With the R code below,
library(ggplot2)
library(ggridges)
iris$m <- iris$Sepal.Length-5.5
pp <- aggregate(m ~ Species, iris, function(x) 1-ecdf(x)(0))
ecdf(x)(0)))
names(pp)[2] <- 'P'
dat <- merge(iris[, c('Species', 'm')], pp)
dev.new(width=6, height=3)
ggplot(dat, aes(x = m, y = Species, fill=P))
stat_density_ridges(quantile_lines = FALSE, alpha = 0.7)
scale_fill_gradientn(colors = c("blue","cyan","gray","gray","yellow","red"), limits = c(0,1))
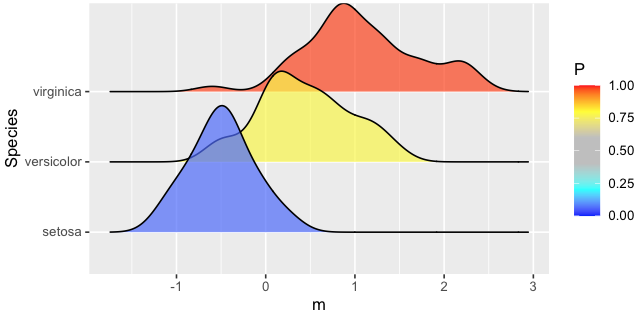
I get the following ridge plot
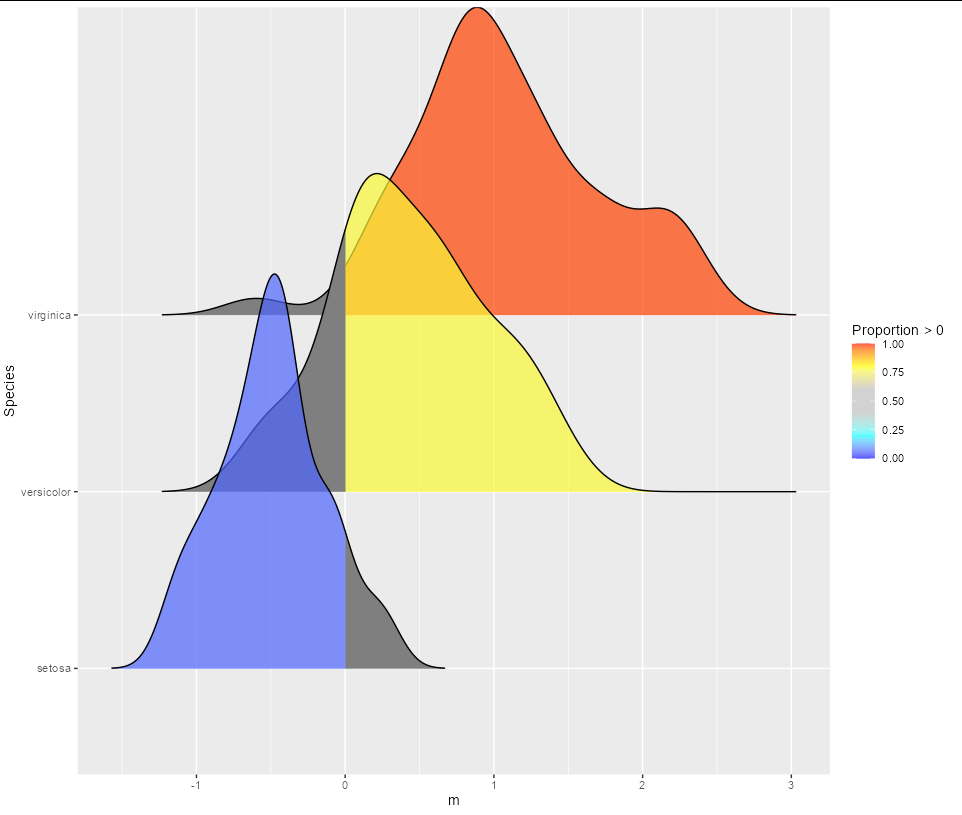
The color indicates the probability or the area under each density curve above zero on the x-axis (i.e., the value in dat$P). I want to modify the ridge plot so that, if dat$P >=0.5, show the color-coded shading only above 0 on the x-axis; if dat$P
< 0.5, show the color-coded shading only below 0 on the x-axis.
Any suggestions?
CodePudding user response:
I think you probably need two different layers here:
ggplot(dat, aes(x = m, y = Species, label = P))
geom_density_ridges_gradient(
aes(fill = if_else(stat(x) > 0, as.numeric(stat(label)), NA_real_)),
quantile_lines = FALSE,
data = dat %>% filter(P > 0.5))
geom_density_ridges_gradient(
aes(fill = if_else(stat(x) < 0, as.numeric(stat(label)), NA_real_)),
quantile_lines = FALSE,
data = dat %>% filter(P < 0.5))
labs(fill = "Proportion > 0")
scale_fill_gradientn(colors = scales::alpha(c("blue","cyan","gray","gray",
"yellow","red"), 0.7),
limits = c(0,1))