Development tools and key technology: Adobe Dreamweaver JavaScript
Author: WeiYongGui
Writing time: April 26, 2020,
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
Introduction of a,
- the DOM, the full name of the Document Object Model Document Object Model (DOM)
- through the DOM in JS to manipulate HTML document, as long as the understanding of DOM can follow one's inclinations of the WEB page operation,
- the document representation is the whole HTML pages document
- object representation transform every parts of the web pages are to an object
- use the model to represent the object, the relationship between the object so we facilitate access to
1, node:
- Node, the Node is constitute the most basic part of our web page, the page each part can be referred to as a Node
- such as: HTML tags, attributes, such as text, notes, the entire document is a node
- although are nodes, but in fact their specific type is different
- such as: label we called element node, called the attribute node, text, called a text node, a document called the document node
- node types, properties and methods is different also,
Node, the Node - constitute the most basic unit of the HTML document,
Common node is divided into four categories
- a document node: the entire HTML document
- element node: HTML tags in HTML document
- an attribute node: attribute of the element
- text node: HTML tags in the text content
The properties of the nodes:
(1) the nodeName node name, it is read-only,
(1) the element node nodeName is the same as the tag name
(2) an attribute node nodeName is the name of the attribute of the
(3) text node nodeName is always # text
(4) document node nodeName is always # document
(2) the value nodeValue node,
1) element node nodeValue is undefined or null
(2) of the text node nodeValue text itself is
(3) attribute node nodeValue is the value of the attribute of the
(3) the nodeType node type, it is read-only, the following several node type:
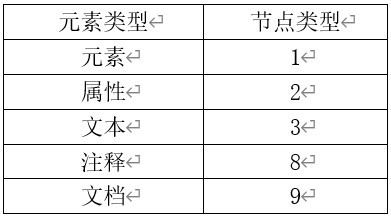
2, a document node (document) :
- document, document node represents the entire HTML document, all the nodes in a web page are its child nodes,
- document object attributes of the object as a window, we don't have to get can directly use the
- through which we can look for the node object within the entire document access, and can create all kinds of the node object through the object
3, the Element node (Element)
- labels are in HTML element node, a node, this is also our most commonly used
- all the tags in the browser page will be converted to an element node, we could be obtained by the method of document element nodes,
- such as:
- the document. The getElementById ()
- according to the id attribute value for an element node object,
4, the Text node (Text)
- a text node represents outside the text content of HTML tags, arbitrary HTML text is a text node,
- it can include literal interpretation of plain text content
- a text node is generally as the child nodes of the element node being
- get the text nodes, the general first to get the element node, through the element node for a text node
- for example:
- element node. FirstChild;
- element node for the first child, generally for a text node
5, an attribute node (Attr)
- an attribute node said is an attribute of the tag, to note here is that an attribute node is not the child nodes of the element nodes, but part of the element node
- could be obtained by element node specified attribute node
- for example:
- element node. GetAttributeNode (" attribute name ");
Attention!!!!!! : generally do not use an attribute node,
Second, the operation of the DOM node
1, get element node
Through the document object call
- getElementById () through the id attribute access to an element node object
- the getElementsByTagName () through the tag name for a group of element node object
- getElementsByName () by the name attribute to obtain a set of element node objects
- getElementsByClassName () by the class name for a group of element node object, this method does not support IE8 and below version
2, and gets the child nodes of the element node
Through specific element node called
The getElementsByTagName ()
- method that returns the tag name of the current node descendant node
-.childnodes
- property, said all child nodes of the current node
- firstChild
- property, said the first child node of the current node
- lastChild
- property, said the last child node of the current node
3, access to the parent node and brother node
Through specific node called
- parentNode
- property, said the parent node of the current node
- previousSibling
- property, said before a brother of the current node node
- nextSibling
- property, said after a brother of the current node node
4, the attribute of element node
? Access: element object. The property name
Example: value
element.
element. The id
Element. The className
? Settings, element object. The property name=new value
Example: element value="https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/hello"
Element. The id="id01
"
Element. The className="newClass"
Other properties
NodeValue
- a text node can nodeValue properties to get and set the contents of a text node
InnerHTML
- element nodes through this property to get and set the tag within the HTML code
5, using CSS selectors for query
QuerySelector ()
QuerySelectorAll ()
- these two methods is done with the document object to invoke, two methods using the same, is passing a selector string as a parameter, method automatically according to the selector string to find elements in web pages,
- different places is querySelector () returns only to find the first element, and querySelectorAll () will return all eligible element,
6, the node changes
Modify here we mainly refers to the operation of the element node
? Create a node
- the document. The createElement method (" tag ")
? Delete node
- the parent node. RemoveChild (child nodes)
? Replace the node
- the parent node. The replaceChild (new nodes, the old node)
? Insert the node
- the parent node. The appendChild (child nodes)
- the parent node. The insertBefore (new nodes, the old node)
Three, to get the style of the element
1, the style of JS modified element: the element. Style. The style name=style value (read: element. Style. The style name),
Through the style attribute set and read are inline style
Display (2, access to elements of the current element syntax: currentStyle. The property name or elements. CurrentStyle [properties])
CurrentStyle is the style of the display can be used to read the current element, if the current element is not set the style, the access to its default value, for example, if there is no set width, get to a value of auto
Note:!!!!!! This property only supports IE, other browsers don't support the
3, in other browsers can use
GetComputedStyle () the method to get the current element to display
This method is the method of the window, can directly use the
Parameter description:
1. Need to get the style element
2. A pseudo element can pass the general pass null
Note: this method returns an object, object encapsulates the current element in the style of the corresponding
Varobj=getComputedStyle (element, null);//use of the method shows that
Getting elements display style:
Obj. The property name or obj [" attribute name "]
If the style is not set, may be obtain the real value, rather than the default value,
For example, if there is no set width, access to the value of 1200 px element (actual value)
Note:!!!!!! This method does not support IE8 and under browser
GetComputedStyle () method with currentStyle properties are read-only attribute, cannot modify attributes,
If need to modify the value of the attribute, can only use style properties
Four, the attribute of the element and the method
Element for each property and method
The following properties and methods can be used for all HTML elements:
nullnullnullnull
