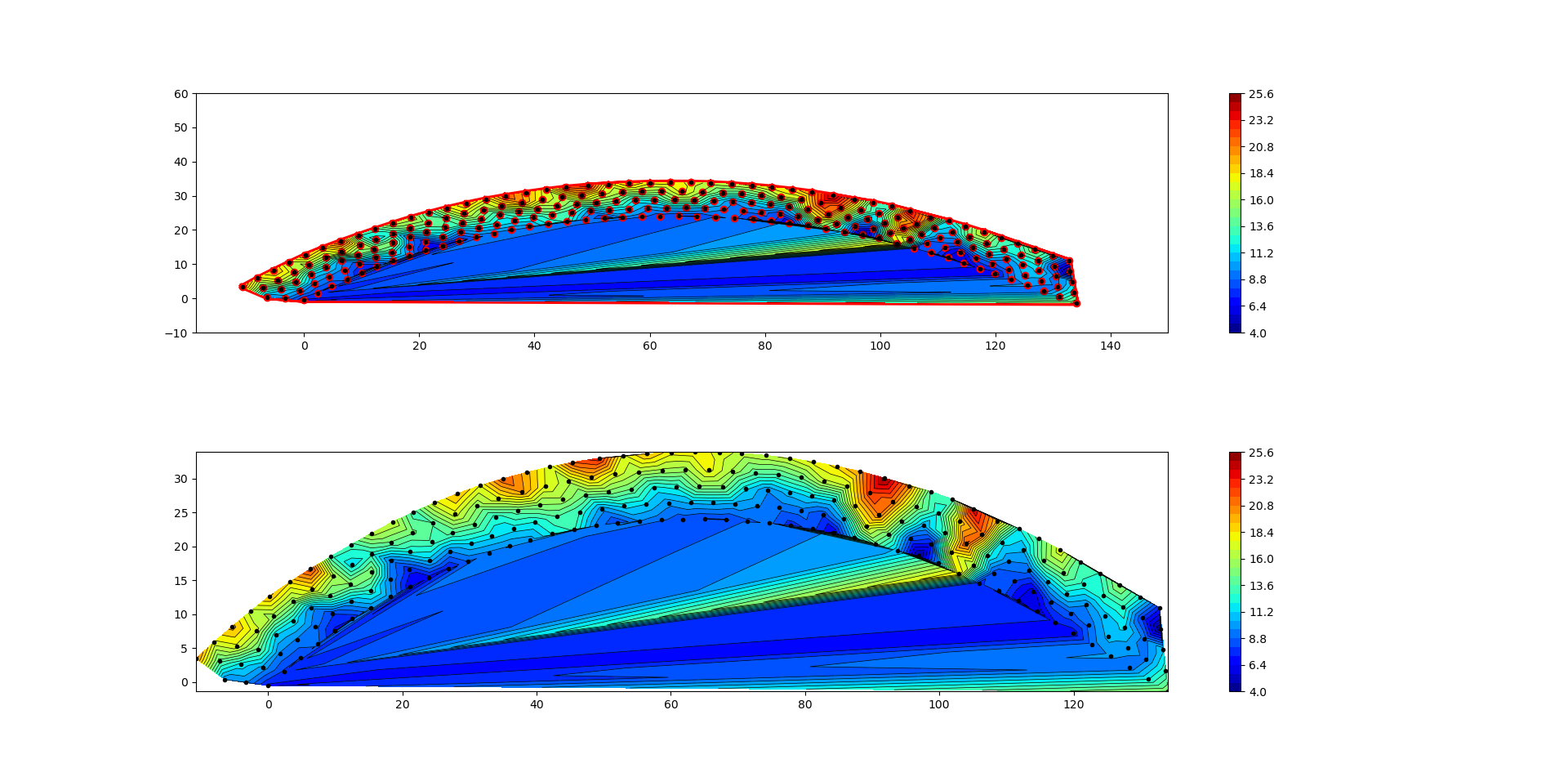
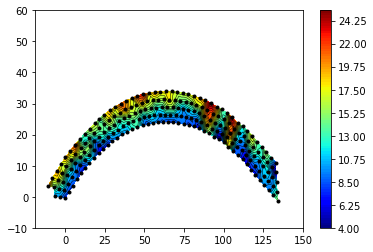
I'm trying to get a interpolated contour surface with triangulation from matplotlib. My data looks like a curve and I can't get rid of the data below the curve. I would like to have the outside datapoints as boundaries.
