I am generating X509 certificates to authorize apps in Azure using .NET using the below code:
private static X509Certificate2 BuildSelfSignedCertificate(string CertificateName, int DaysValid)
{
SubjectAlternativeNameBuilder sanBuilder = new SubjectAlternativeNameBuilder();
sanBuilder.AddIpAddress(IPAddress.Loopback);
sanBuilder.AddIpAddress(IPAddress.IPv6Loopback);
sanBuilder.AddDnsName("localhost");
sanBuilder.AddDnsName(Environment.MachineName);
X500DistinguishedName distinguishedName = new X500DistinguishedName($"CN={CertificateName}");
using RSA rsa = RSA.Create(2048);
var request = new CertificateRequest(distinguishedName, rsa, HashAlgorithmName.SHA256, RSASignaturePadding.Pkcs1);
request.CertificateExtensions.Add(
new X509KeyUsageExtension(X509KeyUsageFlags.DataEncipherment | X509KeyUsageFlags.KeyEncipherment | X509KeyUsageFlags.DigitalSignature, false));
request.CertificateExtensions.Add(
new X509EnhancedKeyUsageExtension(
new OidCollection { new Oid("1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1") }, false));
request.CertificateExtensions.Add(sanBuilder.Build());
var certificate = request.CreateSelfSigned(new DateTimeOffset(DateTime.UtcNow.AddDays(-1)), new DateTimeOffset(DateTime.UtcNow.AddDays(DaysValid)));
#pragma warning disable CA1416 // Validate platform compatibility
certificate.FriendlyName = CertificateName;
#pragma warning restore CA1416 // Validate platform compatibility
return certificate;
}
This works great, but when I import it the cert using the following, the private key is not included:
X509Store store = new(StoreName.My, StoreLocation.LocalMachine);
store.Open(OpenFlags.ReadWrite);
store.Add(cert);
store.Close();
However, if I export the cert to a byte array and create a new X509Certificate2 object from the array, the private key is imported correctly.
var cert = new X509Certificate2(certificate.Export(X509ContentType.Pkcs12, "password"), "password", X509KeyStorageFlags.MachineKeySet | X509KeyStorageFlags.Exportable);
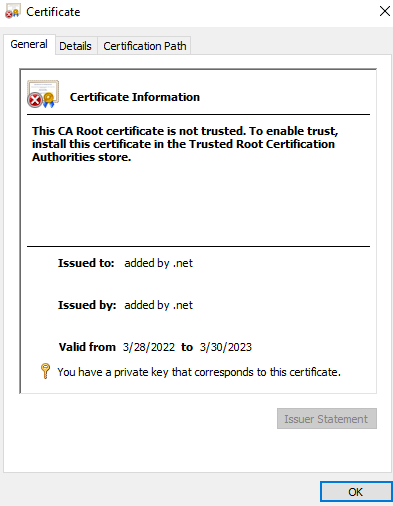
Notice the "You have a private key that corresponds to this certificate" message.
How can I import the cert private key without resorting to this awkward workaround?
CodePudding user response:
How can I import the cert private key without resorting to this awkward workaround?
By creating the key as a persisted key to begin with.
using RSA rsa = RSA.Create(2048);
This line creates an ephemeral (in-memory only) private key. Instead you can do
CngKeyCreationParameters keyParams = new CngKeyCreationParameters
{
ExportPolicy = CngExportPolicies.AllowPlaintextExport,
KeyCreationOptions = CngKeyCreationOptions.MachineKey,
Parameters =
{
new CngProperty("Length", BitConverter.GetBytes(2048), CngPropertyOptions.Persist),
},
};
using CngKey cngKey = CngKey.Create(CngAlgorithm.Rsa, Guid.NewGuid().ToString("D"), keyParams);
using RSA rsa = new RSACng(cngKey);
And now the created certificate is associated with an already-persisted key.
(Note that this snippet uses MachineKey and exportable because that's what the question has as the PFX import flags)