I'm searching for a (probably obvious) way of reducing the time my code takes to run.
At the moment my code looks like this:
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
l = 4000000
def my_func(n):
m = 3 * n
z = n**2
return(m,z)
am = []
az = []
for i in range(l): # question is referring to this loop
am.append(my_func(i)[0])
az.append(my_func(i)[1])
x = range(l)
plt.plot(x, am)
plt.plot(x, az)
plt.show()
In the i-loop my_func always runs twice and discards one of the two returned values, which sounds super inefficient to me. So how can I fill my am array with the first and my az array with the second values my_func returns, without running it twice for every i and only using half the returns every time?
CodePudding user response:
You can unpack the tuple returned from this function:
for i in range(l):
m, z = my_func(i)
am.append(m)
az.append(z)
Code-2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import time
start_time = time.time()
l = 4000000
# def my_func(n):
# m = 3 * n
# z = n**2
# return(m,z)
# am = []
# az = []
# for i in range(l): # question is referring to this loop
# am.append(my_func(i)[0])
# az.append(my_func(i)[1])
x = np.arange(l)
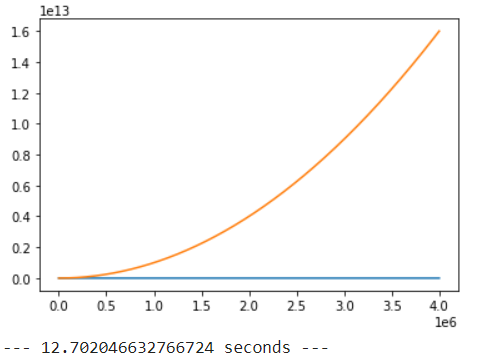
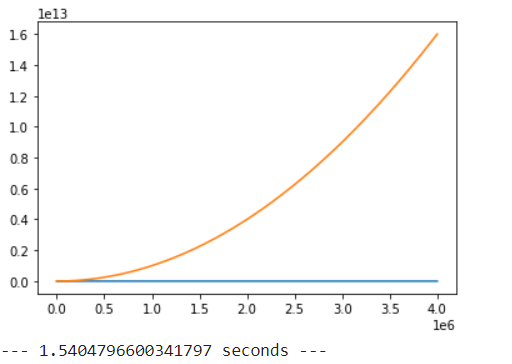
plt.plot(x, 3*x)
plt.plot(x, x*x)
plt.show()
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
Output
Instead of using for loop, you can simply use vectorization to speed up the operation, as shown in the pictures( 5-6 times faster roughly). Also try to not call the same function multiple times to reuse the same value. Better to call it once and store the result.
CodePudding user response:
Just store the value in a variable :
results = my_func(i)
am.append(results[0])
az.append(results[1])
CodePudding user response:
I would use np.vectorize
am, az = np.vectorize(my_func)(range(l))
CodePudding user response:
Do you mean something like the below? Save the returned tuple and append to the lists.
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
l = 4000000
def my_func(n):
m = 3 * n
z = n**2
return(m,z)
am = []
az = []
for i in range(l): # question is referring to this loop
m, z = my_func(i)
am.append(m)
az.append(z)
x = range(l)
plt.plot(x, am)
plt.plot(x, az)
plt.show()