I am trying to find the dynamic height of a UIView at the run time. So, for this I calculated the run time height of UILabels in it and the constraint constants and add them all to get the desired height. But this doesn't seems to be the correct way of doing it, because in case I alter the count of UILabel or constraints in future then I do have to change the code to calculate the dynamic height. So, is there any way to get the height of UIView at run time with any number of labels and constraints in it?
MY CODE
Here uiview is UIView of which I need to calculate the dynamic height, label1 and label2 are the UILabels in which I inserted text programatically. height is a string extension to find dynamic height of UILabel. label1TopConstraint, label1BottonContraint, label2BottomConstraint are constraints IBOutlets.
let label1Height = label1.text!.height(withConstrainedWidth: label1.frame.width, font: label1.font)
let label2Height = label2.text!.height(withConstrainedWidth: label2.frame.width, font: label2.font)
uiviewHeight = label1Height label2Height label1TopConstraint.constant label1BottonContraint.constant label2BottomConstraint.constant
CodePudding user response:
Why do you need those runtime calculations if you already use AutoLayout and can rely on constraints? Here's an example:
A view, containing two labels:
import UIKit
final class LabelsView: UIView {
override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
backgroundColor = .red
let label1 = UILabel()
label1.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
label1.text = "Label 1"
label1.backgroundColor = .red
addSubview(label1)
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([label1.widthAnchor.constraint(equalTo: widthAnchor),
label1.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: centerXAnchor),
label1.heightAnchor.constraint(equalTo: heightAnchor, multiplier: 0.5),
label1.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: topAnchor)])
let label2 = UILabel()
label2.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
label2.text = "Label 2"
label2.backgroundColor = .green
addSubview(label2)
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([label2.widthAnchor.constraint(equalTo: widthAnchor),
label2.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: centerXAnchor),
label2.heightAnchor.constraint(equalTo: label1.heightAnchor),
label2.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: bottomAnchor)])
}
@available(*, unavailable)
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
}
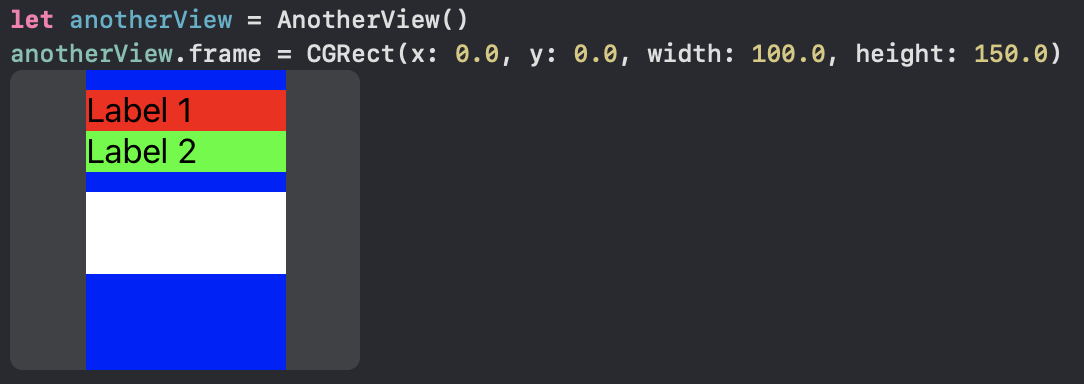
An example usage outcome:
Here's a view that reuses the first one (among others):
final class AnotherView: UIView {
override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
backgroundColor = .blue
let labelsView = LabelsView()
labelsView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
addSubview(labelsView)
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([labelsView.widthAnchor.constraint(equalTo: widthAnchor),
labelsView.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: centerXAnchor),
labelsView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: topAnchor, constant: 10.0)])
let yetAnotherView = UIView()
yetAnotherView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
yetAnotherView.backgroundColor = .white
addSubview(yetAnotherView)
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([yetAnotherView.widthAnchor.constraint(equalTo: widthAnchor),
yetAnotherView.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: centerXAnchor),
yetAnotherView.heightAnchor.constraint(equalTo: labelsView.heightAnchor),
yetAnotherView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: labelsView.bottomAnchor,
constant: 10.0)])
}
@available(*, unavailable)
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
}
An example usage output:
CodePudding user response:
Instead of using multiple constraints on multiple labels, you can use UIStackViews vertically or horizontally according to your preference.
