, 17],
[21, 24, 27],
[31, 34, 37],
[41, 44, 47]]),
array([[ 2, 5, 8],
[12, 15, 18],
[22, 25, 28],
[32, 35, 38],
[42, 45, 48]])]
Used input:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39],
[40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49]])
CodePudding user response:
You can use slicing [start:end:step] in numpy.array. (understanding-slicing)
n = 3
m = inp.shape[1] // n
output = [inp[:, i::3] for i in range(m)]
Example
import numpy as np
inp = np.arange(50).reshape(5, 10)
n = 3
m = inp.shape[1] // n
output = [inp[:, i::3] for i in range(m)]
print(output)
# [
# array([[ 0, 3, 6, 9], [0::3] -> columns : 0, 3, 6, 9
# [10, 13, 16, 19],
# [20, 23, 26, 29],
# [30, 33, 36, 39],
# [40, 43, 46, 49]]),
# array([[ 1, 4, 7], [1::3] -> columns : 1, 4, 7
# [11, 14, 17],
# [21, 24, 27],
# [31, 34, 37],
# [41, 44, 47]]),
# array([[ 2, 5, 8], [2::3] -> columns : 2, 5, 8
# [12, 15, 18],
# [22, 25, 28],
# [32, 35, 38],
# [42, 45, 48]])
# ]
Input array:
#column: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39],
[40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49]])
CodePudding user response:
Another possible solution, based on map:
n = 3
_, ncols = m.shape
out = list(map(lambda x: m[:, np.arange(0, ncols)[x::n]], np.arange(0,n)))
out
Output:
[array([[0, 4, 3, 6],
[6, 8, 1, 9],
[3, 5, 4, 1],
[0, 0, 8, 0],
[0, 8, 7, 4]]),
array([[7, 4, 5],
[2, 9, 6],
[2, 3, 5],
[1, 6, 8],
[8, 2, 2]]),
array([[4, 4, 5],
[8, 5, 2],
[7, 8, 4],
[4, 8, 3],
[0, 2, 6]])]
