I have this association in the DB -
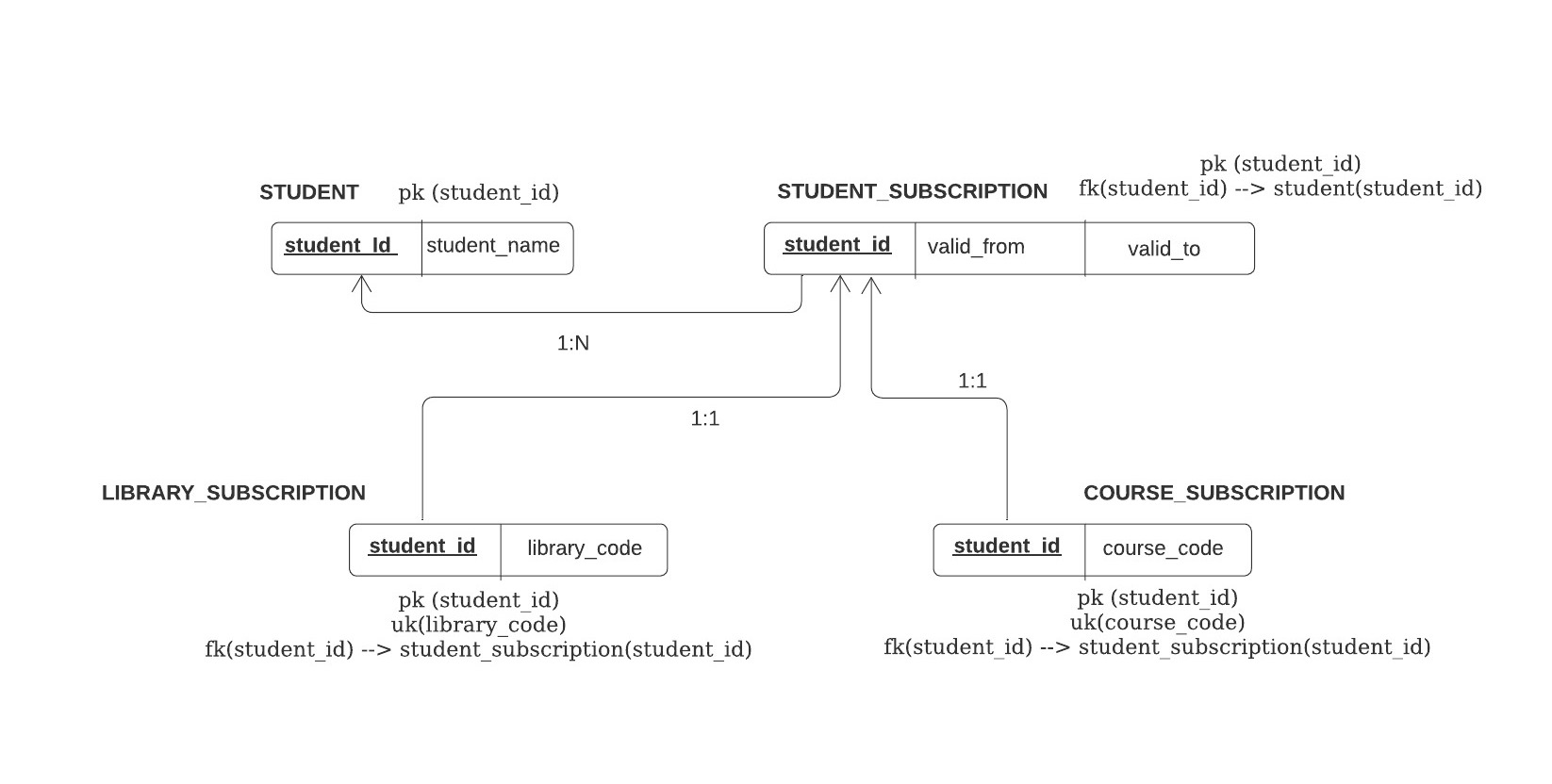
I want the data to be persisted in the tables like this -
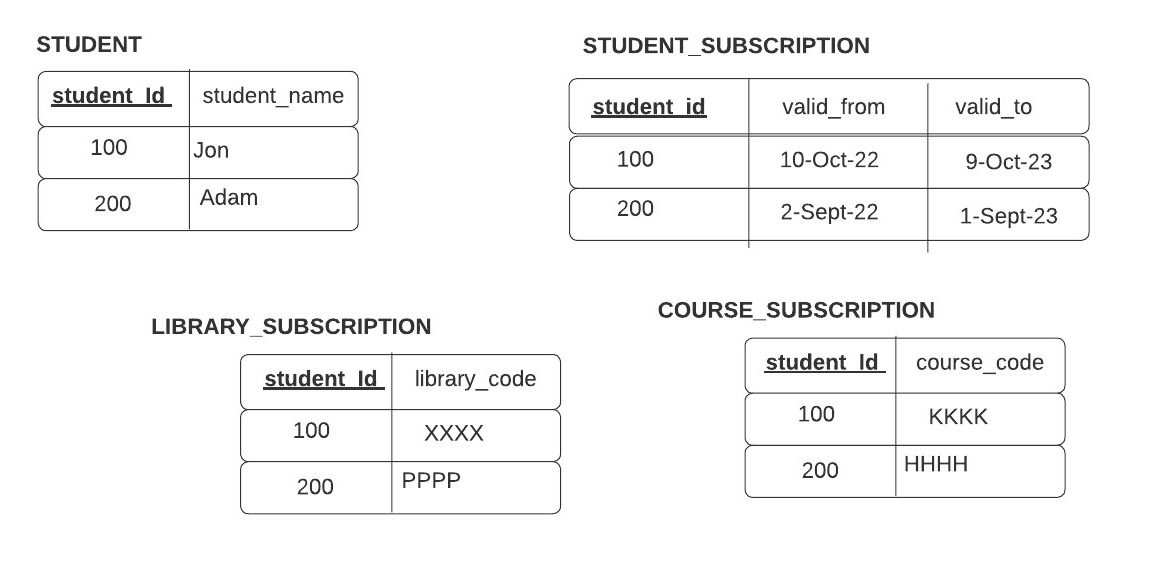
The corresponding JPA entities have been modeled this way (omitted getters/setters for simplicity) -
STUDENT Entity -
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
public class Student {
@Id
@SequenceGenerator(name = "student_pk_generator", sequenceName =
"student_pk_sequence", allocationSize = 1)
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE, generator =
"student_pk_generator")
@Column(name = "student_id", nullable = false)
private Long studentId;
@Column(name = "name", nullable = false)
private String studentName;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "student", cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
private Set<StudentSubscription> studentSubscription;
}
STUDENT_SUBSCRIPTION Entity -
@Entity
@Table(name = "student_subscription")
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED)
public abstract class StudentSubscription {
@Id
private Long studentId;
@ManyToOne(optional = false)
@JoinColumn(name = "student_id", referencedColumnName = "student_id")
@MapsId
private Student student;
@Column(name = "valid_from")
private Date validFrom;
@Column(name = "valid_to")
private Date validTo;
}
LIBRARY_SUBSCRIPTION Entity -
@Entity
@Table(name = "library_subscription",
uniqueConstraints = {@UniqueConstraint(columnNames = {"library_code"})})
@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn(name = "student_id")
public class LibrarySubscription extends StudentSubscription {
@Column(name = "library_code", nullable = false)
private String libraryCode;
@PrePersist
