I am learning KMM. I am now designing a common Location fetching in iOSMain and Android main
My problem is , I don't know to map Swift to Kotlin in iOSMain
For example,
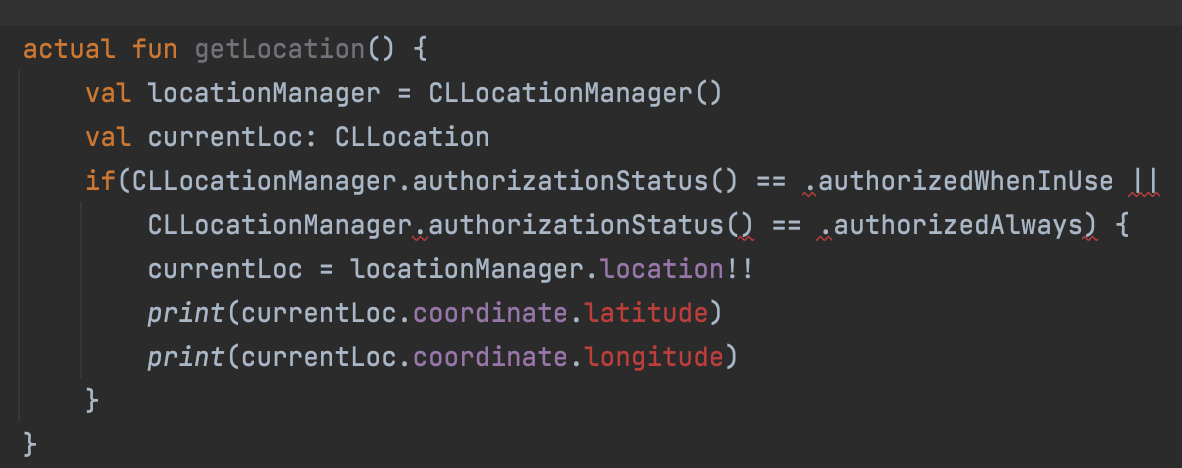
The Swift code for , getting location is
var locationManager = CLLocationManager()
locationManager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
var currentLoc: CLLocation!
if(CLLocationManager.authorizationStatus() == .authorizedWhenInUse ||
CLLocationManager.authorizationStatus() == .authorizedAlways) {
