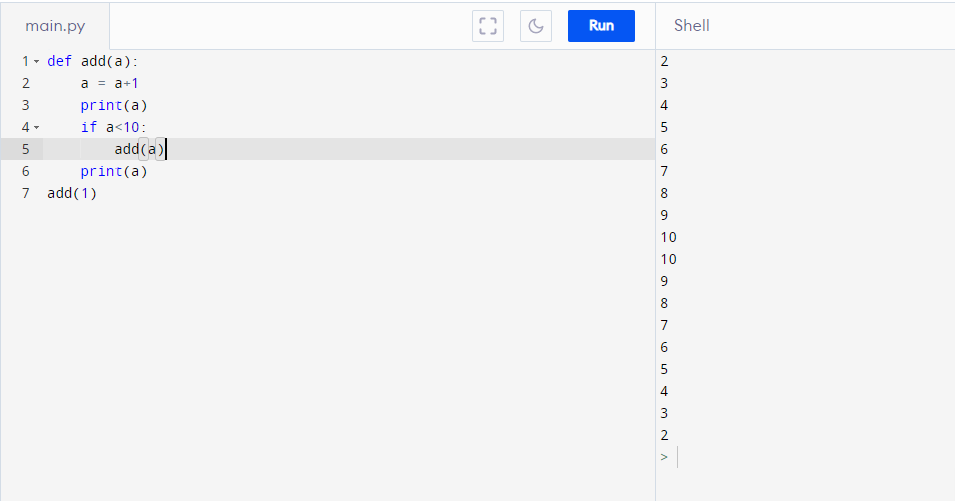
def add(a):
a = a 1
print(a)
if a < 10:
add(a)
print(a)
add(1)
I don't understand why the value of a started reducing after 10 when it should've stopped at 10 even without an else statement. Can anyone explain the reason?
CodePudding user response:
print() debugging
With the help of some f-strings, we can sort this out:
def add(a):
a = a 1
print(f"#1, a: {a}, id: {id(a)}")
if a < 10:
print("recursion")
add(a)
print(f"#2, a: {a}, id: {id(a)}")
add(1)
# stdout:
#1, a: 2, id: 9801280
recursion
#1, a: 3, id: 9801312
recursion
#1, a: 4, id: 9801344
recursion
#1, a: 5, id: 9801376
recursion
#1, a: 6, id: 9801408
recursion
#1, a: 7, id: 9801440
recursion
#1, a: 8, id: 9801472
recursion
#1, a: 9, id: 9801504
recursion
#1, a: 10, id: 9801536
#2, a: 10, id: 9801536
#2, a: 9, id: 9801504
#2, a: 8, id: 9801472
#2, a: 7, id: 9801440
#2, a: 6, id: 9801408
#2, a: 5, id: 9801376
#2, a: 4, id: 9801344
#2, a: 3, id: 9801312
#2, a: 2, id: 9801280
Disassembler
The bytecode for your version of add() doesn't show any BINARY_SUBTRACT operation:
import dis
dis.dis(add)
2 0 LOAD_FAST 0 (a)
2 LOAD_CONST 1 (1)
4 BINARY_ADD
6 STORE_FAST 0 (a)
3 8 LOAD_GLOBAL 0 (print)
10 LOAD_FAST 0 (a)
12 CALL_FUNCTION 1
14 POP_TOP
4 16 LOAD_FAST 0 (a)
18 LOAD_CONST 2 (10)
20 COMPARE_OP 0 (<)
22 POP_JUMP_IF_FALSE 32
5 24 LOAD_GLOBAL 1 (add)
26 LOAD_FAST 0 (a)
28 CALL_FUNCTION 1
30 POP_TOP
6 >> 32 LOAD_GLOBAL 0 (print)
34 LOAD_FAST 0 (a)
36 CALL_FUNCTION 1
38 POP_TOP
40 LOAD_CONST 0 (None)
42 RETURN_VALUE
Explanation
The
ifstatement recursively executesadd()until before the last line of the function, which then just keeps "waiting".All these waiting "stacked" instruction lines will be eventually executed in a LIFO order, because the recent calls were called by, and solve, the old ones.
The end result is that
ais not being decremented, instead is evaluated with the old values from each "waiting" instruction line.
Extra
This kind of recursion can be useful for writing pyramid-like (double top) patterns to the stdout:
def paint_pyramid(a):
a = a 1
print(a*'*')
if a < 5:
paint_pyramid(a)
print(a*'*')
paint_pyramid(0)
# stdout:
*
**
***
****
*****
*****
****
***
**
*