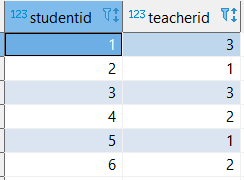
create table mentor (studentid int,teacherid int);
insert into mentor values(1,3),(2,1),(3,3),(4,2),(5,1),(6,2);
select * from mentor;
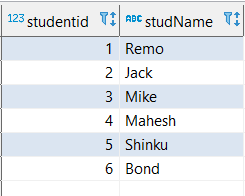
create table studRegister (studentid int,studName nvarchar(30));
insert into studRegister values(1,'Remo'),(2,'Jack'),(3,'Mike'),(4,'Mahesh'),(5,'Shinku'),(6,'Bond');
select * from studRegister ;
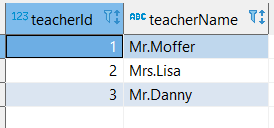
create table teacher(teacherId int, teacherName nvarchar(30));
insert into teacher values(1,'Mr.Moffer'),(2,'Mrs.Lisa'),(3,'Mr.Danny');
select * from teacher;
Student table :
Mentor table
Teacher table
Without using subqueries, Please join the tables
Output To be expected:
| StudentName | TeacherName |
|---|---|
| Remo | Mr.Danny |
| Jack | Mr.Moffer |
| Mike | Mr.Danny |
| Mahesh | Mrs.Lisa |
| Shinku | Mr.Moffer |
| Bond | Mrs.Lisa |
CodePudding user response:
SELECT studRegister.studName, teacher.teacherName
FROM mentor INNER JOIN
studRegister ON mentor.studentid = studRegister.studentid INNER JOIN
teacher ON mentor.teacherid = teacher.teacherId
CodePudding user response:
In order to get the needed result, you need to combine the StudName column from studRegister and the respective teacherName from the teacher table.
In order to do that you need to Join all three tables on their mutual columns. mentor table is the table that contains similar columns to the others, so joining studRegister and mentor table ON their shared column StudentId and after that joining mentor and teacher table ON their teacherId columns is going to get all columns from all three tables combined.
By only selecting StudName and teacherName you will only query those 2 columns without any other in the result.
Here's how the query looks like:
SELECT StudName AS StudentName, teacherName AS TeacherName FROM studRegister sR
INNER JOIN mentor m ON sR.studentId = m.StudentId
INNER JOIN teacher t ON t.teacherId = m.teacherId