I'm not sure of how to use numpy.gradient().
to compute the partial derivatives (2nd order) I was using for loops :
for j in range(1, nx-1):
d2px[:, j] = (p[:, j - 1] - 2 * p[:, j] p[:, j 1]) / dx ** 2
for i in range(1, ny-1):
d2py[i, :] = (p[i - 1, :] - 2 * p[i, :] p[i 1, :]) / dy ** 2
And I tried to replace it with numpy.gradient : (for x here)
dpx = np.gradient(p, [1, dx], axis = 0)
d2px = np.gradient(dpx, [1, dx])
But I always have the same error message :
"ValueError: when 1d, distances must match the length of the corresponding dimension"
with the following code :
x = np.linspace(0, nx, nx) # coordonnées selon x...
dpx = np.gradient(p, x, axis = 0)
d2px_test = np.gradient(dpx, x, axis = 0)
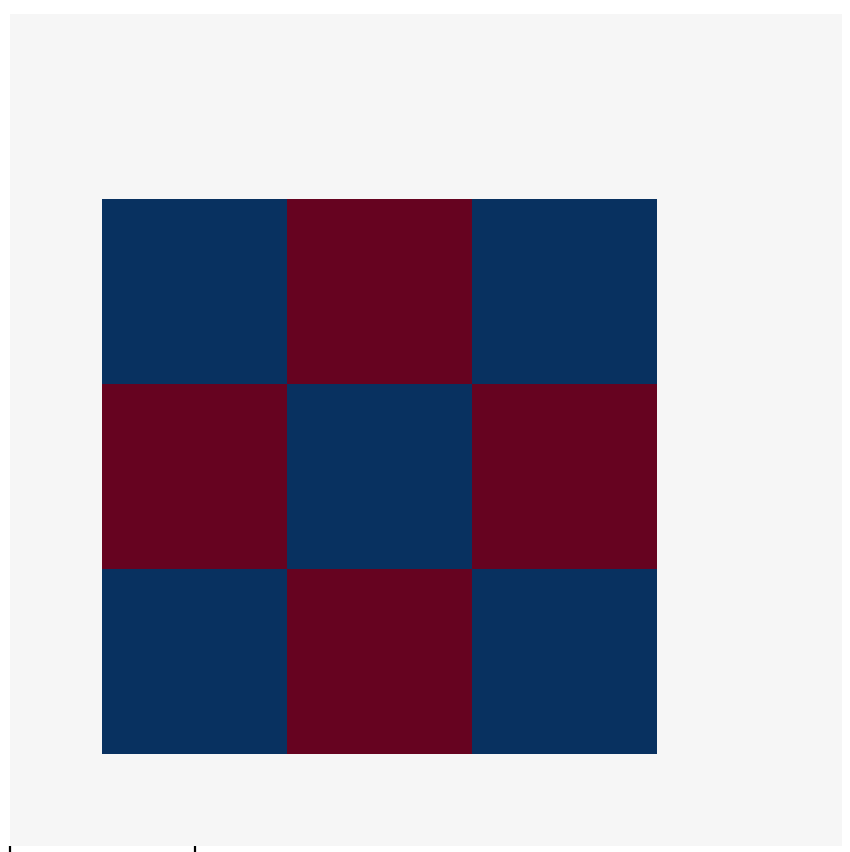
the input p is :
[[ 0.00000000e 00 0.00000000e 00 0.00000000e 00 0.00000000e 00
0.00000000e 00]
[ 0.00000000e 00 6.53832270e-23 -1.19328961e-22 6.53832270e-23
0.00000000e 00]
[ 0.00000000e 00 -1.19328961e-22 2.07190726e-22 -1.19328961e-22
0.00000000e 00]
[ 0.00000000e 00 6.53832270e-23 -1.19328961e-22 6.53832270e-23
0.00000000e 00]
[ 0.00000000e 00 0.00000000e 00 0.00000000e 00 0.00000000e 00
0.00000000e 00]]
The expected output is :