CodePudding user response:
I think your answer lies in layoutIfNeeded and let me explain why
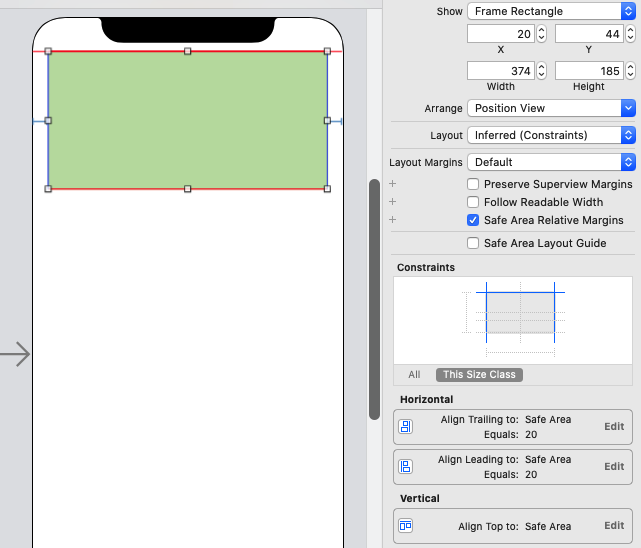
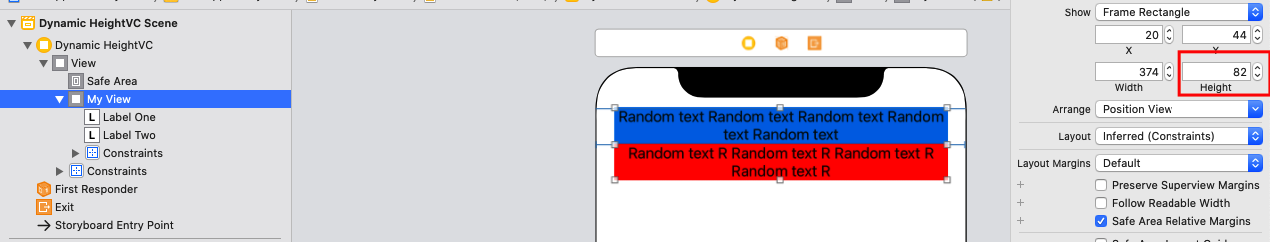
Consider my storyboard set up to set up a Dynamic height UIView which should set its height automatically based on the UILabels within it, note that I did not set the height anchor and so it gives me constraint errors which you can ignore for now as they will be resolved once we are done setting up.
