So I'm studying c# and I've come across the issue where I seem to be getting the error System.Collections.Generic.List`1[Prog2Prov.Program Order] when trying to print out the list and my code currently looks like this. I'm aware that there may be a lot of errors, however, I am still trying to grasp my hands around how c# works. Thanks for all the advice.
List<Order> orders = new List<Order>();
bool close = true;
while (close)
{
Console.WriteLine("What type of order is this?(N=Normal/S=Special/#=End)");
string parcel = Console.ReadLine();
string name, location, date;
int number;
if (parcel == "N")
{
Console.Write("Enter the name of your order: ");
name = Console.ReadLine();
Console.Write("Enter your order number: ");
number = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter your order date: ");
date = Console.ReadLine();
Console.Write("Enter your town: ");
location = Console.ReadLine();
orders.Add(new NormalOrder(name, number, date, location));
}
else if (parcel == "S")
{
Console.Write("Enter the name of your order: ");
name = Console.ReadLine();
Console.Write("Enter your order number: ");
number = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter your order date: ");
date = Console.ReadLine();
Console.Write("Enter your country: ");
location = Console.ReadLine();
orders.Add(new NormalOrder(name, number, date, location));
}
else if (parcel == "#")
{
Console.WriteLine("Do you want to see which countries or town your sent your parcel to?(C=Country/T=Town)");
string shipping = Console.ReadLine();
foreach(var order in orders)
if (shipping == "t")
{
Console.WriteLine(order);
}
else if (shipping == "C")
{
Console.WriteLine(order);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Incorrect input, try again!");
}
}
}
}
class Order
{
protected string orderName { get; set; }
protected int orderNumber { get; set; }
protected string orderDate {get; set;}
}
class NormalOrder : Order
{
private string town { get; set; }
public NormalOrder(string orderName, int orderNumber, string orderDate, string town)
{
this.orderName = orderName;
this.orderNumber = orderNumber;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
this.town = town;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return "Order name: " orderName "\nOrder number: " orderNumber "\nOrder date: " orderDate "\nOrder location:" town.ToList();
}
}
class SpecialOrder : Order
{
private string country;
public SpecialOrder(string orderName, int orderNumber, string orderDate, string country)
{
this.orderName = orderName;
this.orderNumber = orderNumber;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
this.country = country;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return "Order name: " orderName "\nOrder number: " orderNumber "\nOrder date: " orderDate "\nOrder location:" country.ToList();
}
CodePudding user response:
I've come across the issue where I seem to be getting the error System.Collections.Generic.List`1[Prog2Prov.Program Order] when trying to print out the list
There are a few issue's I've found in the above code. First I'll address the actual issue.
if (shipping == "t")
{
Console.WriteLine(orders);
}
You're printing the string representation of your List<Order> which is System.Collections.Generic.List1[Prog2Prov.Program Order]. Instead you need to print each Order in that list. As mentioned in my comments above you can do a simple foreach or linq:
Here's the foreach:
foreach(var o in orders)
Console.WriteLine(o);
Here's linq:
Console.WriteLine(string.Join('\n', orders.Select(o => o.ToString())));
Another option, if you don't want to do this, you can inherit the List<T> and override the ToString in your new class.
using System.Linq;
public class OrderList : List<Order>
{
public override string ToString() => string.Join("\n", this.Select(o => o.ToString()));
Then you can use the new list:
OrderList ol = new OrderList();
ol.Add(new NormalOrder("order 1", 1, DateTime.Now.ToString(), "Nowhere Town"));
ol.Add(new SpecialOrder("special order 2", 2, DateTime.Now.ToString(), "Nowhere Town 2"));
MessageBox.Show(ol.ToString());
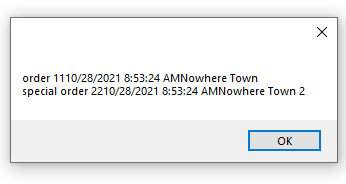
Here's my output from above:
Another issue I seen was:
town.ToList();
As well as:
country.ToList();
Both of these are defined as string, you'll still have an issue when printing them out, you need to remove the ToList() on them.
CodePudding user response:
Use a discriminated union via OneOf library.
var myList = new List<OneOf<SpecialOrder, NormalOrder>>()
{
new NormalOrder(...), new SpecialOrder(...)
};
myList[0].Switch(
special => Console.WriteLine("Special"),
normal => Console.WriteLine("Normal"),
);
However, polymorphism is much better for this scenario
CodePudding user response:
You can add two objects to the same list. You need to create an object list for that.
List<object> list = new List<object>();
list.Add(objType1);
list.Add(objType2);