I have a lot of measurements where I get data that looks something like this:
# Generate example data
x <- 1:100
y <- 100*(1-exp(-0.3*x))
x2 <- 101:200
y2 <- rev(y)
df <- data.frame("x" = c(x, x2),
"y" = c(y, y2))
df$x <- df$x 50
rm(x, x2, y, y2)
x <- 1:50
y <- 25.91818
x2 <- 251:300
y2 <- 25.91818
df2 <- data.frame("x" = c(x, x2),
"y" = c(y, y2))
rm(x, x2, y, y2)
df <- rbind(df, df2)
rm(df2)
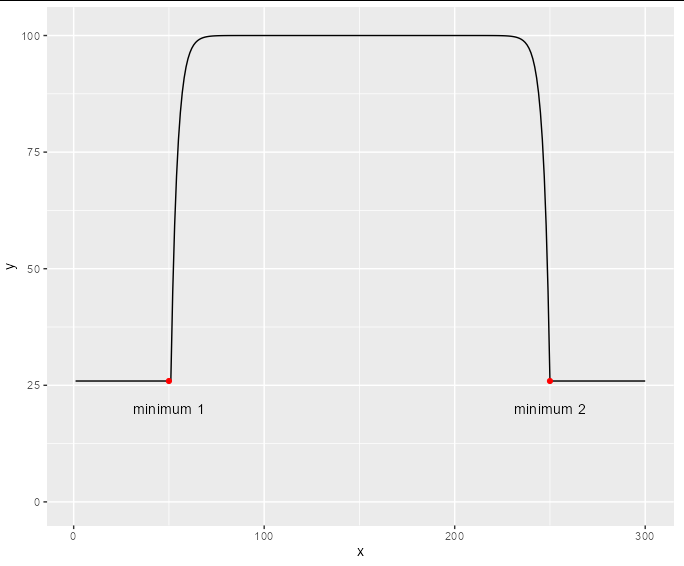
If I plot this I can see that there are left-most and right-most local minima.
library(ggplot2)
p <- ggplot(df, aes(x,y))
geom_line()
geom_point(data = data.frame("x" = c(50, 250), "y" = c(25.91818, 25.91818)),
mapping = aes(x, y), colour = "red")
scale_y_continuous(limits = c(0, 101))
p annotate("text", label = "minimum 1", x = 50, y = 20)
annotate("text", label = "minimum 2", x = 250, y = 20)
What I would like to do is trim those data that are to the left of minimum 1 and right of minimum 2. It's not super straightforward as there may also be local minima between those two points, because the real data doesn't look this ideal. I would also need to apply this process to many many samples, but I think this may be trivial because I could use e.g. dplyr and group_by().
I had some luck plotting the local minima using the ggpmisc package, but I'm not sure how I can use that to actually subset my data. Just for clarity I included the code to do so below, and with the real data it looks a little better:
library(ggpmisc)
p2 <- ggplot(df, aes(x, y))
geom_line()
ggpmisc::stat_peaks(col="red", span=3)
p2
I hope this is clear and I'm happy to clarify any questions. Thank you in advance.
CodePudding user response:
You could do this using the following steps:
- Sort your data according to its x co-ordinates
- On your sorted data, find the
diffof the y co-ordinates, which will be 0 (or close to 0) for the flat sections at either end (as well as any flat sections in between) - Starting from the left, find the first point where the
diffis not zero (or at least is above a minimal threshold). Store this index as a variable calledleft - Starting from the right, find the first point where the
diffis not zero (or at least is above a minimal threshold). Store this index as a variable calledright - Subset your data frame so it only contains the data between rows
left:right
So, in your example we would have:
# Define a minimal threshold above which we are not at the minimum line
minimal_change <- 1e-6
df <- df[order(df$x),] # Step 1
left <- which(diff(df$y) > minimal_change)[1] # Step 2
right <- nrow(df) - which(diff(rev(df$y)) > minimal_change)[1] 1 # Step 3
df <- df[left:right, ] # Step 4
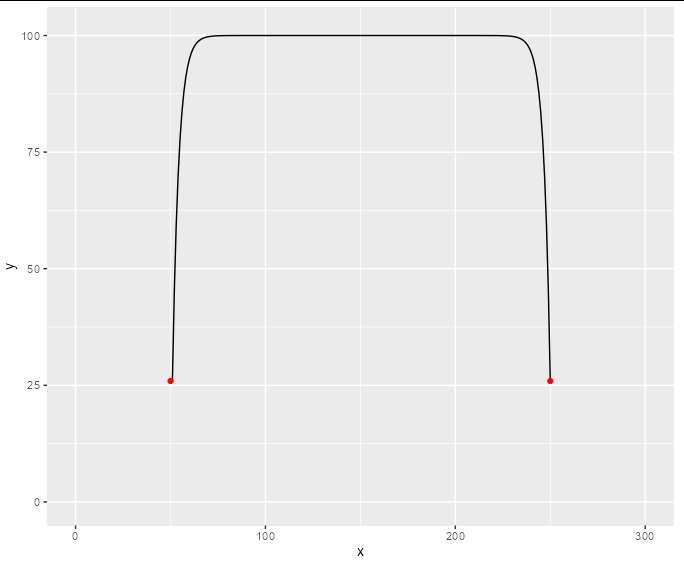
Now we can plot the result:
ggplot(df, aes(x, y))
geom_line()
geom_point(data = data.frame("x" = c(50, 250), "y" = c(25.91818, 25.91818)),
mapping = aes(x, y), colour = "red")
scale_y_continuous(limits = c(0, 101))
scale_x_continuous(limits = c(0, 300))