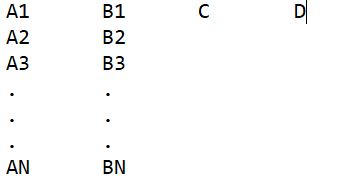
I have 2 numpy arrays of same length lets call them A and B and 2 scalar values named C and D. I want to store these values into a single txt file. I thought of the following structure:
It doesnt have to have this format I just thought its convenient and clear. I know how to write a the numpy arrays into a txt file and read them out again, but I struggle how to write the txt file as a combination of arrays and scalar values and how to read them out again from txt to numpy.
A = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
B = np.array([5, 4, 3, 2, 1])
C = [6]
D = [7]
np.savetxt('file.txt', (A, B))
A_B_load = np.loadtxt('file.txt')
A_load = A_B_load[0,:]
B_load= A_B_load[1,:]
This doesnt give me the same column structure that I proposed but stores the arrays in rows but that doesnt really matter.
I found one solution which is a bit unhandy since I have to fill up the scalar values with 0 for them to become of the same length like the arrays A and B there must be a smarter solution.
A = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
B = np.array([5, 4, 3, 2, 1])
C = [6]
D = [7]
fill = np.zeros(len(A)-1)
C = np.concatenate((C,fill))
D = np.concatenate((D, fill))
np.savetxt('file.txt', (A,B,C,D))
A_B_load = np.loadtxt('file.txt')
A_load = A_B_load[0,:]
B_load = A_B_load[1,:]
C_load = A_B_load[2,0]
D_load = A_B_load[3,0]
CodePudding user response:
A smarter solution could be to use pandas instead of numpy (if that is an option for you):
df = pd.concat([pd.DataFrame(arr) for arr in [A,B,C,D]], axis=1)
df.to_csv("test.txt", na_rep="", sep=" ", header=False, index=False)
a = pd.read_csv("test.txt", sep=" ", header=None).values
The first line creates a dataframe by concatenating all your arrays. Pandas' default behaviour is to replace missing values with NaNs. The second line writes the output file replacing NaNs by an empty string (as you seem to care about the file size). The last line gives you a numpy array:
In [45]: a
Out[45]:
array([[ 1., 5., 6., 7.],
[ 2., 4., nan, nan],
[ 3., 3., nan, nan],
[ 4., 2., nan, nan],
[ 5., 1., nan, nan]])
CodePudding user response:
In [123]: A = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
...: B = np.array([5, 4, 3, 2, 1])
...: C = [6]
...: D = [7]
savetxt is designed to write a 2d array in a consistent csv form - a neat table with the same number of columns in each row.
In [124]: arr = np.stack((A,B), axis=1)
In [125]: arr
Out[125]:
array([[1, 5],
[2, 4],
[3, 3],
[4, 2],
[5, 1]])
Here's one possible write format:
In [126]: np.savetxt('foo.txt', arr, fmt='%d', header=f'{C} {D}', delimiter=',')
...:
In [127]: cat foo.txt
# [6] [7]
1,5
2,4
3,3
4,2
5,1
I put the scalars in a header line, since they don't match with the arrays.
loadtxt can recreate that arr array:
In [129]: data = np.loadtxt('foo.txt', dtype=int, skiprows=1, delimiter=',')
In [130]: data
Out[130]:
array([[1, 5],
[2, 4],
[3, 3],
[4, 2],
[5, 1]])
The header line can be read with:
In [138]: with open('foo.txt') as f:
...: header = f.readline().strip()
...: line = header[1:]
...:
In [139]: line
Out[139]: ' [6] [7]'
I should have saved it as something that's simpler to parse, like '# 6,7'
Your accepted answer creates a dataframe with nan values and blanks in the csv
In [143]: import pandas as pd
In [144]: df = pd.concat([pd.DataFrame(arr) for arr in [A,B,C,D]], axis=1)
...: df.to_csv("test.txt", na_rep="", sep=" ", header=False, index=False)
In [145]: df
Out[145]:
0 0 0 0
0 1 5 6.0 7.0
1 2 4 NaN NaN
2 3 3 NaN NaN
3 4 2 NaN NaN
4 5 1 NaN NaN
In [146]: cat test.txt
1 5 6.0 7.0
2 4
3 3
4 2
5 1
Note that np.nan is a float, so some of the columns are float as a result. loadtxt can't handle those "blank" columns; np.genfromtxt is better at that, but it needs a delimiter like , to mark them.
Writing and reading the full length arrays is easy. But mixing types gets messy.
Here's a format that would be easier to write and read:
In [149]: arr = np.zeros((5,4),int)
...: for i,var in enumerate([A,B,C,D]):
...: arr[:,i] = var
...:
In [150]: arr
Out[150]:
array([[1, 5, 6, 7],
[2, 4, 6, 7],
[3, 3, 6, 7],
[4, 2, 6, 7],
[5, 1, 6, 7]])
In [151]: np.savetxt('foo.txt', arr, fmt='%d', delimiter=',')
In [152]: cat foo.txt
1,5,6,7
2,4,6,7
3,3,6,7
4,2,6,7
5,1,6,7
In [153]: np.loadtxt('foo.txt', delimiter=',', dtype=int)
Out[153]:
array([[1, 5, 6, 7],
[2, 4, 6, 7],
[3, 3, 6, 7],
[4, 2, 6, 7],
[5, 1, 6, 7]])