I have several XML files which I want to read in to a pandas dataframe and merge them into one dataframe with a unified time stamp.
For example the dataframes look like that:
# PTU.xml:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf8'?>
<PtuResults>
<Row DataSrvTime="2021-07-08T08:58:14.3942671" SP="950.067" PFH="950.067" T="291.810" Hum="84.035" Alt="590.081" Status="0" />
<Row DataSrvTime="2021-07-08T08:58:36.8831974" SP="950.935" PFH="949.456" T="291.569" Hum="89.576" Alt="582.223" Status="0" />
<Row DataSrvTime="2021-07-08T08:58:36.8835716" SP="950.256" PFH="949.207" T="291.072" Hum="91.548" Alt="588.357" Status="0" />
</PtuResults>
# - or -
#
# AMS.xml:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf8'?>
<AdditionalSensorData>
<Row MeasurementOffset="-0.403" DataSrvTime="2021-07-08T08:43:29.0616419" GpsTO="12" XData=" C7 10 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2FE 320 0 0 230 165 111 224 1201 13BF 13CB B 0 58 1 278 B695" />
<Row MeasurementOffset="-0.253" DataSrvTime="2021-07-08T08:43:30.0866790" GpsTO="35" XData=" C2 16 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 320 0 0 0 23A 133 111 223 118C 1236 1237 9 0 6B 1 278 9B2" />
<Row MeasurementOffset="-0.103" DataSrvTime="2021-07-08T08:43:31.1107931" GpsTO="58" XData=" CB E 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2FE 341 0 0 230 179 111 222 11E0 1396 13A2 10 0 7C 2 278 3ECA" />
</AdditionalSensorData>
First, I am reading in the XML-files:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# Mypath with datafiles:
path = 'c:/mypath/'
# Names of specific files:
PTU = 'PTU.xml'
GPS = 'GPS.xml'
AMS = 'AMS.xml'
data_PTU = ET.parse(path PTU).getroot()
data_GPS = ET.parse(path GPS).getroot()
data_AMS = ET.parse(path AMS).getroot()
I defined a principal routine for the transformation into a Pandas dataframe with the attribute names as column names:
def parse_XML(xml_file, df_cols):
xroot = ET.parse(xml_file).getroot()
rows = []
for attribute in xroot:
res = []
res.append(attribute.attrib.get(df_cols[0]))
for element in df_cols[:]:
if attribute is not None and attribute.find(element) is not None:
res.append(attribute.find(element))
else:
res.append(None)
rows.append({df_cols[i]: res[i]
for i, _ in enumerate(df_cols)})
out_df = pd.DataFrame(rows, columns=df_cols)
return out_df
And finally I am using for example
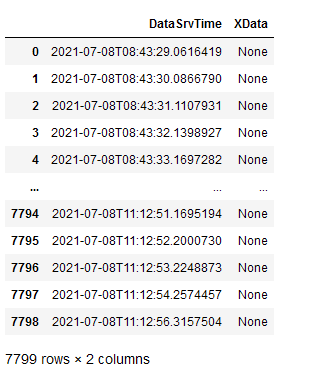
parse_XML(path AMS,["DataSrvTime", "XData"])
# -or-
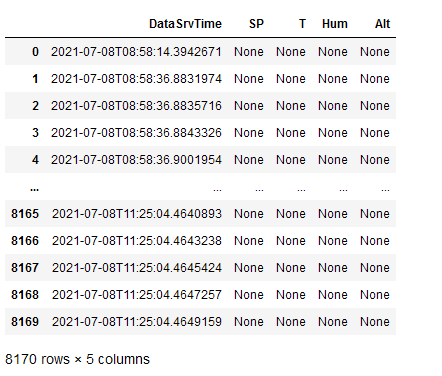
parse_XML(path PTU, ["DataSrvTime", "SP", "T", "Hum", "Alt"])
to make a dataframe. The result shows a dataframe with the first column as index column, the second column as "DataSrvTime" in this case and any following column filled with "None"s. If I change the order to
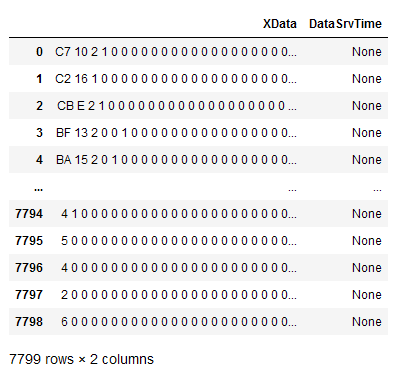
parse_XML(path AMS,["XData", "DataSrvTime"])
for example XData is shown but DataSrvTime column contains "None"s. Does anyone see where my mistake is?
If the reading into a dataframe is perfect the further plan is to merge all the different dataframes (AMS, PTU, GPS for example) with (Pandas) resample('S').mean() and (Pandas) dataframe.interpolate() to a unifying timestamp into one dataframe.
Would you recommend another solution?
Thanks for reading and helping out.
CodePudding user response:
Given your attribute-centric XML is relatively flat, consider the new IO method, pandas.read_xml. Then, merge the two data frames or run an iterative join using concat on a list of data frames which requires the datetime to be set as index.
pd.merge
final_df = pd.merge(
pd.read_xml('PTU.xml'), pd.read_xml('AMS.xml'),
on = "DataSrvTime", how = "outer"
)
pd.concat
df_list = [
pd.read_xml(f).set_index("DataSrvTime")
for f in
['PTU.xml', 'GPS.xml', 'AMS.xml']
]
final_df = pd.concat(df_list, axis=0)