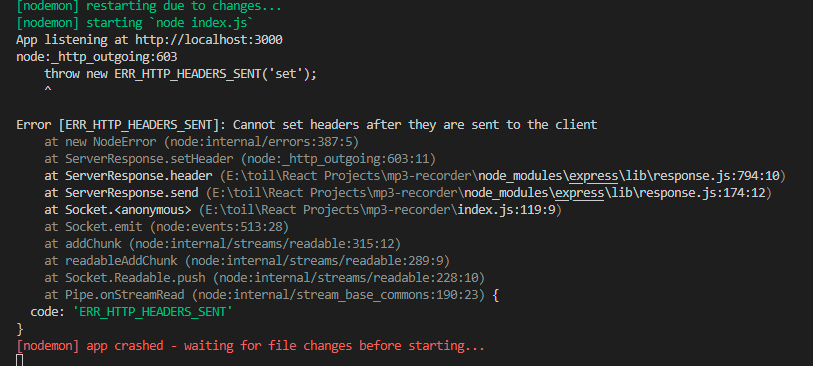
I am trying to run a python file (which is actually running a Deep learning model) on a button click using Node JS. I am trying to achieve this using input form in html and routes in index.js file. But this is causing this error after running for a while:
I just want to run the python file in the background, no arguments, no input or output.
This is my index.html file:
<form action="/runpython" method="POST">
<button type="submit">Run python</button>
</form>
And this is my index.js file:
function callName(req, res) {
var spawn = require("child_process").spawn;
var process = spawn("python", ["denoising.py"]);
process.stdout.on("data", function (data) {
res.send(data.toString());
});
}
app.post("/runpython", callName);
Note: This works fine if I have simple print statement in my .py file
print("Hello World!")
But running below code in .py file creates an issue
"""# import modules"""
"""# loading previously trained model"""
import noisereduce as nr
import numpy as np
import librosa
import librosa.display
import IPython.display as ipd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.models import load_model
import soundfile as sf
model = load_model(
r'model/denoiser_batchsize_5_epoch_100_sample_2000_org_n_n.hdf5', compile=True)
"""# testing on real world audio
"""
# function of moving point average used for minimizing distortion in denoised audio.
def moving_average(x, w):
return np.convolve(x, np.ones(w), 'valid') / w
# audio , sr = librosa.load(r'real_world_data/noise speech.wav' , res_type='kaiser_fast')
audio, sr = librosa.load(r'real_world_data/winona.wav', res_type='kaiser_fast')
# audio, sr = librosa.load(r'real_world_data/babar.wav', res_type='kaiser_fast')
# audio, sr = librosa.load(r'real_world_data/sarfaraz_eng.wav', res_type='kaiser_fast')
print(audio)
print(len(audio))
ipd.Audio(data=audio, rate=22050)
real_audio_spec = np.abs(librosa.stft(audio))
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
img = librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(
real_audio_spec, ref=np.max), y_axis='log', x_axis='time', ax=ax)
ax.set_title('Power spectrogram input real audio ')
fig.colorbar(img, ax=ax, format="% 2.0f dB")
ipd.Audio(data=audio, rate=22050)
start = 0
end = 65536
print(len(audio))
print(len(audio)/22050)
split_range = int(len(audio) / 65536)
print(split_range)
predicted_noise = []
input_audio = []
for i in range(split_range):
audio_frame = audio[start:end]
input_audio.append(audio_frame)
audio_reshape = np.reshape(audio_frame, (1, 256, 256, 1))
prediction = model.predict(audio_reshape)
prediction = prediction.flatten()
predicted_noise.append([prediction])
start = start 65536
end = end 65536
predicted_noise = np.asarray(predicted_noise).flatten()
input_audio = np.asarray(input_audio).flatten()
real_pred_noise_spec = np.abs(librosa.stft(predicted_noise))
"""## input audio to model"""
ipd.Audio(data=input_audio, rate=22050)
sf.write('input_audio.wav', input_audio.astype(np.float32), 22050, 'PCM_16')
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
img = librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(
real_pred_noise_spec, ref=np.max), y_axis='log', x_axis='time', ax=ax)
ax.set_title('Power spectrogram pred noise of real audio ')
fig.colorbar(img, ax=ax, format="% 2.0f dB")
ipd.Audio(data=predicted_noise, rate=22050)
sf.write('predicted_noise.wav', predicted_noise.astype(
np.float32), 22050, 'PCM_16')
ipd.Audio(data=moving_average(predicted_noise, 8), rate=22050)
denoised_final_audio = input_audio - predicted_noise
real_denoised_audio_spec = np.abs(librosa.stft(denoised_final_audio))
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
img = librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(
real_denoised_audio_spec, ref=np.max), y_axis='log', x_axis='time', ax=ax)
ax.set_title('Power spectrogram final denoised real audio ')
fig.colorbar(img, ax=ax, format="% 2.0f dB")
ipd.Audio(data=denoised_final_audio, rate=22050)
sf.write('denoised_final_audio_by_model.wav',
denoised_final_audio.astype(np.float32), 22050, 'PCM_16')
"""## moving point average of the real world denoised signal"""
real_world_mov_avg = moving_average(denoised_final_audio, 4)
print(real_world_mov_avg)
print(len(real_world_mov_avg))
ipd.Audio(data=real_world_mov_avg, rate=22050)
"""## noise reduce library"""
# !pip install noisereduce
"""### nr on real world audio"""
# if you cant import it. than you need to install it using 'pip install noisereduce'
"""#### using noise reduce directly on the real world audio to see how it works on it. """
reduced_noise_direct = nr.reduce_noise(
y=audio.flatten(), sr=22050, stationary=False)
ipd.Audio(data=reduced_noise_direct, rate=22050)
sf.write('denoised_input_audio_direct_by_noisereduce_no_model.wav',
reduced_noise_direct.astype(np.float32), 22050, 'PCM_16')
"""#### using noise reduce on model denoised final output. to make it more clean."""
# perform noise reduction
reduced_noise = nr.reduce_noise(y=real_world_mov_avg.flatten(
), sr=22050, y_noise=predicted_noise, stationary=False)
# wavfile.write("mywav_reduced_noise.wav", rate, reduced_noise)
ipd.Audio(data=reduced_noise, rate=22050)
sf.write('denoised_final_audio_by_model_than_noisereduce_applied.wav',
reduced_noise.astype(np.float32), 22050, 'PCM_16')
print("python code executed")
If there is any alternative, then please let me know. I am new to Node JS and this is the only workable method I found
CodePudding user response:
Why are you using res.send(data.toString());, I don't see any use of this line in your code. Try removing the mentioned code and run again.