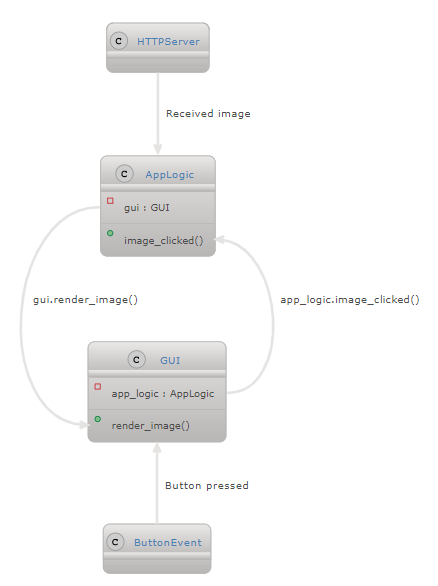
I would like to know, what is the concept of information flow in GUI based apps, or any other app with same problem. When you have two seperate classes and their objects, how is the messeging process done between them. For example you have a GUI and AppLogic.
Scenario 1: Button is pressed -> GUI is processing event -> calls AppLogic method image_clicked()
Scenario 2: HTTPServer gets a message -> AppLogic receives image -> AppLogic calls GUI method render_image()
The problem is that you cannot reference classes each other because the first class does not know the second one (here AppLogic does not know GUI class):
class AppLogic():
gui : GUI
def image_clicked(self):
pass #not important
class GUI():
app_logic : AppLogic
def render_image(self):
pass #not important
I know this is more like go to school and study problem, but I would like to know how these problems are sovled, or some common practices. At least link with some detailed information. I am not able to name the problem right to find the answer.
Edit:
I can use this code without explicit type declaration and it works. But when I want to call functions of gui in AppLogic class definition, intellisense does not hint anything, because it does not know the type of attribute gui. And I don't think that it is good practice to use code like that.
class AppLogic():
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.gui = None
def image_clicked(self):
pass #not important
class GUI():
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.app_logic = None
def render_image(self):
pass #not important
app = AppLogic()
gui = GUI()
app.gui = gui
gui.app_logic = app
CodePudding user response:
You need to initialize your variables.
gui = Gui()
then you can call the methods
For example:
class AppLogic:
gui: Gui
def image_clicked(self):
gui = Gui()
gui.render_image()
class Gui:
logic: AppLogic
def render_image(self) :
pass
Or you can initialize your variable directly
gui: Gui = Gui()
I hope this answers your question
CodePudding user response:
from LogicClass import Logic
class Gui:
logic: AppLogic = AppLogic()
def render_image(self) :
pass
and:
from GuiClass import Gui
class AppLogic:
gui: Gui
def image_clicked(self):
gui = Gui()
gui.render_image()
CodePudding user response:
from Gui import Gui
class Logic:
def __init__(self):
self.gui = Gui()
if __name__ == "__main__":
Logic()
and
class Gui:
def __init__(self):
print("GUI")