currentLoc = locationManager.location
print(currentLoc.coordinate.latitude)
print(currentLoc.coordinate.longitude)
}
Kotlin side implementation:
In the above code:
How to use the Swift's
.authorizedWhenInUseand.authorizedAlwaysin Kotlin Code ?And the in
currentLoc.coordinate.longitude, thelongitudeandlatitudeis not resolving . Why ?
Please help me
CodePudding user response:
Mapping Swift (Objective-C) to Kotlin
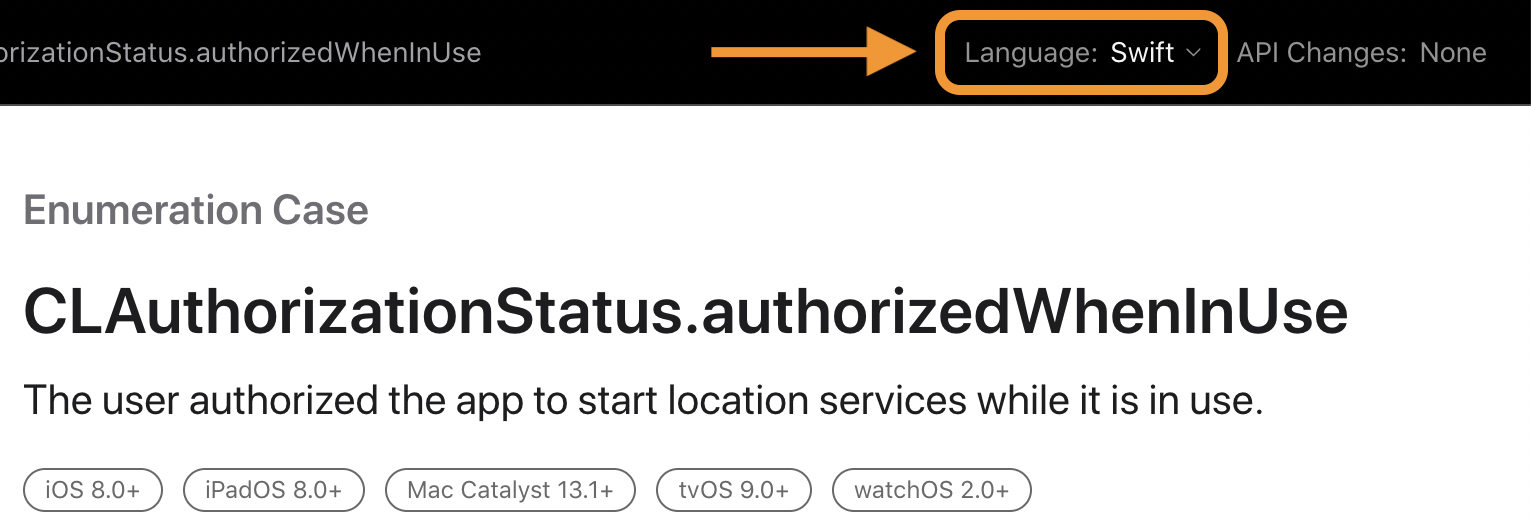
