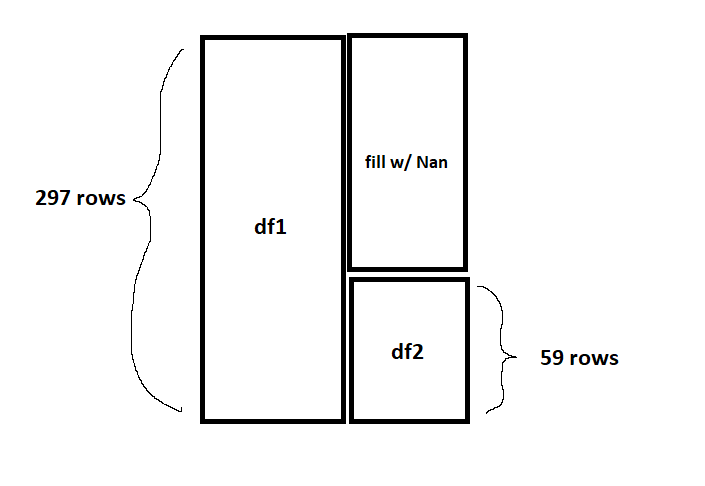
I have two one-column dataframes. One of which is 297 rows in length (I'll call this df1) and the other is 59 rows in length (I'll call this df2). I want to merge them together so that df2 matches with the bottom 59 rows of df1. The remaining 238 rows in the newly added df2 will be filled with NaN. How should I do this?
CodePudding user response:
Assuming that df1 is at least as long as df2, set the index of df2 with the end of that of df1 and concat:
out = pd.concat([df1, df2.set_axis(df1.index[-len(df2):])], axis=1)
example input:
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'col1': list('ABCDEFGH')})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'col2': list('WXYZ')})
output:
col1 col2
0 A NaN
1 B NaN
2 C NaN
3 D NaN
4 E W
5 F X
6 G Y
7 H Z
intermediate df2 with part of df1's index:
df2.set_axis(df1.index[-len(df2):])
col2
4 W
5 X
6 Y
7 Z
generalization
you can generalize to align to other parts, for example to align to the bottom minus 1 row:
skip = 1
pd.concat([df1, df2.set_axis(df1.index[-len(df2)-skip:-skip])], axis=1)
output:
col1 col2
0 A NaN
1 B NaN
2 C NaN
3 D W
4 E X
5 F Y
6 G Z
7 H NaN
CodePudding user response:
Let's assume you have this data in order to simulate the shape of your DataFrames:
df_one = pd.DataFrame(data=np.linspace(1, 297, 297), columns=["one"])
df_two = pd.DataFrame(data=np.linspace(101, 159, 59), columns=["two"])
You can create an empty DataFrame with a shape of df_one.shape[0] minus df_two.shape[0]:
data_nan = [np.nan for _ in range(df_one.shape[0] - df_two.shape[0])]
df_nan = pd.DataFrame(data=data_nan, columns=["two"])
Then create a temporary Dataframe with pd.concat:
# df_nan in first place so non NaN values will be in the bottom part
# .reset_index(drop=True) to keep indexes consistency
df_tmp = pd.concat([df_nan, df_two]).reset_index(drop=True)
And in the end...
# axis = 1 because you want to "append" a new column, not rows
df = pd.concat([df_one, df_tmp], axis=1).reset_index(drop=True)
CodePudding user response:
You can do a simple trick. reverse both dataframes, concatenate them and reverse them back. For reversing you can use df.iloc[::-1] or df.reindex(index=df.index[::-1])
You will need to reset index as well. You can use
df = df.reindex(index=df.index[::-1]).reset_index(drop=True)
