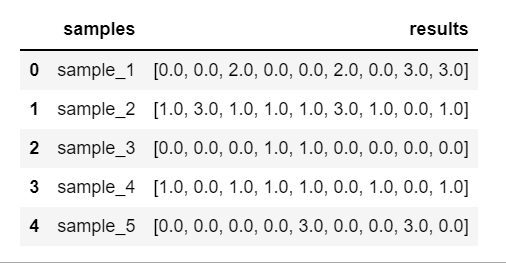
I have a dataframe (df) that has two columns (samples, results)
df = pd.DataFrame({'samples': ['sample_1', 'sample_2', 'sample_3', 'sample_4', 'sample_5'],
'results': [[0.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,3.0,3.0],
[1.0,3.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,3.0,1.0,0.0,1.0],
[0.0,0.0,0.0,1.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0],
[1.0,0.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,0.0,1.0,0.0,1.0],
[0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,3.0,0.0]]})
I applied function (f) to calculate the count of each value, e.g. for sample_1, we have 5 numbers of (0), zero number of 1, two numbers of 2 and 3. For sample_2, we have 1 number of (0), 6 number of 1, zero number of 2 and 2 number of 3, etc.
from collections import Counter
def f(x):
d = Counter(x)
return ((d.get(0, 0), d.get(1, 0), d.get(2, 0), d.get(3, 0)))
The output:
I want to remove any zero value from (counts) column, so the expercted ouptput is:
Ihave tried this code to remove zero values but it not working!
def trim_zeros_in_rows(ndarr):
return np.array([np.trim_zeros(row) for row in ndarr])
print(trim_zeros_in_rows(df['counts']))
CodePudding user response:
Using a list comprehension seems to do the trick (if you don't care about the type, you get rid of the tuple() call):
df['count'].apply(lambda x: tuple([y for y in x if y != 0]))
Giving you:
0 (5, 2, 2)
1 (1, 6, 2)
2 (7, 2)
3 (3, 6)
4 (7, 2)
Name: count, dtype: object