private void generateLibraryCode() {
this.libraryCode = // some logic to generate unique libraryCode
}
}
COURSE_SUBSCRIPTION Entity -
@Entity
@Table(name = "course_subscription",
uniqueConstraints = {@UniqueConstraint(columnNames = {"course_code"})})
@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn(name = "student_id")
public class CourseSubscription extends StudentSubscription {
@Column(name = "course_code", nullable = false)
private String courseCode;
@PrePersist
private void generateCourseCode() {
this.courseCode = // some logic to generate unique courseCode
}
}
Now, there is a Student entity already persisted with the id let's say - 100. Now I want to persist this student's library subscription. For this I have created a simple test using Spring DATA JPA repositories -
@Test
public void testLibrarySubscriptionPersist() {
Student student = studentRepository.findById(100L).get();
StudentSubscription librarySubscription = new LibrarySubscription();
librarySubscription.setValidFrom(//some date);
librarySubscription.setValidTo(//some date);
librarySubscription.setStudent(student);
studentSubscriptionRepository.save(librarySubscription);
}
On running this test I am getting the exception -
org.springframework.dao.InvalidDataAccessApiUsageException: detached entity passed to persist: com.springboot.data.jpa.entity.Student; nested exception is org.hibernate.PersistentObjectException: detached entity passed to persist: com.springboot.data.jpa.entity.Student
To fix this I attach a @Transactional to the test. This fixed the above exception for detached entity, but the entity StudentSubscription and LibrarySubscription are not getting persisted to the DB. In fact the transaction is getting rolled back.
