I have a spreadsheet with a lot of code that breaks down completely depending on the machine I use it on if the date formatting in a =TEXT() function does not work as it was supposed to.
I have 2 computers at at home with the same version of Excel- a desktop and a laptop, both with English subscription versions of Excel. It works on desktop, but not on laptop, apparently different regional settings. Then again it works on a German machine with German regional settings - where it is supposed to work.
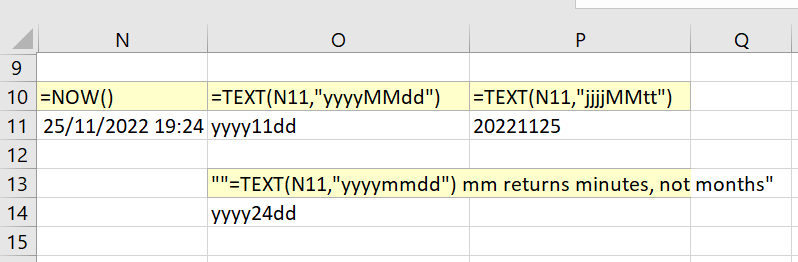
What I assumed was, that using yyyymmdd would produce 20221125 for today regardless of a machine. Turns out it is not so, as seen in the picture. Super irritating.
In order to mitigate that I now check the result of a
=TEXT(A1,"yyyymmdd")
=TEXT(A1,"jjjjMMTT")
and so on where A1 is a known date and I now that result of that field should be 20000101 for example. The other alternative that also worked is to look for letters from "yyyymmdd" in a result of the TEXT formula.
Once I found the correct string I can use it further to format all dates.
It is doable, but super irritating.
Is there a way to know the regional settings without jumping through hoops?
CodePudding user response:
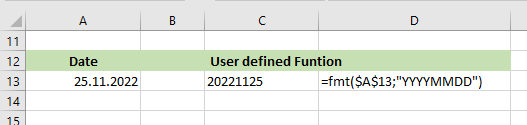
You can do it with a VBA User defined Funktion (UDF) like this:
Public Function FMT$(ByVal Value, ByVal strFormat)
'used instead of the Text Function in Excel (Formula) to provide a date format which is region specific
'https://superuser.com/questions/730371/how-to-prevent-excel-to-use-the-os-regional-settings-for-date-patterns-in-formul
FMT = VBA.Format$(Value, strFormat)
End Function
CodePudding user response:
Instead of using the date string, use a defined name:
eg: =Text(N11, dtFormat)
Enter this Auto-Open event code in the Workbook module:
Option Explicit
'change text function date code
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
Dim yrCode As String, mnthCode As String, dyCode As String
Dim dtCode As String
Dim nM As Name
With Application
yrCode = WorksheetFunction.Rept(.International(xlYearCode), 4)
mnthCode = WorksheetFunction.Rept(.International(xlMonthCode), 2)
dyCode = WorksheetFunction.Rept(.International(xlDayCode), 2)
End With
'Can only add a name if it is absent
For Each nM In ThisWorkbook.Names
If nM.Name = "dtFormat" Then
nM.Delete
Exit For
End If
Next nM
dtCode = yrCode & mnthCode & dyCode
ThisWorkbook.Names.Add _
Name:="dtFormat", _
RefersTo:="=""" & dtCode & """", _
Visible:=False
End Sub
The code determines the proper format characters, and ensures that dtFormat is properly defined based on the machine on which the workbook is opened.
CodePudding user response:
With an UDF you can do it like this:
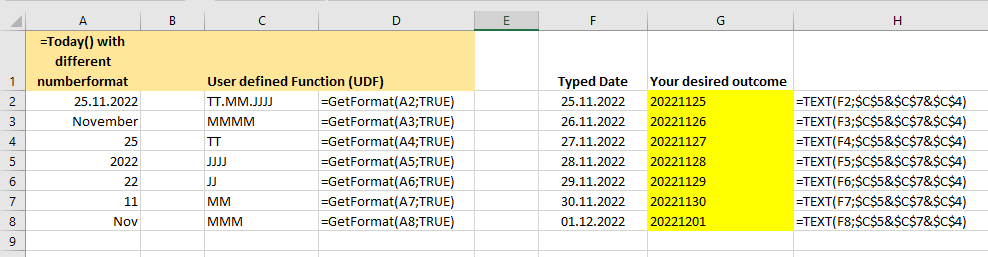
Public Function GetFormat$(Cell As Range, Optional ByVal UseLocal As Boolean)
'get the date region settings of this computer
' https://superuser.com/questions/730371/how-to-prevent-excel-to-use-the-os-regional-settings-for-date-patterns-in-formul
' =GetFormat($A$1, TRUE)
If UseLocal Then
GetFormat = Cell.NumberFormatLocal
Else
GetFormat = Cell.NumberFormat
End If
End Function