[[ 0.00000000e 00 0.00000000e 00 0.00000000e 00 0.00000000e 00
0.00000000e 00]
[ 0.00000000e 00 -2.50095415e-20 3.69424377e-20 -2.50095415e-20
0.00000000e 00]
[ 0.00000000e 00 4.45848648e-20 -6.53039374e-20 4.45848648e-20
0.00000000e 00]
[ 0.00000000e 00 -2.50095415e-20 3.69424377e-20 -2.50095415e-20
0.00000000e 00]
[ 0.00000000e 00 0.00000000e 00 0.00000000e 00 0.00000000e 00
0.00000000e 00]]
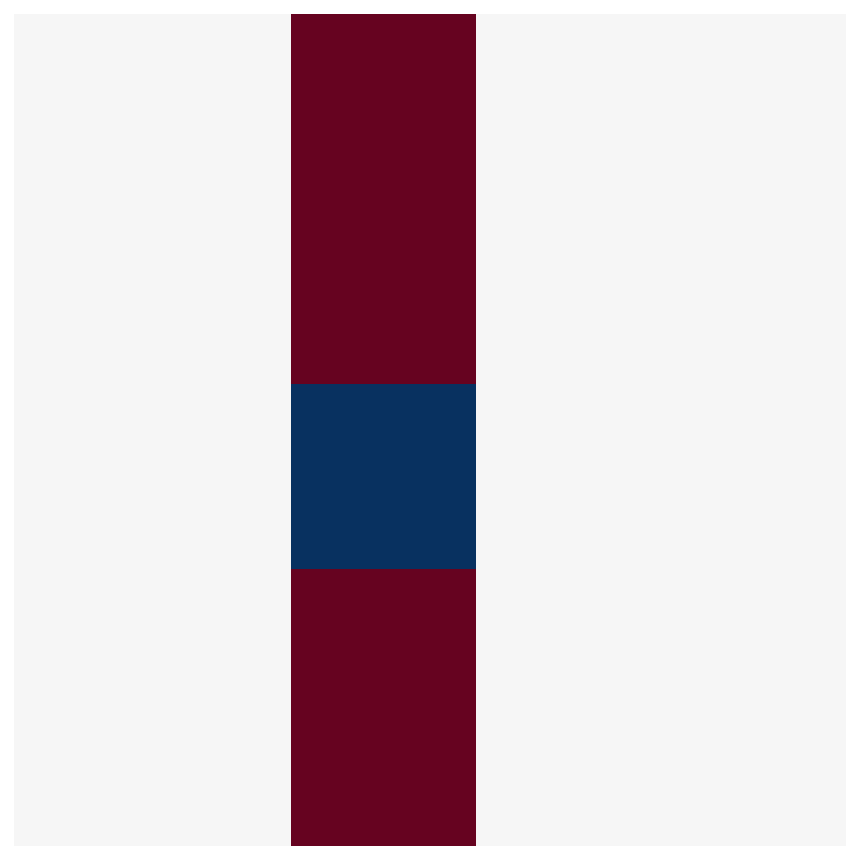
And the actual output is :
[[ 0.00000000e 00 -8.00305329e-23 1.42671568e-22 -8.00305329e-23
0.00000000e 00]
[ 0.00000000e 00 -2.09226327e-23 3.81852676e-23 -2.09226327e-23
0.00000000e 00]
[ 0.00000000e 00 3.81852676e-23 -6.63010323e-23 3.81852676e-23
0.00000000e 00]
[ 0.00000000e 00 -2.09226327e-23 3.81852676e-23 -2.09226327e-23
0.00000000e 00]
[ 0.00000000e 00 -8.00305329e-23 1.42671568e-22 -8.00305329e-23
0.00000000e 00]]
In terms of visualisation : the expected output is :
And the actual output (with np.gradient) is :
Thanks for your help.
CodePudding user response:
You can simply vectorize the operation
d2px2 = (p[:, :-2] - 2 * p[:, 1:-1] p[:, 2:]) / dx ** 2
d2py2 = (p[:-2, :] - 2 * p[1:-1, :] p[2:, :]) / dy ** 2
np.allclose(d2px2, d2px[:, 1:])
# True
np.allclose(d2py2, d2py[1:, :])
# True