I'm trying to do a web App with ASP.NET Core 3.1. I have an existing SQL Database with full of users. I have only read access to this database, so I can't change nothing. My question is, can I somehow use it to authentication to Login instead of AspNetUsers table? (I don't need registration, nor forget password, etc., just a safety login)
My User database has these columns: Id(varchar),Name(varchar),Rank(int),Password(varchar),Email(varchar),Phone(varchar)
CodePudding user response:
use it to authentication to Login instead of AspNetUsers table
Below is a demo, you can refer to it.
LoginModel
public class LoginModel
{
[Required]
[Display(Name ="Username")]
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
public string Password { get; set; }
public bool RememberLogin { get; set; }
public string ReturnUrl { get; set; }
}
UserModel
public class UserModel
{
public int UserId { get; set; }
public string Username { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
public string Role { get; set; }
}
AccountController
[Note] I set fake data, you can get it directly from the database.
public class AccountController : Controller
{
//Sample Users Data, it can be fetched with the use of any ORM
public List<UserModel> users = null;
public AccountController()
{
users = new List<UserModel>();
users.Add(new UserModel() { UserId = 1, Username = "Anoop", Password = "123", Role = "Admin" });
users.Add(new UserModel() { UserId = 2, Username = "Other", Password = "123", Role = "User" });
}
public IActionResult Login(string ReturnUrl = "/")
{
LoginModel objLoginModel = new LoginModel();
objLoginModel.ReturnUrl = ReturnUrl;
return View(objLoginModel);
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Login(LoginModel objLoginModel)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
var user = users.Where(x => x.Username == objLoginModel.UserName && x.Password == objLoginModel.Password).FirstOrDefault();
if (user == null)
{
//Add logic here to display some message to user
ViewBag.Message = "Invalid Credential";
return View(objLoginModel);
}
else
{
//A claim is a statement about a subject by an issuer and
//represent attributes of the subject that are useful in the context of authentication and authorization operations.
