I am new to programming, and I just learned about array. However, in one of the quiz questions, I can't figure out why my answer is wrong. I tried to explain my thinking.
The question is:
int[] b = { 1, 2, 3 };
int[] c = b;
c[0] = b[2];
c[1] = b[1];
c[2] = b[0];
System.out.println(c[0] c[1] c[2]);
My thinking is although array is a reference type, int[] c = b can still be treated as
int [] c = { 1, 2, 3 }; // the same as int [] b
c[0] = b[2] means c[0] = c[0] b[2] = 1 3 = 4
c[1] = b[1] means c[1] = c[1] b[1] = 2 2 = 4
c[2] = b[0] means c[2] = c[2] b[0] = 3 1 = 4
So I thought that the output is 12. However, the answer is 15.
I am so sorry for asking such a basic question, but I was wondering if anyone can help me understand how to come up with 15. Thank you so much!
CodePudding user response:
actually java copies arrays by their references not values. so in the last line of your code, b[0] is changed to 4 so
c[2] = b[0] means c[2] = c[2] b[0] = 3 4 = 7
so your output is 15. If you want to copy an array without reference,you can do this:
int[] c = Arrays.copyOf(b, b.length);
now, your output should be 12.
CodePudding user response:
Since you set c = b, this means that whatever changes you make onto c will be reflected onto b and vice verca, since they reference the same array. If you wanted b and c to be separate arrays, you should use Arrays.copy().
For your problem, we can now go step by step to analyze how the values change during each step:
int[] b = { 1, 2, 3 };
int[] c = b;
c[0] = b[2];
//c[0] = c[0] b[2] = 1 3 = 4
//b[0] = 4
// b and c = {4, 2, 3}
c[1] = b[1];
//c[1] = c[1] b[1] = 2 2 = 4
//b[1] = 4
//b and c = {4, 4, 3}
c[2] = b[0];
//c[2] = c[2] b[0] = 3 4 = 7
//b[2] = 7
//b and c = {4, 4, 7}
System.out.println(c[0] c[1] c[2]);
//4 4 7 = 15 :)
I hope this helped! Please let me know if you need any further clarification or details :)
CodePudding user response:
As c and b refer to the same array, when c[0] is changed to 4, it means that b[0] is also 4. Thus, the result of c[2] = b[0] is 3 4 = 7, and the total sum of all elements is 4 4 7 = 15.
Assigning a reference to array int[] c = b; creates just an alias and it does NOT create a new instance of the array as in the case of its copying (using methods 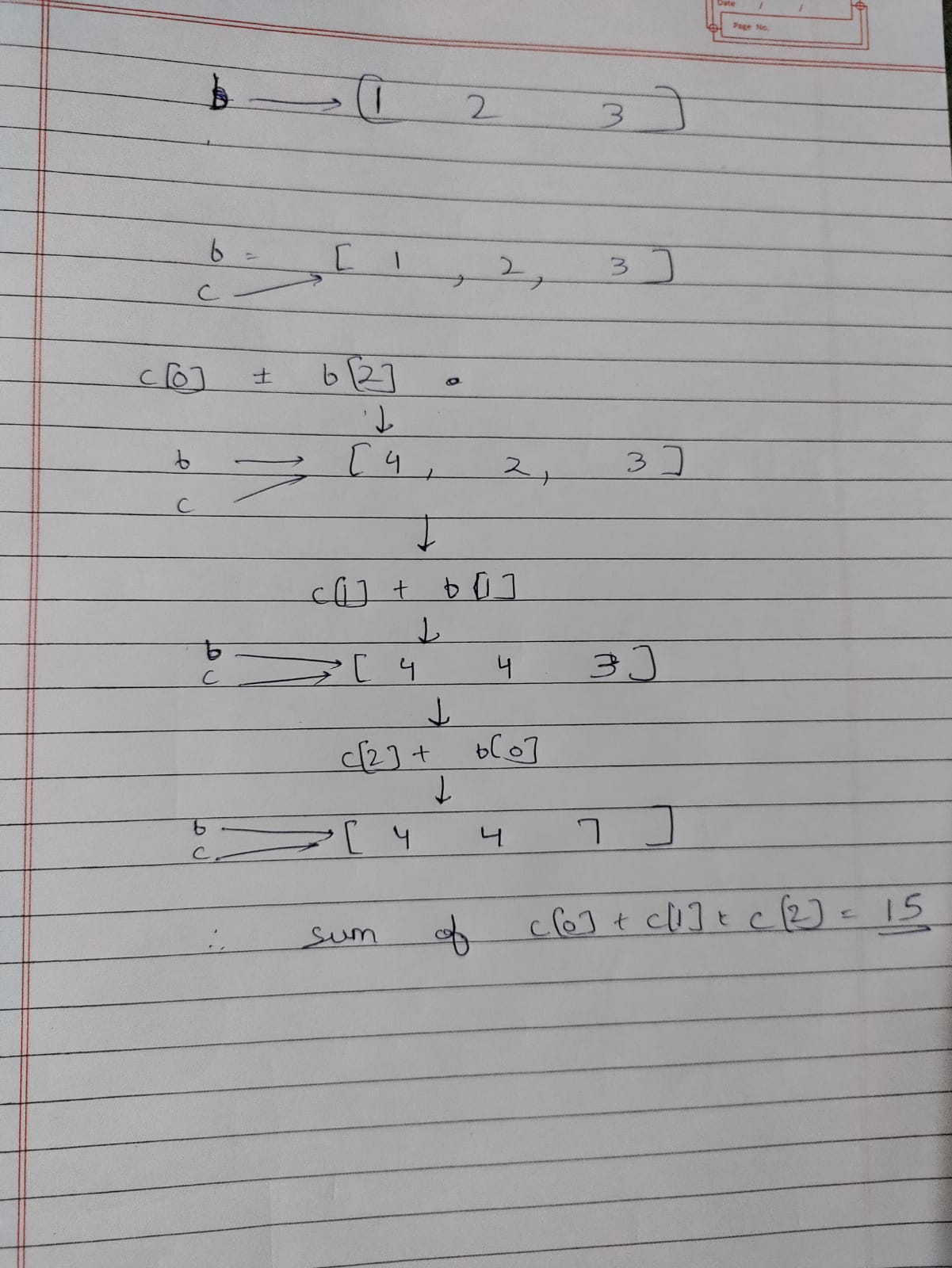
then output will be 4 4 7 which is 15.