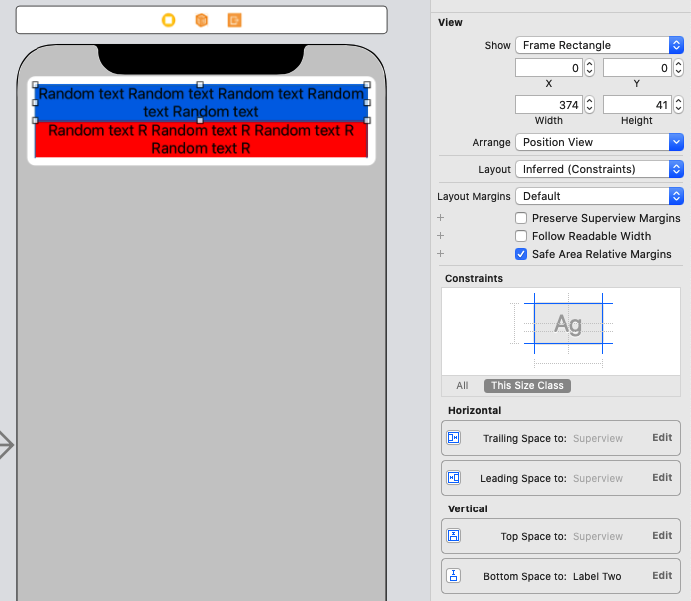
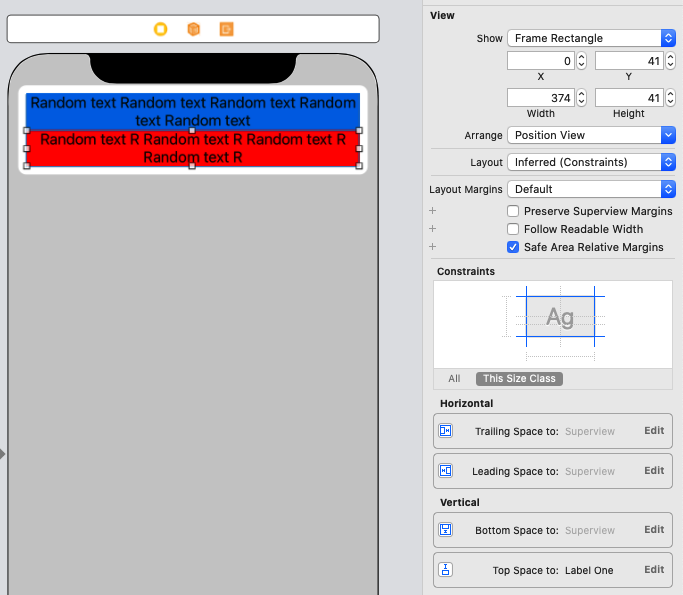
Next I add two labels to this view which have numberOfLines = 0
Top Label constraints
Bottom Label constraints
After this, the constraint errors go away and notice the height of the view the labels are contained in is 82:
Now I add this code which dynamically changes the text in the label
class DynamicHeightVC: UIViewController
{
@IBOutlet var myView: UIView!
@IBOutlet weak var labelOne: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var labelTwo: UILabel!
var longText = """
Some really long text that should make the UI label
expand beyond a few lines and make the UIView expand
along with it.
"""
var reallyLongText = """
Some really long text that should make the UI label
expand beyond a few lines and make the UIView expand
along with it. Some really long text that should make
the UI label expand beyond a few lines and make the
UIView expand along with it.
"""
override func viewDidLoad()
{
super.viewDidLoad()
labelOne.text = longText
labelTwo.text = reallyLongText
print("View height \(myView.frame.height)")
}
}
The output is View height 82.0 which is the value we saw on the storyboard and it is clearly wrong as the view's height is bigger:
So the issue is once you set the text, the constraints get updated and the frames will get updated at a later / different runloop which might not be useful to you since you want to do some calculations with it now.
If you want the frames to be updated in the next run loop, you need to call view.setNeedsLayout().
If you want the frames to be updated immediately, you need to call view.layoutIfNeeded()
After making this change, the code is as follows:
class DynamicHeightVC: UIViewController
{
@IBOutlet var myView: UIView!
@IBOutlet weak var labelOne: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var labelTwo: UILabel!
var longText = """
Some really long text that should make the UI label
expand beyond a few lines and make the UIView expand
along with it.
"""
var reallyLongText = """
Some really long text that should make the UI label
expand beyond a few lines and make the UIView expand
along with it. Some really long text that should make
the UI label expand beyond a few lines and make the
UIView expand along with it.
"""
override func viewDidLoad()
{
super.viewDidLoad()
labelOne.text = longText
labelTwo.text = reallyLongText
view.layoutIfNeeded()
print("Label 1 height \(labelOne.frame.height)")
print("Label 2 height \(labelTwo.frame.height)")
print("View height \(myView.frame.height)")
}
}
And now the console displays the correct, updated height:
Label 1 height 101.5
Label 2 height 183.0
View height 284.5