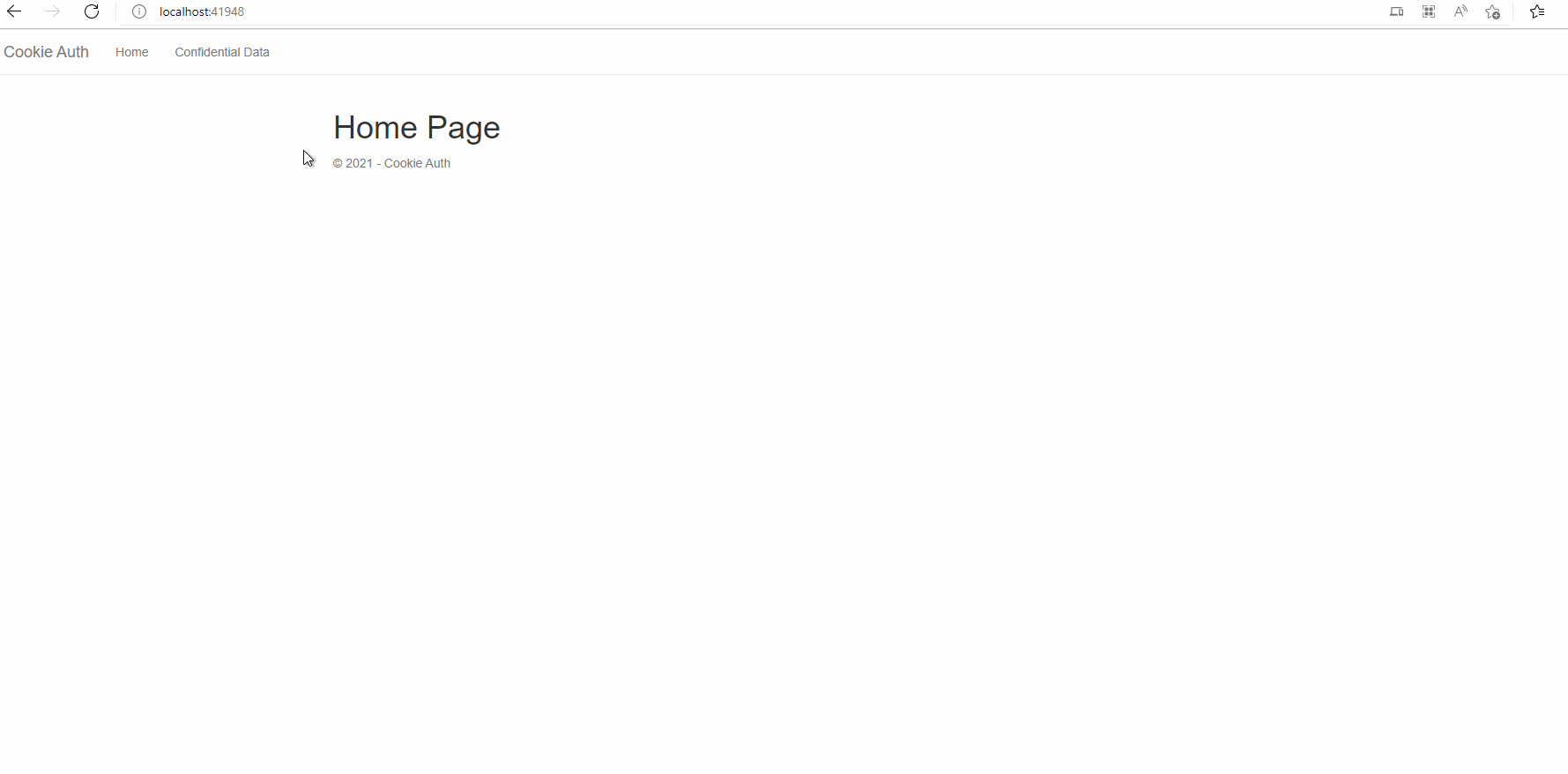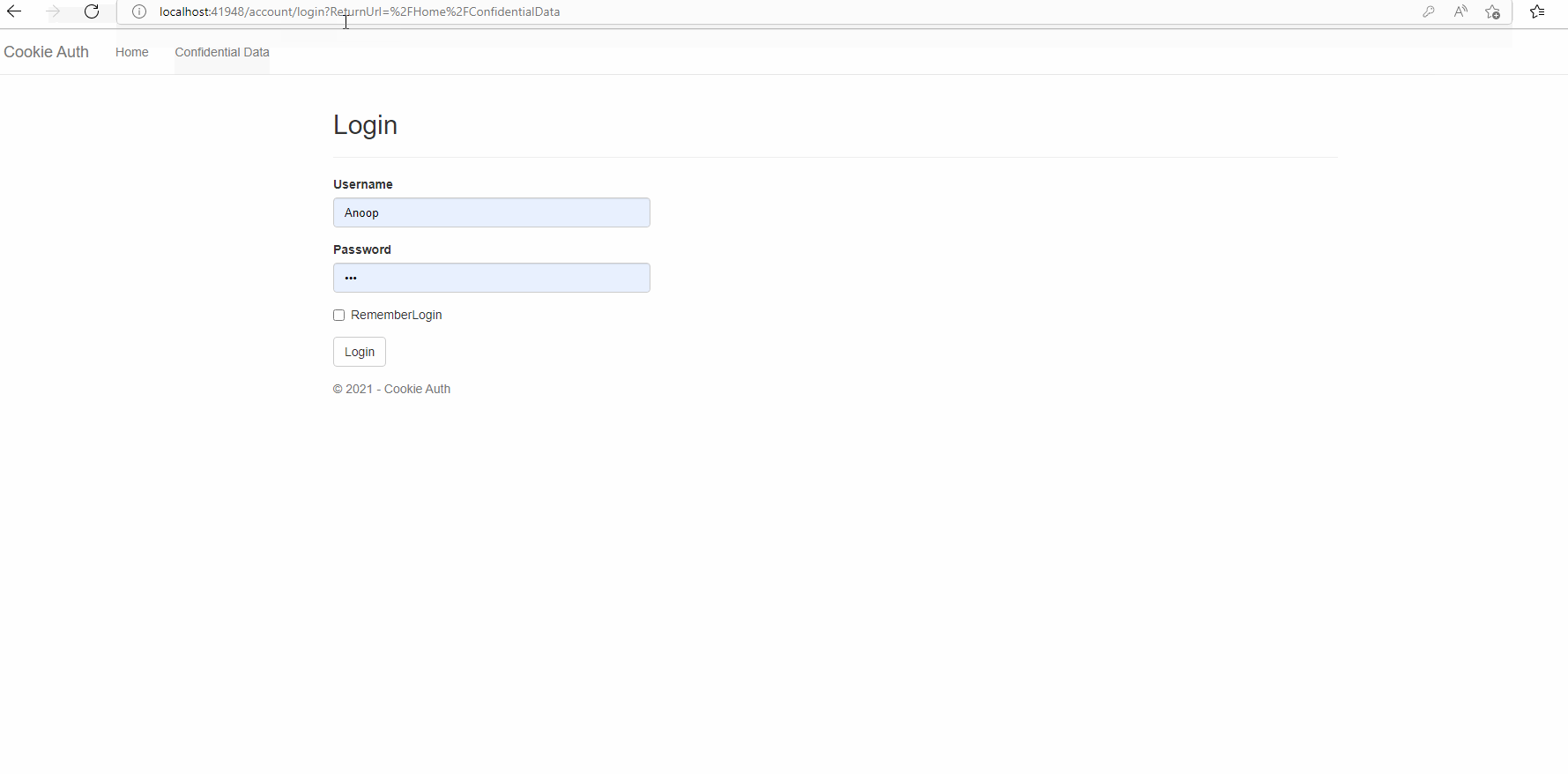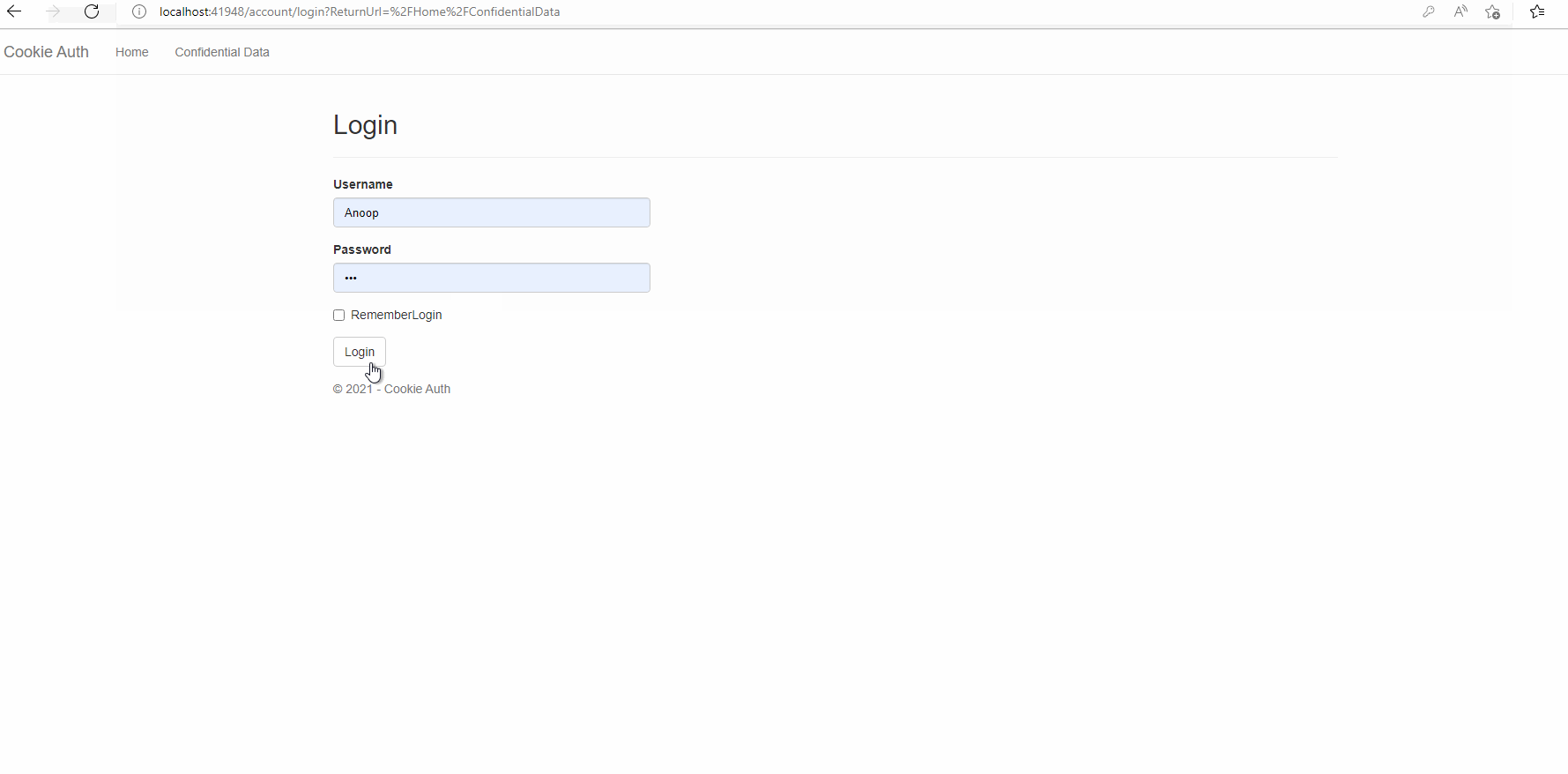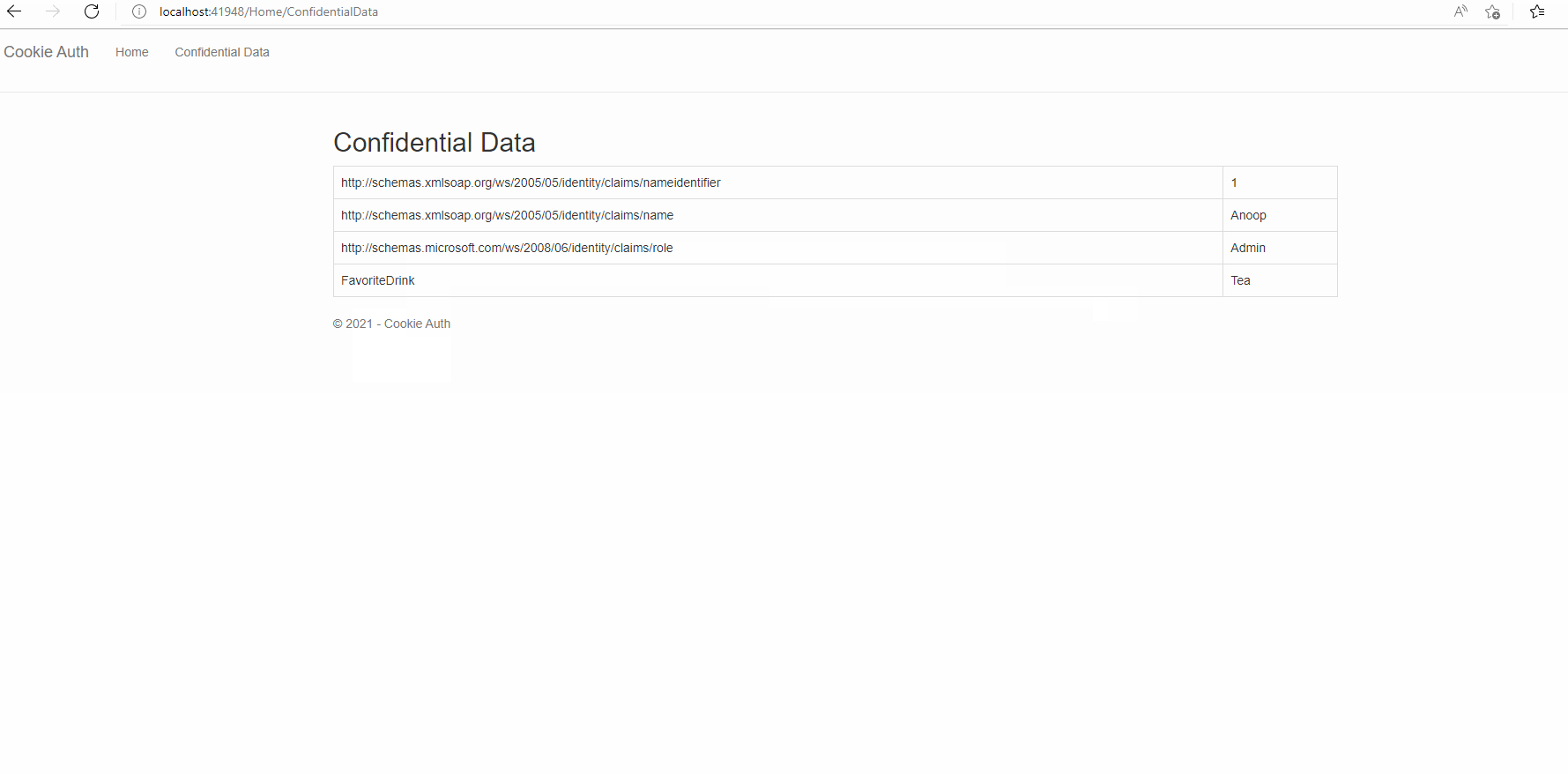
var claims = new List<Claim>() {
new Claim(ClaimTypes.NameIdentifier,Convert.ToString(user.UserId)),
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name,user.Username),
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role,user.Role),
new Claim("FavoriteDrink","Tea")
};
//Initialize a new instance of the ClaimsIdentity with the claims and authentication scheme
var identity = new ClaimsIdentity(claims, CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme);
//Initialize a new instance of the ClaimsPrincipal with ClaimsIdentity
var principal = new ClaimsPrincipal(identity);
//SignInAsync is a Extension method for Sign in a principal for the specified scheme.
//await HttpContext.SignInAsync(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme,
// principal, new AuthenticationProperties() { IsPersistent = objLoginModel.RememberLogin });
await HttpContext.SignInAsync(
