I'm trying to write a function which wraps an input value within an input range (inclusive lower-bound, exclusive upper-bound), so that the output value is always within that range.
For example, 4.9.wrapped(within: 3..<5) == 4.9, and 5.wrapped(within: 3..<5) == 3.
(3..<5 is Swift syntax for [3, 5)).
I wrote the below algorithm, which almost works perfectly, except when the input value is less than the lower-bound of the input range, then the output's inclusivity flips.
For example, when the input range is [3, 5) and the input value is 20, then the range output correctly reflects as [3, 5) in the output, but when the input value is 1 with the same input range, then the output incorrectly reflects a (3, 5] range.
Example code in Swift
public extension FloatingPoint {
func wrapped(within range: Range<Self>) -> Self {
let breadth = range.upperBound - range.lowerBound
let offset: Self
if self < range.lowerBound {
offset = breadth
}
else {
offset = 0
}
let baseResult = (self - range.lowerBound).truncatingRemainder(dividingBy: breadth)
return baseResult range.lowerBound offset
}
}
Example code as pseudocode
function (value: Number, rangeLowerBoundInclusive: Number, rangeUpperBoundExclusive: Number) returns Number {
let breadth be (rangeUpperBoundExclusive - rangeLowerBoundInclusive)
if (value is less than rangeLowerBoundInclusive)
let offset be breadth
else
let offset be 0
let baseResult be ((value - rangeLowerBoundInclusive) mod breadth)
return baseResult rangeLowerBoundInclusive offset
}
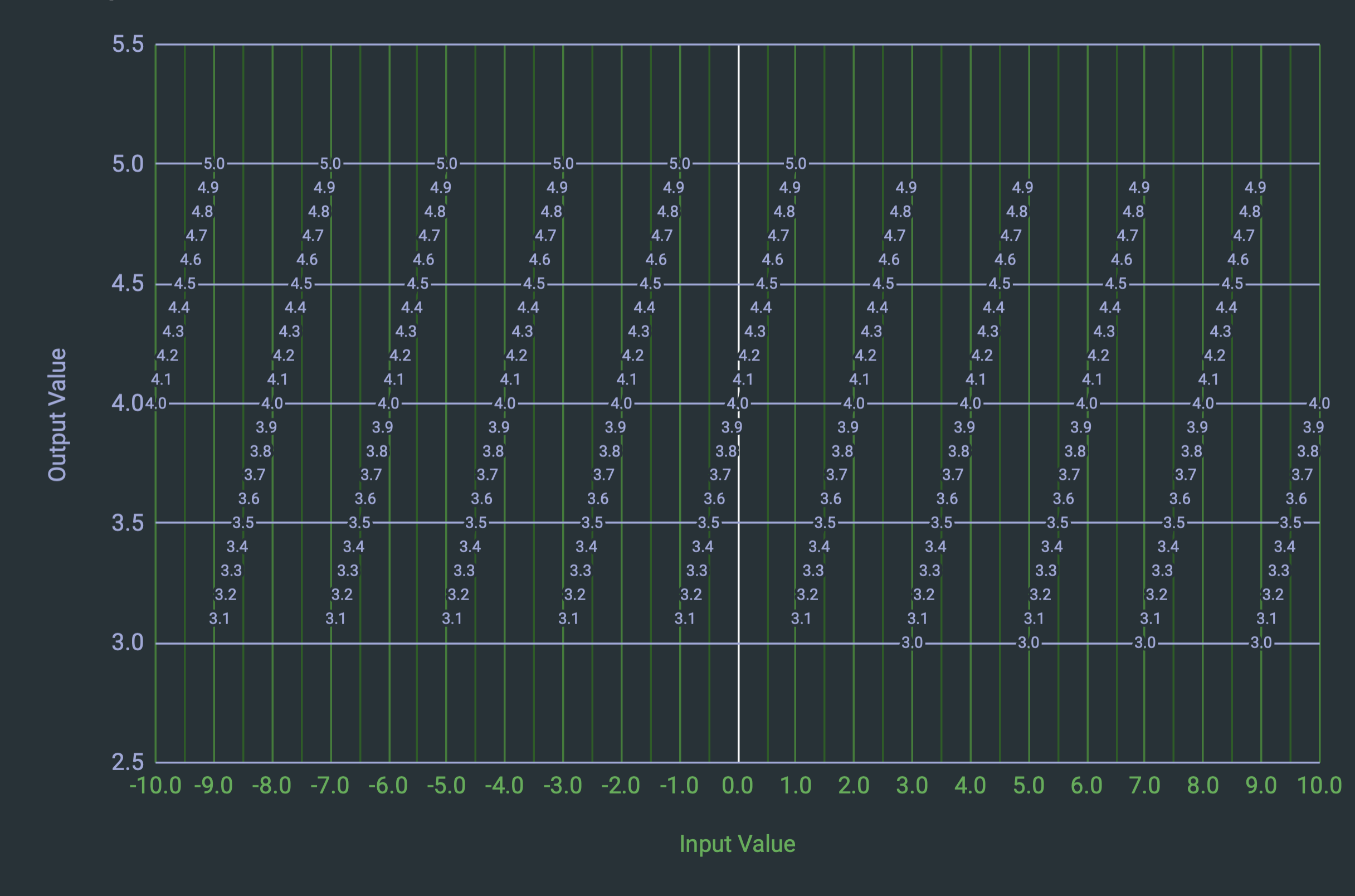
Output Visualization
Here is a visualization of the output for all input values from -10 to 10, stepping 0.1 at a time, with the range [3, 5):
As you can see, the input values less than 3.0 all appear within the range (3, 5], and the input values greater than or equal to 3.0 all appear within the range [3, 5). Why is this, and how can I make it so that all values are within [3, 5)?
CodePudding user response:
The edge case is when self - lowerBound is divisible by breadth at left side of the range.
In this situation, baseResult is 0, your code will wrongly add offset of breadth, then the result becomes 5.
You want to return lowerBound baseResult breadth only when baseResult < 0 (different from your code: self < range.lowerBound).