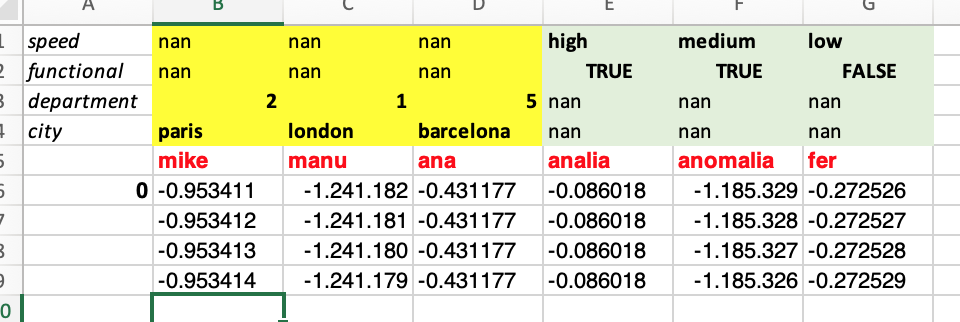
Assuming I have a DF like:
person_names = ['mike','manu','ana','analia','anomalia','fer']
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(5, 6), columns = person_names)
df
I also have two dictionaries, for easy purposes assuming only two:
# giving a couple of dictionaries like:
d = {'mike':{'city':'paris', 'department':2},
'manu':{'city':'london', 'department':1},
'ana':{'city':'barcelona', 'department':5}}
d2 = {'analia':{'functional':True, 'speed':'high'},
'anomalia':{'functional':True, 'speed':'medium'},
'fer':{'functional':False, 'speed':'low'}}
The result I would to achieve is a df having a multindex as shown in the excel screenshot here:
The dictionaries contain values for SOME of the column names.
Not only I need to create the multiindex based on dictionaries but take into account that the keys of the dictionaries are different for both dictionaries, I would also like to keep the original names of the columns as first level of the multiindex.
Any suggestion?
CodePudding user response:
# Easier to use joins when transposed.
dft = df.T
dd2 = pd.DataFrame(d2).T
dd = pd.DataFrame(d).T
# We join indexes together, and then add primary df
dd.join(dd2, how="outer").join(dft).T
Results in
Out[44]:
ana analia anomalia fer manu mike
city barcelona NaN NaN NaN london paris
department 5 NaN NaN NaN 1 2
functional NaN True True False NaN NaN
speed NaN high medium low NaN NaN
0 -0.132317 2.513232 0.481609 -0.948312 1.425882 1.969711
1 -0.893227 -0.208046 -0.190703 -0.200429 -0.960934 -0.568568
2 -0.39221 1.442398 0.77165 0.73143 -1.832893 -0.667037
3 -0.245534 -0.037821 1.194735 0.765611 1.787658 0.65847
4 -0.943287 -0.151373 0.572972 0.079812 1.38536 -1.854453
You can use .set_index prior to the last transposition (.T) To properly set multi index, if required.
CodePudding user response:
Here's a way to do what your question asks for an arbitrary number of dictionaries, with the levels of the MultiIndex in the sequence shown in the OP:
dcts = (d, d2)
out = df.T
all_keys = []
for dct in reversed(dcts):
keys = list(reversed(dct[next(iter(dct))].keys()))
all_keys = keys
out[keys] = [[dct[name][key] if name in dct else None for key in keys] for name in out.index]
out = out.reset_index().rename(columns={'index':'person name'}).set_index(all_keys).T
Output:
speed NaN high medium low
functional NaN True True False
department 2.0 1.0 5.0 NaN NaN NaN
city paris london barcelona NaN NaN NaN
person name mike manu ana analia anomalia fer
0 -0.8392 -0.531491 0.191687 1.147941 0.292531 0.4075
1 0.644307 0.550632 -0.241302 2.20928 -0.91035 -0.514395
2 0.305059 0.123411 0.846471 -0.151596 -0.410483 -1.661958
3 -0.763649 0.109589 2.215242 0.530734 0.261605 0.472373
4 0.153886 -0.782931 1.179735 -0.339259 0.314743 -0.088172
Note that there because of MultiIndex grouping, some values of the levels speed and functional are shown just once and not repeated for columns to the right with the same level value.