Recently I started working on demo Spring Boot application and I was unable to run the unit test when starting the application. The purpose of this approach is we need to run all unit tests before starting the application.
Code of the Sample Demo Application is as follows.
Main class DemoApplication,
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
Model class School,
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class School {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
Main class Unit test,
package com.example.demo;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private School school;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
school.setName("test");
String schoolName = school.getName();
Assertions.assertThat(schoolName).isNotNull();
}
@Test
void main() {
DemoApplication.main(new String[]{});
school.setName("test");
String schoolName = school.getName();
Assertions.assertThat(schoolName).isNotNull();
}
}
School Unit test,
package com.example.demo;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
public class SchoolTests {
@Test
public void getTodoTest() {
School school = new School();
String name = "test";
school.setName(name);
Assert.assertEquals(name, school.getName());
}
}
pom.xml file,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.6</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
What are the additional configurations that need to be done to run the unit tests at the startup?
CodePudding user response:
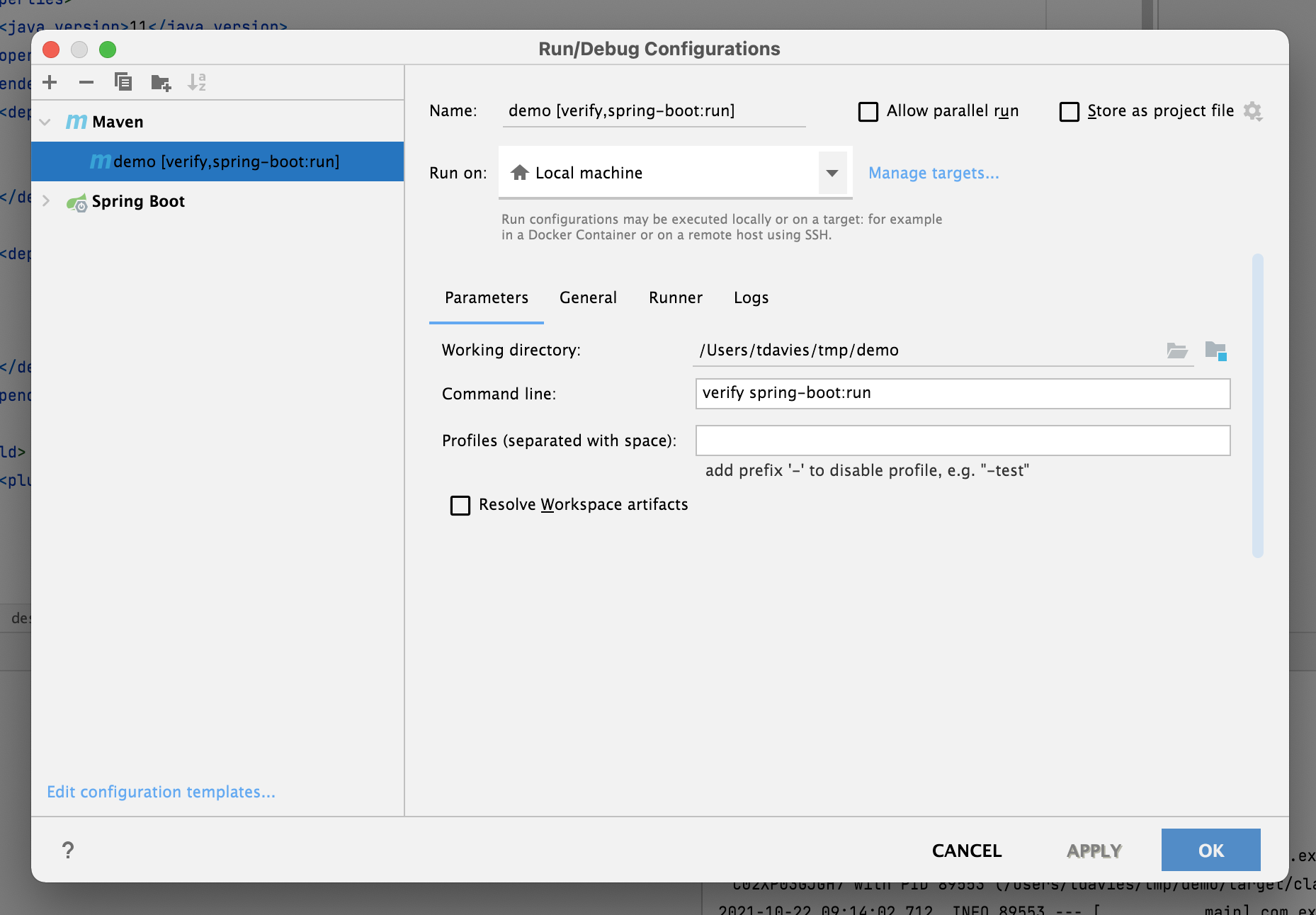
If you want to do this via Intellij, you can create a Run Configuration that runs the verify and spring-boot:run goals:
As other people have said, this is something you would only want to do while developing.
CodePudding user response:
Some suggestions:
- let's separate your local development and release, deployment procedure: use some kind of CI/CD process
- you can build, run your unit tests and other static code analyzers is your CI process (for instance in gitlab-ci)
- when you develop your application you can run unit tests without running your application, and you can run your application without running unit tests in your local machine, it is more efficient.
- when you finish your development issue you can push it to version control that can run your CI or CI/CD process. If you work in a team I suggest to use some kind of branching/version control strategy like gitflow, trunk based development etc.