This is the code example;
func GetValue(c echo.Context) error {
//other implementation details
value, err := service.GetValue()
if err != nil {
return c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, errorresponse.Error(4003, err))
}
//if I set same value here, it works as expected
//value.Value = []int8{48, 48, 48, 54, 54, 49, 56, 54, 32, 32, 32, 32, 32, 32, 32}
return c.JSON(http.StatusOK, value)
}
//this is type service.GetValue() returns
type ValueGetResponse struct {
Value interface{}
ValueType string
}
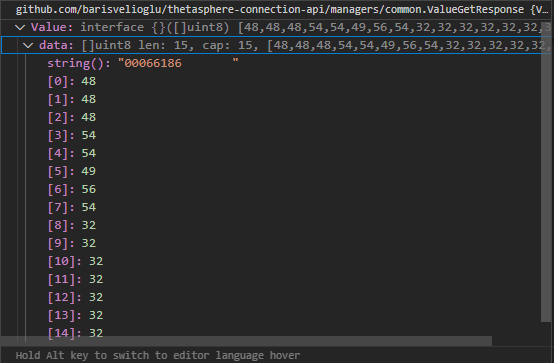
If I use the value which comes from service.GetValue() method, the api gives me a response like below. It converts it to a some kind of string which I dont know. When I check the value.Value property, the reflect.TypeOf(value.Value) says, it is a []int8 as type. Also the VSCode debugger approves it.
THE OBJECT USED IN REQUEST:
THE RESPONSE:
{
"Value": "MDAwNjYxODYgICAgICAg",
"ValueType": "[]uint8"
}
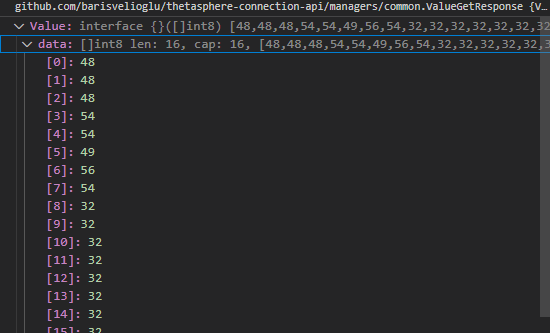
If I set expected value manually, it works as expected and I do not understand why the first one is not.
value.Value = []int8{48, 48, 48, 54, 54, 49, 56, 54, 32, 32, 32, 32, 32, 32, 32}
THE OBJECT USED IN REQUEST:
THE RESPONSE:
{
"Value": [
48,
48,
48,
54,
54,
49,
56,
54,
32,
32,
32,
32,
32,
32,
32,
32
],
"ValueType": "[]uint8"
}
CodePudding user response:
In Golang byte is alias for uint8 and when you use json.Marshal it returns []byte which is same type as your data. So when you receive this type of data it is translated to string.
You need to cast uint8 to other int type or implement Marshaler interface
Cast
bytes, err := service.GetValue()
value := make([]int8, 0)
for _, v := range bytes {
value = append(value, int8(v))
}
Marshaler
type CustomType []uint8
func (u CustomType) MarshalJSON() ([]byte, error) {
var result string
if u == nil {
result = "null"
} else {
result = strings.Join(strings.Fields(fmt.Sprintf("%d", u)), ",")
}
return []byte(result), nil
}
func GetValue(c echo.Context) error {
var value CustomType
bytes, err := service.GetValue()
value = bytes
return c.JSON(http.StatusOK, value)
}