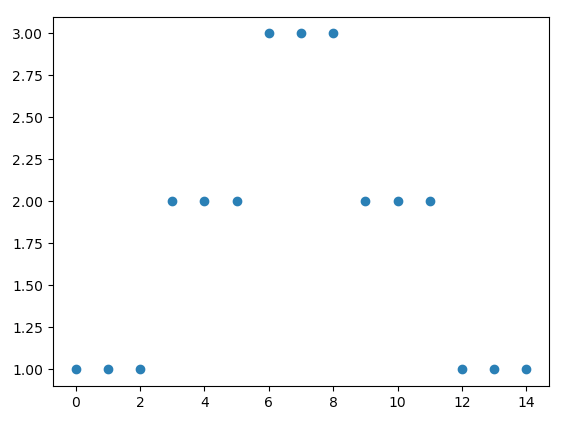
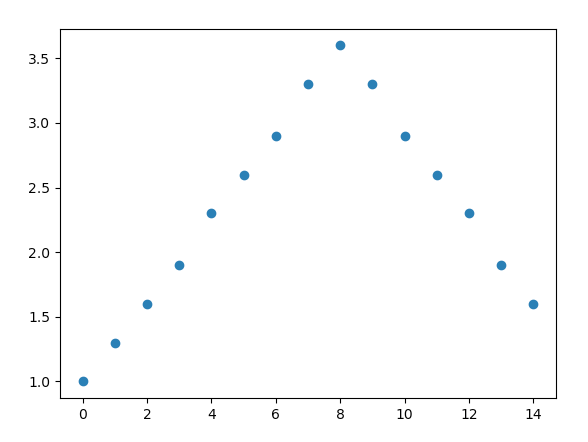
I have some discrete data in an array, such that:
arr = np.array([[1,1,1],[2,2,2],[3,3,3],[2,2,2],[1,1,1]])
whose plot looks like:
I also have an index array, such that each unique value in arr is associated with a unique index value, like:
ind = np.array([[1,1,1],[2,2,2],[3,3,3],[4,4,4],[5,5,5]])
What is the most pythonic way of converting arr from discrete values to continuous values, so that the array would look like this when plotted?:
therefore, interpolating between the discrete points to make continuous data
CodePudding user response:
I found a solution to this if anyone has a similar issue. It is maybe not the most elegant so modifications are welcome:
def ref_linear_interp(x, y):
arr = []
ux=np.unique(x) #unique x values
for u in ux:
idx = y[x==u]
try:
min = y[x==u-1][0]
max = y[x==u][0]
except:
min = y[x==u][0]
max = y[x==u][0]
try:
min = y[x==u][0]
max = y[x==u 1][0]
except:
min = y[x==u][0]
max = y[x==u][0]
if min==max:
sub = np.full((len(idx)), min)
arr.append(sub)
else:
sub = np.linspace(min, max, len(idx))
arr.append(sub)
return np.concatenate(arr, axis=None).ravel()
y = np.array([[1,1,1],[2,2,2],[3,3,3],[2,2,2],[1,1,1]])
x = np.array([[1,1,1],[2,2,2],[3,3,3],[4,4,4],[5,5,5]])
z = np.arange(1, 16, 1)
CodePudding user response:
Here is an answer for the symmetric solution that I would expect when reading the question:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# create the data as described
numbers = [1,2,3,2,1]
nblock = 3
df = pd.DataFrame({
"x": np.arange(nblock*len(numbers)),
"y": np.repeat(numbers, nblock),
"label": np.repeat(np.arange(len(numbers)), nblock)
})
Expecting a constant block size of 3, we could use a rolling window:
df['y-smooth'] = df['y'].rolling(nblock, center=True).mean()
plt.plot(df['x'], df['y-smooth'])
If the block size is allowed to vary, we could determine the block centers and interpolate peace wise.
centers = df[['x', 'y', 'label']].groupby('label').mean()
xnew = np.linspace(centers['x'].min(), centers['x'].max(), 25)
ynew = np.interp(xnew, centers['x'], centers['y'])
plt.plot(xnew, ynew)