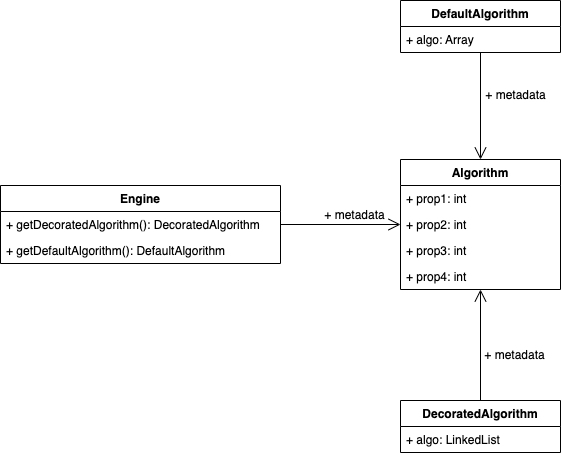
So, I'm in the process of designing a small system for which I'm starting out with making a class diagram. (Before however I proceed, I guess it is fair to say, that the properties visualized here have different naming in the real system)
The small snippet displays the following:
- Engine can generate either a
DefaultAlgorithmor aDecoratedAlgorithm Engine,DecoratedAlgorithmandDefaultAlgorithmhaveAlgorithmas an associated propertyEngineneeds the properties fromAlgorithmin order to generate eitherDefaultAlgorithmorDecoratedAlgorithmDefaultAlgorithmandDecoratedAlgorithmboth need the properties fromAlgorithmbecause those properties are metadata that tells how the algorithms were generated.DefaultAlgorithmandDecoratedAlgorithmwill besides being consumed by other classes (that readsalgoand corresponding properties) also be persisted in a database where nested properties might not be desirable.
When I look at above diagram, I dont feel that things look quite right, for example will the properties of Algorithm be deeply nested, making me have to write awkward code to access the properties.
To me, possible alternative options could be:
- Extend
DefaultAlgorithm,EngineandDecoratedAlgorithmwithAlgorithm, not caring about "Composition over inheritance" - Carelessly repeat myself and add the properties to respectively
DefaultAlgorithm,EngineandDecoratedAlgorithm
I know this might be a broad question, but what I hope with this question is to get some feedback on my thought process (Since I fear that I might be overthinking this)
CodePudding user response:
If you want to use the DefaultAlgorithm or the DecoratedAlgorithm in place of Algorithm, they should either all implement a common interface, or the more specialised algorithms should inherit from the general Algorithm.
Repeating doesn’t seem to be a wise approach, because if Algorithm would evolve and change some properties, you’d need to change all the others as well. This is not compliant with the open/closed principle.
If you go for the extensiin approach, you could make your properties protected. Nevertheless, this is not a good idea in view of the history rule of Liskov’s Substitution Principle: protected members are a leakage of internal details that proved to cause very nasty bugs.
In this regard, the problem is elsewhere. Rather than querying the algorithm to get the properties, you should tell the algorithm to to something (up to the algorithm to see which property is relevant). Tell, don’t ask. This would lead to more OO, in the spirit of the principle of the least knowledge.
If you implement this principle, “deeply nested properties”, i.e. properties that are themselves objects of a complex class, should no longer be a problem. By the way, nested properties in UML are equivalent to associations (the property being an owned association end). Persisting such classes is supported by well known techniques (serialising, transformstion to a flat rdbms model, etc…)