- How to use the Swift's .authorizedWhenInUse and .authorizedAlways in Kotlin Code ?
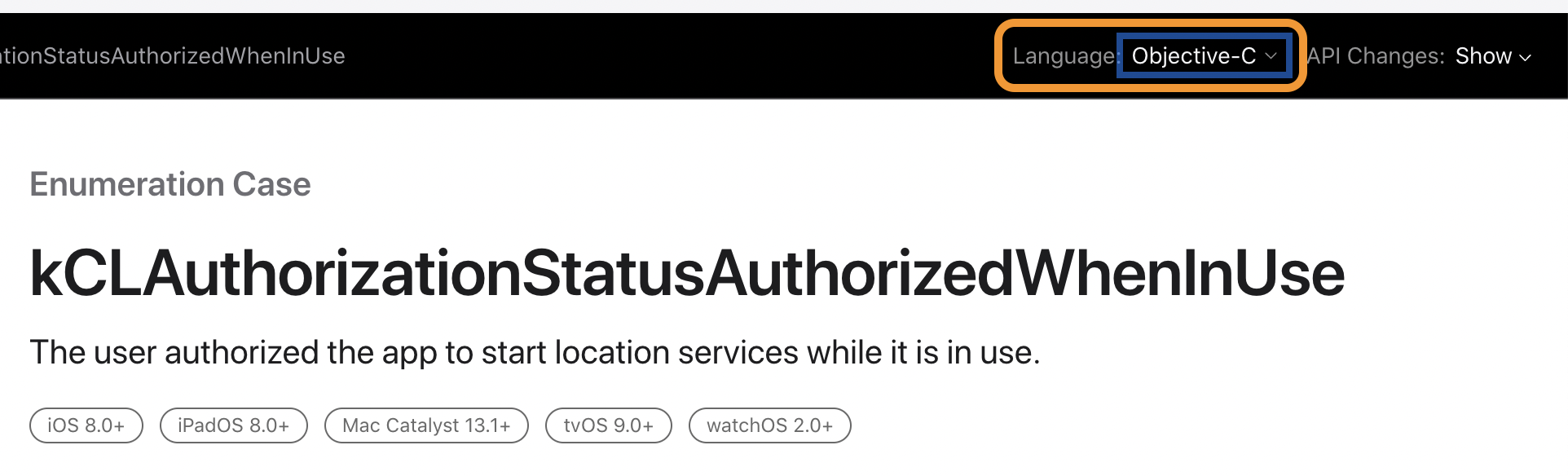
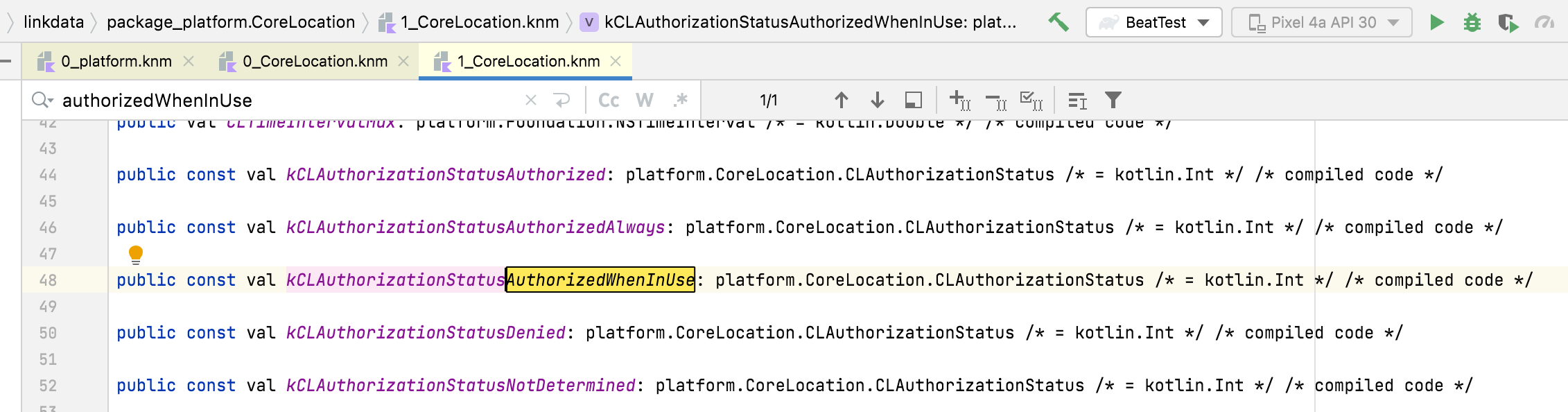
Given this, you should be able to use kCLAuthorizationStatusAuthorizedWhenInUse in your Kotlin code.
Referencing iOS Frameworks
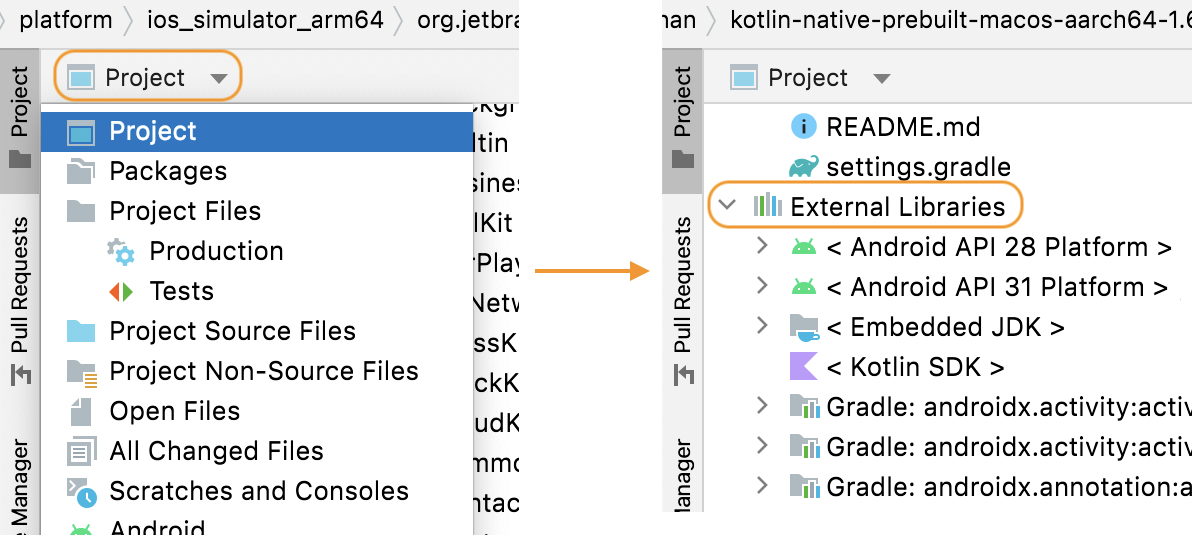
Since you already have some reference code, you could also simply Command Click (or Command B) one of the objects (for example, CLLocationManager) which should open up the compiled Kotlin code.
