I am learning how variables are passed to functions by value, while arrays are passed by reference.
I ran my script to verify that, however the pointer addresses are different. Why is that?
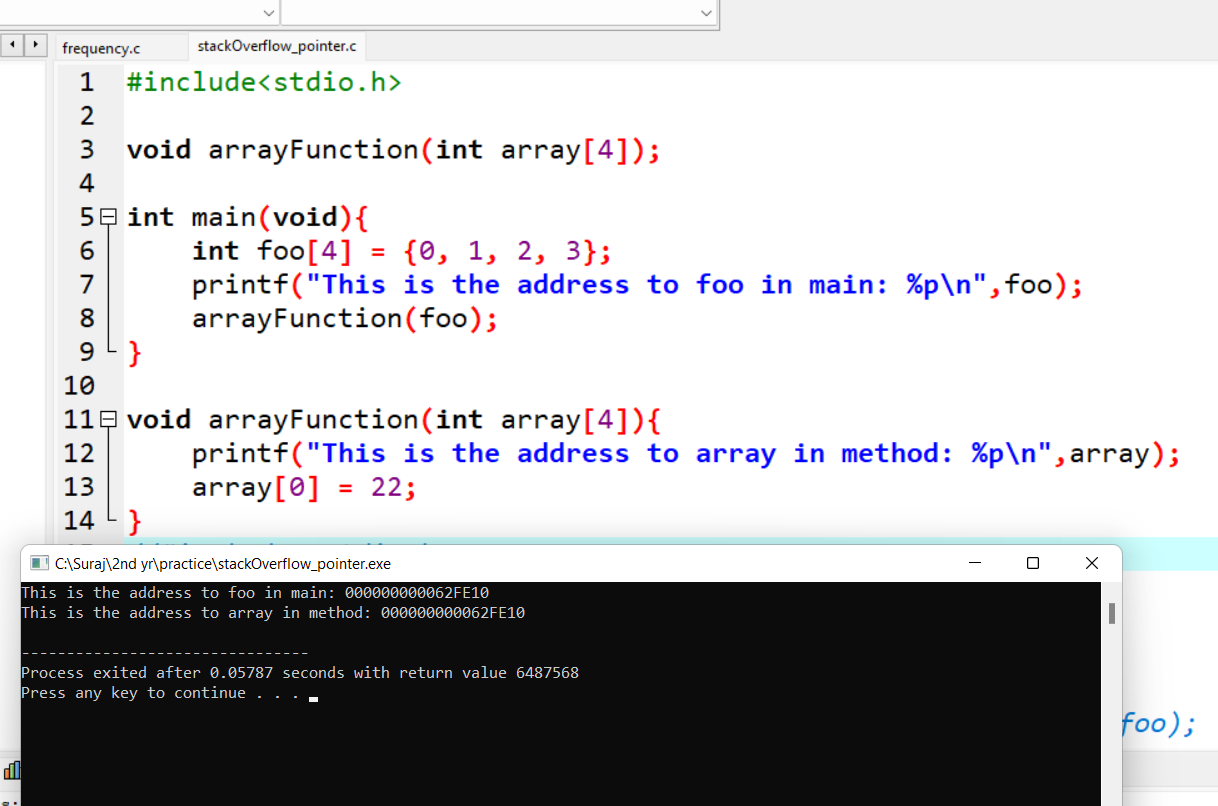
void arrayFunction(int array[4]);
int main(void){
int foo[4] = {0, 1, 2, 3};
printf("This is the address to foo in main: %p\n",&foo);
arrayFunction(foo);
}
void arrayFunction(int array[4]){
printf("This is the address to array in method: %p\n", &array);
array[0] = 22;
}
CodePudding user response:
The is the address of foo aka &foo[0] is conceptually copied to a new variable. Or said differently the pointer is still passed by value.
CodePudding user response:
&array is the address of the array variable in the stack of the called function. However that's implemented as a pointer that points to the same array elements.
Here is a modified version of your program showing that:
#include <stdio.h>
void arrayFunction(int array[4]);
int main(void){
int foo[4] = {0, 1, 2, 3};
printf("This is the address to foo in main: \t%p\n",&foo[0]);
arrayFunction(foo);
}
void arrayFunction(int array[4]){
printf("This is the address to array in method: \t%p\n", &array[0]);
array[0] = 22;
}
CodePudding user response:
There is a subtle difference between the array and the normal element. If arr[10] is declared, then only (arr) gives the address of the first emement. In your code, you have print address of the pointer pointing to that first element '&arr'. Just remove the '&' and both will show the same address.
#include<stdio.h>
void arrayFunction(int array[4]);
int main(void){
int foo[4] = {0, 1, 2, 3};
printf("This is the address to foo in main: %p\n",foo);
arrayFunction(foo);
}
void arrayFunction(int array[4]){
printf("This is the address to array in method: %p\n",array);
array[0] = 22;
}