principal, new AuthenticationProperties() { IsPersistent = objLoginModel.RememberLogin });
return LocalRedirect(objLoginModel.ReturnUrl);
}
}
return View(objLoginModel);
}
public async Task<IActionResult> LogOut() {
//SignOutAsync is Extension method for SignOut
await HttpContext.SignOutAsync(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme);
//Redirect to home page
return LocalRedirect("/");
}
}
In HomeController, use [Authorize] on ConfidentialData() method
public class HomeController : Controller
{
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
[Authorize]
public IActionResult ConfidentialData()
{
return View();
}
}
ConfidentialData view
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Confidential Data";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<h2>Confidential Data</h2>
@if (User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
<table >
@foreach (var claim in User.Claims) {
<tr><td>@claim.Type</td><td>@claim.Value</td></tr>
}
</table>
}
Register Authentication in startup
services.AddAuthentication(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddCookie(x => x.LoginPath = "/account/login");
...
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
Result:
Read Use cookie authentication without ASP.NET Core Identity to know more.
Login form
@model LoginModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Login";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<h2>Login</h2>
<hr />
<div >
<div >
<form asp-action="Login">
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" ></div>
@if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(ViewBag.Message))
{
<span >
@ViewBag.Message
</span>
}
@Html.HiddenFor(x => x.ReturnUrl)
<div >
<label asp-for="UserName" ></label>
<input asp-for="UserName" />
<span asp-validation-for="UserName" ></span>
</div>
<div >
<label asp-for="Password" ></label>
<input asp-for="Password" />
<span asp-validation-for="Password" ></span>
</div>
<div >
<div >
<label>
<input asp-for="RememberLogin" /> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.RememberLogin)
</label>
</div>
</div>
<div >
<input type="submit" value="Login" />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>