Manually you can also access all iOS frameworks from the "Project" View of Android Studio → "External Libraries" and then search for the iOS framework that you are searching for.
Here, you can dig through the frameworks to find what you're looking for. Not knowing the equivalent Objective-C API, you could just search for "authorizedWhenInUse" and can find it:
Dealing with C-structs
- currentLoc.coordinate.longitude , the longitude and latitude is not resolving
This is more complicated...
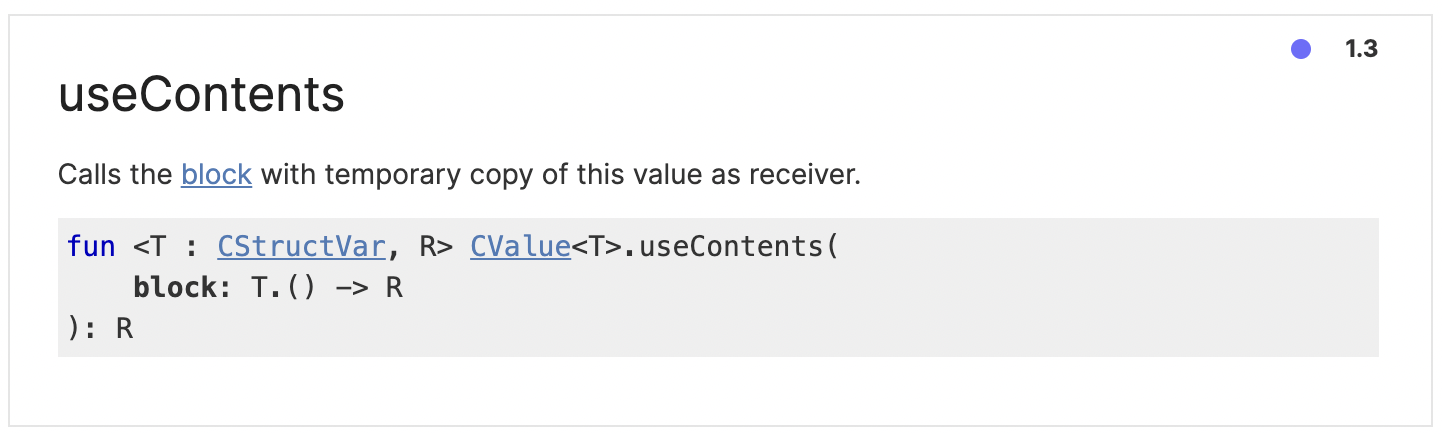
The location property is of type CLLocationCoordinate2D and (the important part!) is that it is contained within a CValue:
@kotlinx.cinterop.ExternalObjCClass public open class CLLocation : platform.darwin.NSObject, platform.Foundation.NSCopyingProtocol, platform.Foundation.NSSecureCodingProtocol {
...
public final val coordinate: kotlinx.cinterop.CValue<platform.CoreLocation.CLLocationCoordinate2D> /* compiled code */
Therefore, your code could be written as follows (compiled and confirmed that this runs and generates a location on a physical device):
val locationManager = CLLocationManager()
val currentLoc: CLLocation?
if (locationManager.authorizationStatus == kCLAuthorizationStatusAuthorizedWhenInUse ||
locationManager.authorizationStatus == kCLAuthorizationStatusAuthorizedAlways) {
currentLoc = locationManager.location
currentLoc?.coordinate?.useContents {
println("latitude = ${latitude}")
println("longitude = ${longitude}")
}
}