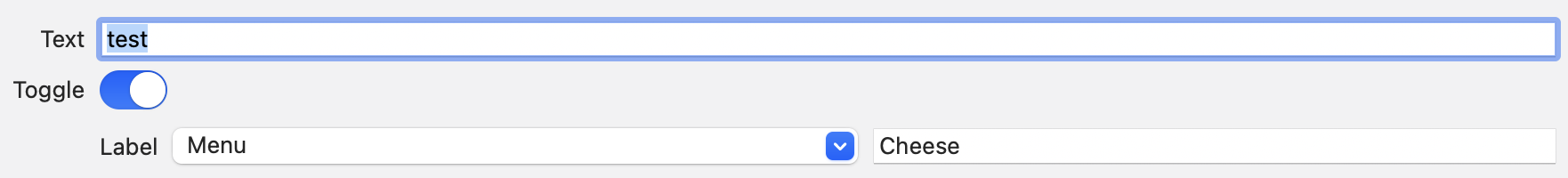
I am trying to include a custom HStack row in a SwiftUI Form as follows:
var body: some View {
Form {
TextField("Text", text: .constant("test"))
Toggle("Toggle", isOn: .constant(true))
.toggleStyle(SwitchToggleStyle())
HStack {
Text("Label")
MenuButton("Menu") {
Button(action: {
print("Clicked Pizza")
}) { Text("Pizza") }
Button(action: {
print("Clicked Pasta")
}) { Text("Pasta") }
}
TextField("Topping", text: .constant("Cheese"))
.labelsHidden()
}
}
.padding()
}
resulting in
However, I would like Label to be vertically aligned with Toggle and Menu vertically aligned with the toggle.
Is there a standard way of choosing the alignment mode for the custom HStack row?
CodePudding user response:
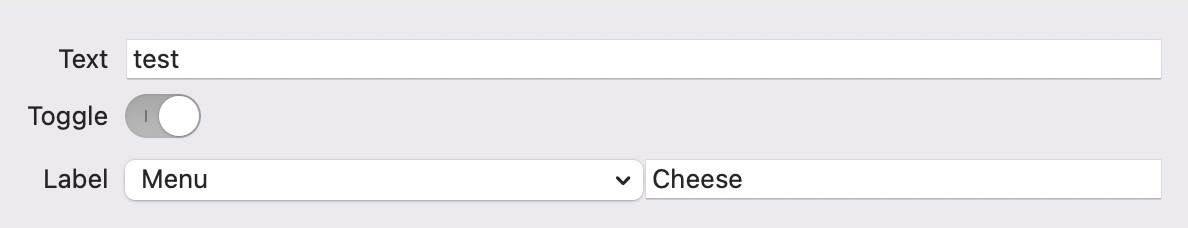
You can wrap your content inside a VStack and use its alignment modifier to align all the content to the leading e.g:
VStack(alignment: .leading)
like this:
var body: some View {
Form {
VStack (alignment: .leading){
TextField("Text", text: .constant("test"))
Toggle("Toggle", isOn: .constant(true))
.toggleStyle(SwitchToggleStyle())
HStack {
Text("Label")
MenuButton("Menu") {
Button(action: {
print("Clicked Pizza")
}) { Text("Pizza") }
Button(action: {
print("Clicked Pasta")
}) { Text("Pasta") }
}
TextField("Topping", text: .constant("Cheese"))
.labelsHidden()
}
.frame(width: .infinity, height: .infinity)
}
}
.padding()
}
However, this view has not been backported to earlier versions of macOS, so if you need to support earlier versions you'll need another approach.
