I am fairly new to web scraping and am attempting to pull dividend history from yahoo finance for analysis.
How can I reformat a date I scraped? It includes a comma, which causes the year to be in the same column as the dividend when printed to a csv file. I need the date in one column, and the dividend in another. The date needs to be stored in a format that it can be used in python such as MM-DD-YYYY. I've been at this for hours and can't seem to figure it out. Do I need the csv module?
I have included the complete code for reference, the relevant formatting snippet below, and the output at the end.
import os
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import time, requests, pandas, lxml
from lxml import html
from yahoofinancials import YahooFinancials
ticker = input("Enter ticker: ")
#scrape dividends
def format_date(date_datetime):
date_timetuple = date_datetime.timetuple()
date_mktime = time.mktime(date_timetuple)
date_int = int(date_mktime)
date_str = str(date_int)
return date_str
def subdomain(symbol, start, end):
format_url = "{0}/history?period1={1}&period2={2}"
tail_url = "&interval=capitalGain|div|split&filter=div&frequency=1d"
subdomain = format_url.format(symbol, start, end) tail_url
return subdomain
def header(subdomain):
hdrs = {"authority": "finance.yahoo.com",
"method": "GET",
"path": subdomain,
"scheme": "https",
"accept": "text/html,application/xhtml xml",
"accept-encoding": "gzip, deflate, br",
"accept-language": "en-US,en;q=0.9",
"cache-control": "no-cache",
"dnt": "1",
"pragma": "no-cache",
"sec-fetch-mode": "navigate",
"sec-fetch-site": "same-origin",
"sec-fetch-user": "?1",
"upgrade-insecure-requests": "1",
"user-agent": "Mozilla/5.0"}
return hdrs
def scrape_page(url, header):
page = requests.get(url, headers=header)
element_html = html.fromstring(page.content)
table = element_html.xpath('//table')
table_tree = lxml.etree.tostring(table[0], method='xml')
panda = pandas.read_html(table_tree)
return panda
def clean_dividends(symbol, dividends):
index = len(dividends)
dividends = dividends.drop(index-1) #Drop the last row of the dataframe
dividends = dividends.set_index('Date') #Set the row index to the column labelled Date
dividends = dividends['Dividends'] #Store only the dividend column indexed by date into a variable
dividends = dividends.str.replace('\Dividend', '', regex = True) #Remove all the strings in the dividend column
dividends = dividends.astype(float) #Convert the dividend amounts to float values from strings
dividends.name = symbol #Change the name of the resulting pandas series object to the symbol
return dividends
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = datetime.today() - timedelta(days=3650)
end = datetime.today()#properly format the date to epoch time
start = format_date(start)
end = format_date(end)#format the subdomain
sub = subdomain(ticker, start, end)#customize the request header
hdrs = header(sub)
#concatenate the subdomain with the base URL
base_url = "https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/"
url = base_url sub
dividends = scrape_page(url, hdrs) #scrape the dividend history table from Yahoo Finance
clean_div = clean_dividends(ticker, dividends[0]) #clean the dividend history table
print(clean_div)
#print to csv file
# check whether the file exists
if os.path.exists(ticker "_div_hist.csv"):
# delete the file
os.remove(ticker "_div_hist.csv")
f = open(ticker "_div_hist.csv", "w")
f.write(str(clean_div))
f.close()
This is a snippet of the relevant code:
def clean_dividends(symbol, dividends):
index = len(dividends)
dividends = dividends.drop(index-1) #Drop the last row of the dataframe
dividends = dividends.set_index('Date') #Set the row index to the column labelled Date
dividends = dividends['Dividends'] #Store only the dividend column indexed by date into a variable
dividends = dividends.str.replace('\Dividend', '', regex = True) #Remove all the strings in the dividend column
dividends = dividends.astype(float) #Convert the dividend amounts to float values from strings
dividends.name = symbol #Change the name of the resulting pandas series object to the symbol
return dividends
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = datetime.today() - timedelta(days=3650)
end = datetime.today()#properly format the date to epoch time
start = format_date(start)
end = format_date(end)#format the subdomain
sub = subdomain(ticker, start, end)#customize the request header
hdrs = header(sub)
#concatenate the subdomain with the base URL
base_url = "https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/"
url = base_url sub
dividends = scrape_page(url, hdrs) #scrape the dividend history table from Yahoo Finance
clean_div = clean_dividends(ticker, dividends[0]) #clean the dividend history table
print(clean_div)
#print to csv file
# check whether the file exists
if os.path.exists(ticker "_div_hist.csv"):
# delete the file
os.remove(ticker "_div_hist.csv")
f = open(ticker "_div_hist.csv", "w")
f.write(str(clean_div))
f.close()
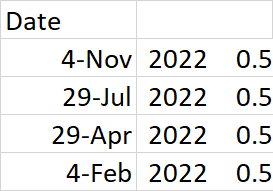
Here is the a shortened example of the output in both terminal and csv format:
Enter ticker: C
Date
Nov 04, 2022 0.51
Jul 29, 2022 0.51
Apr 29, 2022 0.51
Feb 04, 2022 0.51
Name: C, dtype: float64
Thank you for any help that you can provide.
CodePudding user response:
You can convert MonthName Day, Year format into datetime format that you are wishing for with following code snippet:
from datetime import datetime
dateString = "Nov 04, 2022"
datetimeObject = datetime.strptime(dateString, '%b %d, %Y')
print(datetimeObject.strftime('%d-%m-%Y'))
#Output string is '04-11-2022'
If you wish to convert the date into any format in easier way, you can use timestamps. All you need to do is using datetimeObject.timestamp() to obtain timestamp. After that you can use datetime.fromtimestamp(timestamp) function to obtain datetime object from timestamp any time.
So, after that you you can use datetime formatting to get any datetime string you like.
Here is the link that you can learn more about datetime formatting: https://docs.python.org/3/library/datetime.html#strftime-and-strptime-behavior
CodePudding user response:
That is hardly a minimalist reproduction of your problem. What you want to know is how to separate the date and dividend from a string in the format "month day, year dividend". No body wants to wade through the rest of the code. Please in future, try to distill your issue to the most basic code required to reproduce the problem. Having said that, look at the following code:
from datetime import datetime
div_str = 'Feb 04, 2002 0.51'
mon, day, year, div = div_str.split()
date_str = ' '.join([year, mon, day.replace(',', '')])
my_date = datetime.strptime(date_str, "%Y %b %d")
print("Date is: {}".format(my_date.strftime("%Y %m %d")))
print("Div is: {}".format(div))