Getting this exception in the logs -
INFO 3515 --- [ main] o.s.t.c.transaction.TransactionContext : Rolled back transaction for test: [DefaultTestContext@35390ee3 testClass = SpringDataJpaApplicationTests, testInstance = com.springboot.data.jpa.SpringDataJpaApplicationTests@48a12036, testMethod = testLibrarySubscriptionPersist@SpringDataJpaApplicationTests, testException = [null], mergedContextConfiguration = [MergedContextConfiguration@5e01a982 testClass = SpringDataJpaApplicationTests, locations = '{}', classes = '{class com.springboot.data.jpa.SpringDataJpaApplication}', contextInitializerClasses = '[]', activeProfiles = '{}', propertySourceLocations = '{}', propertySourceProperties = '{org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTestContextBootstrapper=true}', contextCustomizers = set[org.springframework.boot.test.context.filter.ExcludeFilterContextCustomizer@18ece7f4, org.springframework.boot.test.json.DuplicateJsonObjectContextCustomizerFactory$DuplicateJsonObjectContextCustomizer@264f218, org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockitoContextCustomizer@0, org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplateContextCustomizer@2462cb01, org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.actuate.metrics.MetricsExportContextCustomizerFactory$DisableMetricExportContextCustomizer@928763c, org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.properties.PropertyMappingContextCustomizer@0, org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebDriverContextCustomizerFactory$Customizer@7c3fdb62, org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTestArgs@1, org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTestWebEnvironment@1ad282e0], contextLoader = 'org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootContextLoader', parent = [null]], attributes = map['org.springframework.test.context.event.ApplicationEventsTestExecutionListener.recordApplicationEvents' -> false]]
Now I have couple of questions -
Why am I getting detached entity exception. When we fetch an entity from the DB, Spring Data JPA must be using entityManager to fetch the entity. The fetched entity gets automatically attached to the persistence context right ?
On attaching @Transactional on the test, why the transaction is getting rolledback, and no entity is getting persisted. I was expecting the two entities - StudentSubscription and LibrarySubscription should've been persisted using the joined table inheritance approach.
I tried many things but no luck. Seeking help from, JPA and Spring DATA experts :-)
Thanks in advance.
CodePudding user response:
Let me add a few details that outline a couple of design problems with your code that significantly complicate the picture. In general, when working with Spring Data, you cannot simply look at your tables, create cookie-cutter entities and repositories for those and expect things to simply work. You need to at least spend a bit of time to understand the Domain-Driven Design building blocks entity, aggregate and repository.
Repositories manage aggregates
In your case, Student treats StudentSubscriptions like an entity (full object reference, cascading persistence operations) but at the same time a repository to persist the …Subscriptions exists. This fundamentally breaks the responsibility of keeping consistency of the Student aggregate, as you can simply remove a …Subscription from the store via the repository without the aggregate having a chance to intervene. Assuming the …Subscriptions are aggregates themselves, and you'd like to keep the dependency in that direction, those must only be referred to via identifiers, not via full object representations.