Earlier versions of macOS
Building on the preference key code from @Nhat Nguyen Duc, the key is to use alignment guides rather than padding. Creating a custom view, and with a customised preference that only measures the width:
struct LabeledHStack<Content: View>: View {
var label: String
var content: () -> Content
@State var labelWidth: CGFloat = 0
init(_ label: String, @ViewBuilder content: @escaping () -> Content) {
self.label = label
self.content = content
}
var body: some View {
HStack {
Text(label)
.readSize { self.labelWidth = $0 }
content()
}
.alignmentGuide(.leading) { _ in labelWidth 10 } // see note
}
}
struct WidthPreferenceKey: PreferenceKey {
static var defaultValue: CGFloat = 0
static func reduce(value: inout CGFloat, nextValue: () -> CGFloat) { }
}
extension View {
func readWidth(onChange: @escaping (CGFloat) -> Void) -> some View {
background(
GeometryReader { geometryProxy in
Color.clear
.preference(key: WidthPreferenceKey.self, value: geometryProxy.size.width)
}
)
.onPreferenceChange(WidthPreferenceKey.self, perform: onChange)
}
}
Note that in the custom view I've added 10 pixels to quickly emulate the spacing between a label and its form elements. There is probably a better way to make this work for accessibility sizes, etc., (e.g., the use of a @ScaledMetric value).
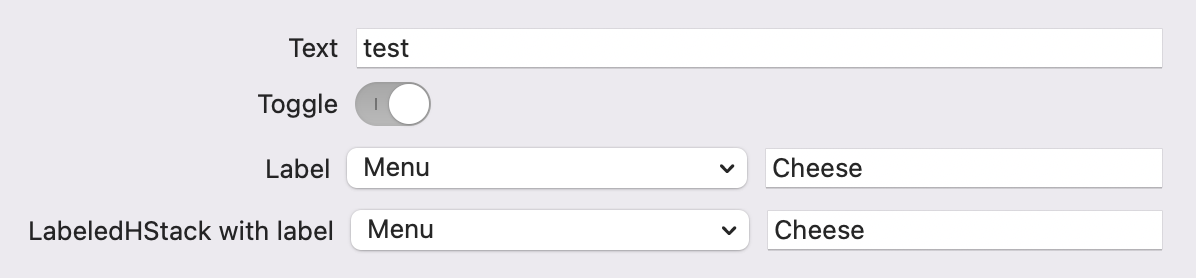
Below has a line with macOS13's LabeledContent, followed by LabeledHStack:
CodePudding user response:
macOS 13
LabeledContent {
HStack {
// ...
}
} label: {
Text("Count")
}
- Read more about
LabeledContenthere
Previous version
Idea: Calculate the size of the label using GeometryReader, and offset the view by its width.
@State private var textSize = CGSize.zero
var body: some View {
Form {
TextField("Text", text: .constant("test"))
.padding(.leading, -textSize.width)
Toggle("Toggle", isOn: .constant(true))
.toggleStyle(SwitchToggleStyle())
.padding(.leading, -textSize.width)
HStack {
Text("Label")
.readSize { textSize in
self.textSize = textSize
}
MenuButton("Menu") {
Button("Pizza") {
print("Clicked Pizza")
}
Button("Pasta") {
print("Clicked Pasta")
}
}
TextField("Topping", text: .constant("Cheese"))
.labelsHidden()
}
.padding(.leading, -textSize.width - 10)
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity)
}
.padding(.leading, textSize.width 10)
.padding()
}
extension View
extension View {
func readSize(onChange: @escaping (CGSize) -> Void) -> some View {
background(
GeometryReader { geometryProxy in
Color.clear
.preference(key: SizePreferenceKey.self, value: geometryProxy.size)
}
)
.onPreferenceChange(SizePreferenceKey.self, perform: onChange)
}
}
struct SizePreferenceKey
struct SizePreferenceKey: PreferenceKey {
static var defaultValue: CGSize = .zero
static func reduce(value: inout CGSize, nextValue: () -> CGSize) { }
}
- Bonus: For a button that contains only label, you can use
Button(<#String#>) { <#Action#> }
instead of
Button(action: { <#Action#> }) { Text(<#String#>) }