I found the option to mask the data with this code, but I can't figure out how to define the mask to get what I want
triang.set_mask()
These are the values for the inner curve:
x_after y_after z_after strain_after
39 117.2757 8.7586 0.1904 7.164
40 119.9474 7.152 0.1862 6.6456
37 111.8319 12.0568 0.1671 6.273
38 114.5314 10.4186 0.1651 5.7309
41 122.7482 5.4811 0.1617 9.1563
36 108.8823 13.4417 0.1421 8.8683
42 125.5035 3.8309 0.141 9.7385
33 99.8064 17.6315 0.1357 9.8613
32 96.8869 18.6449 0.1197 4.4147
35 105.8846 14.6086 0.1079 7.7055
28 84.2221 22.0191 0.1076 6.2098
26 77.8689 23.158 0.1067 7.5833
29 87.354 21.2974 0.1044 11.4365
27 81.0778 22.6443 0.1019 8.3794
24 71.4004 23.7749 0.0968 8.6207
34 102.8772 15.9558 0.0959 18.2025
23 68.2124 23.962 0.0939 7.9201
25 74.6905 23.4465 0.0901 9.0361
30 90.5282 20.398 0.0864 14.1051
31 93.802 19.335 0.0794 10.4563
43 128.3489 2.1002 0.0689 9.0292
22 65.0282 24.1107 0.0654 7.99
21 61.7857 24.0129 0.0543 8.2589
20 58.5831 23.9527 0.0407 9.0087
0 -0.0498 -0.5159 0.0308 7.1073
19 55.3115 23.7794 0.0251 9.6441
5 12.5674 9.3369 0.0203 7.2051
2 4.8147 3.6074 0.0191 8.0103
1 2.363 1.5329 0.0184 7.8285
18 52.0701 23.526 0.016 8.0149
3 7.4067 5.5988 0.0111 8.9994
7 18.2495 12.5836 0.0098 9.771
9 23.9992 15.4145 0.0098 6.7995
16 45.5954 22.5274 0.0098 12.9428
4 9.9776 7.5563 0.0093 6.9804
17 48.9177 23.0669 0.0084 9.3782
13 35.9812 20.0588 0.0066 9.6005
6 15.3578 11.0027 0.0062 9.7801
15 42.2909 21.8663 0.0052 12.0288
11 29.816 17.8723 0.0049 8.9085
8 21.1241 14.0893 0.0032 6.5716
10 26.8691 16.7093 0.0014 6.9672
44 131.1371 0.4155 0.0 11.9578
14 39.0687 20.991 -0.0008 9.9907
12 32.9645 18.9796 -0.0102 9.3389
45 134.083 -1.3928 -0.0616 15.29
CodePudding user response:
I managed to find a way to not plot the triangles at the bottom by using the following code:
xtri = x_after[triangles] - np.roll(x_after[triangles], 1, axis=1)
ytri = y_after[triangles] - np.roll(y_after[triangles], 1, axis=1)
maxi = np.max(np.sqrt(xtri**2 ytri**2), axis=1)
max_radius = 4.5
triang.set_mask(maxi > max_radius)
CodePudding user response:
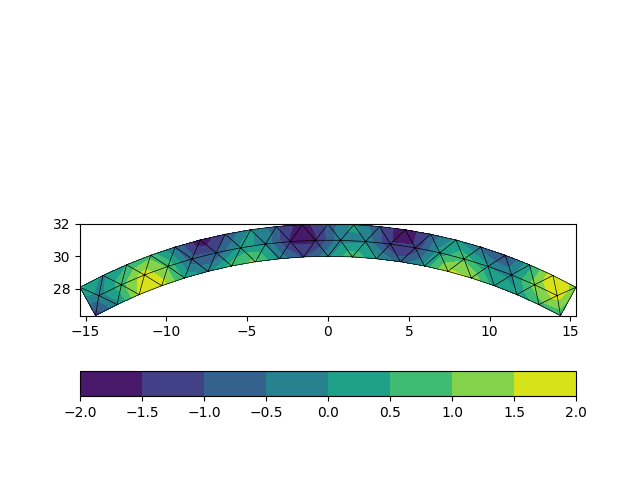
Most of my code is devoted to build the x, y arrays and the list of triangles in terms of the numbering of the nodes, but I suppose that you already have (or at least you can get) a list of triangles from the mesher program that you have used... if you have the triangles it's as simple as plt.tricontourf(x, y, triangles, z).
And here it is the code complete of the boring stuff.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
th0 = th2 = np.linspace(-0.5, 0.5, 21)
th1 = np.linspace(-0.475, 0.475, 20)
r = np.array((30, 31, 32))
x = np.concatenate(( np.sin(th0)*r[0],
np.sin(th1)*r[1],
np.sin(th2)*r[2]))
y = np.concatenate(( np.cos(th0)*r[0],
np.cos(th1)*r[1],
np.cos(th2)*r[2]))
z = np.sin(x)-np.cos(y)
nodes0 = np.arange( 0, 21, dtype=int)
nodes1 = np.arange(21, 41, dtype=int)
nodes2 = np.arange(41, 62, dtype=int)
triangles = np.vstack((
np.vstack((nodes0[:-1],nodes0[1:],nodes1)).T,
np.vstack((nodes0[1:-1],nodes1[1:],nodes1[:-1])).T,
np.vstack((nodes2[:-1],nodes1,nodes2[1:])).T,
np.vstack((nodes1[:-1],nodes1[1:],nodes2[1:-1])).T,
(0, 21, 41),
(20, 61, 40)
))
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_aspect(1)
tp = ax.triplot(x, y, triangles, color='k', lw=0.5, zorder=4)
tc = ax.tricontourf(x, y, triangles, np.sin(x)-np.cos(y))
plt.colorbar(tc, location='bottom')
plt.show()