I have columns nickname, password, enabled and authority in my user scheme. Column authority is a foreign key to scheme authority. I have columns authority in my authority scheme.
My schemes are different from those Spring Security waits by default. That's why I have to write this code in configuration.
@Bean
public UserDetailsManager users(DataSource dataSource) {
JdbcUserDetailsManager users = new JdbcUserDetailsManager(dataSource);
users.setUsersByUsernameQuery(
"SELECT nickname, CONCAT('{noop}', password), true "
"FROM \"user\" WHERE nickname = ?"
);
users.setAuthoritiesByUsernameQuery(
"SELECT u.nickname, a.authority "
"FROM authority a "
"LEFT JOIN \"user\" u "
"ON a.authority=u.authority WHERE nickname = ?"
);
return users;
}
It works well. But I think it is not the best solution because of the raw SQL queries in my code.
Is there a way not to write SQL queries?
I also use Spring Data JPA in my project.
I an idea have to write my implementation of AuthenticatedProvider and use UserService inside it.
CodePudding user response:
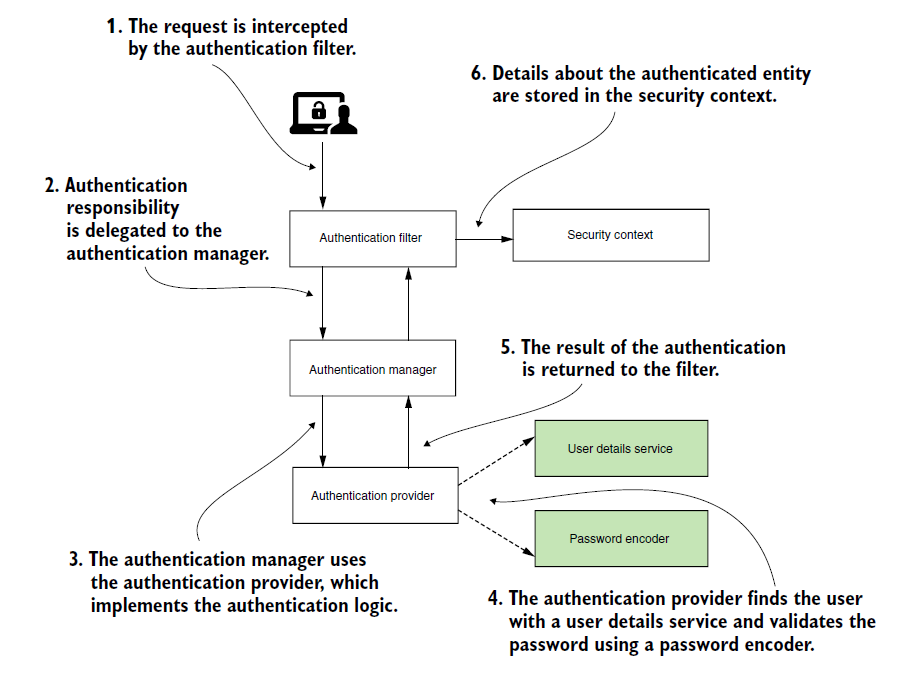
The image is from: Spring Security In Action by Laurentiu Spilca.
You could always implement the interface/contract UserDetailsService https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/current/api/org/springframework/security/core/userdetails/UserDetailsService.html
and load users with model classes that also implements another interface/contract UserDetails. https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/current/api/org/springframework/security/core/userdetails/UserDetails.html
and configure your UserDetailsService as a bean so that AuthenticationProvider could retrieve at run time(autowired). You should also provide a PasswordEncoder in the same configuration class as a bean. [No need to implement a provider if you use default authentication logic(compare passwords from db and given password by using a password encoder)]
Your database schema should allow you to provide the information contained in UserDetails service contract/interface.
NOTE: GrantedAuthorities starting with ROLE_ are identified as roles.