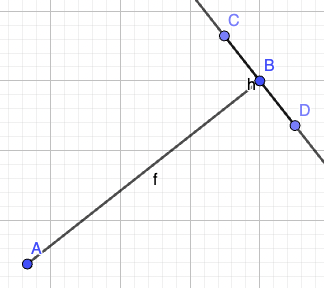
I'm writing code in Swift and I wan't to draw CAShapeLayers with BezierPaths as it's presented in the image below.
How can I calculate C and D points if points A and B are known (as distance between them) and length between points C and D is also known?
After C and D points are calculated, a line between them would be drawn using UIBezierPath like this:
let path: UIBezierPath = UIBezierPath()
path.move(to: CGPoint(x: Cx, y: Cy))
path.addLine(to: CGPoint(x: Dx, y: Dy))
layer.path = path.cgPath
Thanks for your help and time.
CodePudding user response:
Here's the math that I would use :)
First you can calculate the angle in the Cartesian plane from A to B:
theta_AB = atan2(By-Ay, Bx-Ax)
The angle of the perpendicular line CD is just theta pi/2
theta_CD = theta_AB pi/2
Then assume that d is the known distance between C and D.
Then you have:
Cx = Bx cos(theta_CD) * d/2
Cy = By sin(theta_CD) * d/2
Dx = Bx - cos(theta_CD) * d/2
Dy = By - sin(theta_CD) * d/2
So putting it all together with (hopefully) correct Swift syntax, you'd have:
let theta_AB = atan2(By-Ay, Bx-Ax);
let theta_CD = theta_AB Double.pi/2.0;
let Cx = Bx cos(theta_CD) * d/2;
let Cy = By sin(theta_CD) * d/2;
let Dx = Bx - cos(theta_CD) * d/2;
let Dy = By - sin(theta_CD) * d/2;
let C : CGPoint = CGPoint(x: Cx, y: Cy);
let D : CGPoint = CGPoint(x: Dx, y: Dy);
Or something like that
CodePudding user response:
You can figure this out with algebra and the Pythagorean theorem, or trig.
Trig seems easier. Here is my off-the-cuff attempt to solve the problem using trig (not tested):
Let’s call point A’s coordinates (Ax,Ay) and B’s coordinates (Bx,By)
The angle between your line segment AB and the horizontal would be
theta = atan2(By-Ay, Bx-Ax)
The angle between line segment BD and the vertical line that drops from B would be theta pi/2. (Swift’s trig libraries use radians, and pi/2 radians is 90°, or an angle perpendicular to the original angle.) Let’s call the perpendicular angle theta2.
Let’s call the length of your line segment CD L. The length of line segments BD and BC will both be half of that, or L/2.
The change in y from your point B to point D would be:
deltaY = L/2 • cos(theta2)
The change in x from your point B to point D would be
deltaX = L/2 • sin(theta2)
The coordinates of point D would be
Dx = Bx deltaX
Dy = By deltaY
The coordinates of point C would be
Cx = Bx - deltaX
Cy = By - deltaY
CodePudding user response:
This is a math question. It really doesn't matter which language but I will post the Swift solution.
To figure out the angle from another point and the point with a certain angle and distance you will need those helpers:
extension CGPoint {
func angle(from location: CGPoint) -> Double {
let deltaY = location.y - y
let deltaX = location.x - x
let angle = atan2(deltaY, deltaX) * 180 / .pi
return angle
// if you need the angle reversing y directon
// return angle < 0 ? abs(angle) : 360 - angle
}
func moving(distance: Double, at angle: Double) -> CGPoint {
.init(
x: x distance * __cospi(angle/180),
y: y distance * __sinpi(angle/180)
)
}
}
let pointA: CGPoint = .zero
let pointB: CGPoint = .init(x: 100, y: 100)
let angleAfromB = pointA.angle(from: pointB) // 45
let angleBfromA = pointB.angle(from: pointA) // 225
let pointE = pointA.moving(distance: 1, at: 0) // {x 1 y 0}
let pointF = pointA.moving(distance: 1, at: 90) // {x 0 y 1}
let pointG = pointA.moving(distance: 1, at: 180) // {x -1 y 0}
let pointH = pointA.moving(distance: 1, at: 270) // {x 0 y -1}
let path = UIBezierPath()
path.move(to: pointA)
path.addLine(to: pointB)
path.close()
path.stroke()
let pointC = pointB.moving(distance: 50, at: angleAfromB 90)
let pointD = pointB.moving(distance: 50, at: angleAfromB - 90)
let pathCD = UIBezierPath()
path.move(to: pointC)
path.addLine(to: pointD)
path.close()
path.stroke()