The arrangement also adds cognitive load, as there are now two ways to add a subscription:
- Create a
…Subscriptioninstance, assign theStudent, persist the subscription via the repository. - Load a
Student, create a…Subscription, add that to the student, persist theStudentvia it's repository.
While that's already a smell, the bidirectional relationship between the …Subscription and Student imposes the need to manually manage those in code. Also, the relationships establish a dependency cycle between the concepts, which makes the entire arrangement hard to change. You already see that you have accumulated a lot of (mapping) complexity for a rather simple example.
What would better alternatives look like?
Option 1 (less likely): Students and …Subscriptions are "one"
If you'd like to keep the concepts close together and there's no need to query the subscriptions on their own, you could just avoid those being aggregates and remove the repository for them. That would allow you to remove the back-reference from …Subscription to Student and leave you with only one way of adding subscriptions: load the Student, add a …Subscription instance, save the Student, done. This also gives the Student aggregate its core responsibility back: enforcing invariants on its state (the set of …Subscription having to follow some rules, e.g. at least one selected etc.)
Option 2 (more likely): Students and …Subscriptions are separate aggregates (potentially from separate logical modules)
In this case, I'd remove the …Subscriptions from the Student entirely. If you need to find a Students …Subscriptions, you can add a query to the …SubscriptionRepository (e.g. List<…Subscription> findByStudentId(…)). As a side effect of this you remove the cycle and Student does not (have to) know anything about …Subscriptions anymore, which simplifies the mapping. No wrestling with eager/lazy loading etc. In case any cross-aggregate rules apply, those would be applied in an application service fronting the SubscriptionRepository.
Heuristics summarized
- Clear distinction between what's an aggregate and what not (the former get a corresponding repository, the later don't)
- Only refer to aggregates via their identifiers.
- Avoid bidirectional relationships. Usually, one side of the relationship can be replaced with a query method on a repository.
- Try to model dependencies from higher-level concepts to lower level ones (
Students withSubscriptionss probably make sense, a…Subscriptionwithout aStudentmost likely doesn't. Thus, the latter is the better relationship to model and solely work with.)
CodePudding user response:
- Why am I getting detached entity exception. When we fetch an entity from the DB, Spring Data JPA must be using entityManager to fetch the entity. The fetched entity gets automatically attached to the persistent context right ?
Right, but only for as long as the entityManager stays open. Without the transactional, as soon as you return from studentRepository.findById(100L).get();, the entityManager gets closed and the object becomes detached.
When you call the save, a new entityManager gets created that doesn't contain a reference to the previous object. And so you have the error.
The @Trannsaction makes the entity manager stay open for the duration of the method.
At least, that's what I think it's happening.
- On attaching @Transactional on the test, why the transaction is getting rolledback,
With bi-directional associations, you need to make sure that the association is updated on both sides. The code should look like:
@Test
@Transactional
public void testLibrarySubscriptionPersist() {
Student student = studentRepository.findById(100L).get();
StudentSubscription librarySubscription = new LibrarySubscription();
librarySubscription.setValidFrom(//some date);
librarySubscription.setValidTo(//some date);
// Update both sides:
librarySubscription.setStudent(student);
student.getStudentSubscription().add(librarySubscription);
// Because of the cascade, saving student should also save librarySubscription.
// Maybe it's not necessary because student is managed
// and the db will be updated anyway at and of the transaction.
studentSubscriptionRepository.save(student);
}
In this case, you could also use EntityManager#getReference:
@Test
@Transactional
public void testLibrarySubscriptionPersist() {
EntityManager em = ...
StudentSubscription librarySubscription = new LibrarySubscription();
librarySubscription.setValidFrom(//some date);
librarySubscription.setValidTo(//some date);
// Doesn't actually load the student
Student student = em.getReference(Student.class, 100L);
librarySubscription.setStudent(student);
studentSubscriptionRepository.save(librarySubscription);
}
I think any of these solutions should fix the issue. Hard to say without the whole stacktrace.
