Why does a pointer hold two memory locations? What is the use case for the 2nd memory location?
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
string animal;
string *rabbit = &animal;
cout << rabbit << " 1st memory location \n" << \
&rabbit << " 2nd memory location";
return 0;
}
CodePudding user response:
A pointer holds one memory address. &rabbit is the address of the rabbit variable itself.
CodePudding user response:
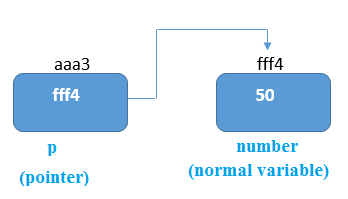
As the above image shows pointer p is holding the memory address of another variable which has a value of 50.
eg.
cout<<p; //fff4 address of number
cout<<*p; //value at location fff4 will be printed that is 50
cout<<&p; //address of pointer p which is aaa3 will be printed
learn more about pointers
CodePudding user response:
As when we declare pointer rabbit it will hold some space in the memory . And when we call pointer &rabbit it will hold the address of rabbit.