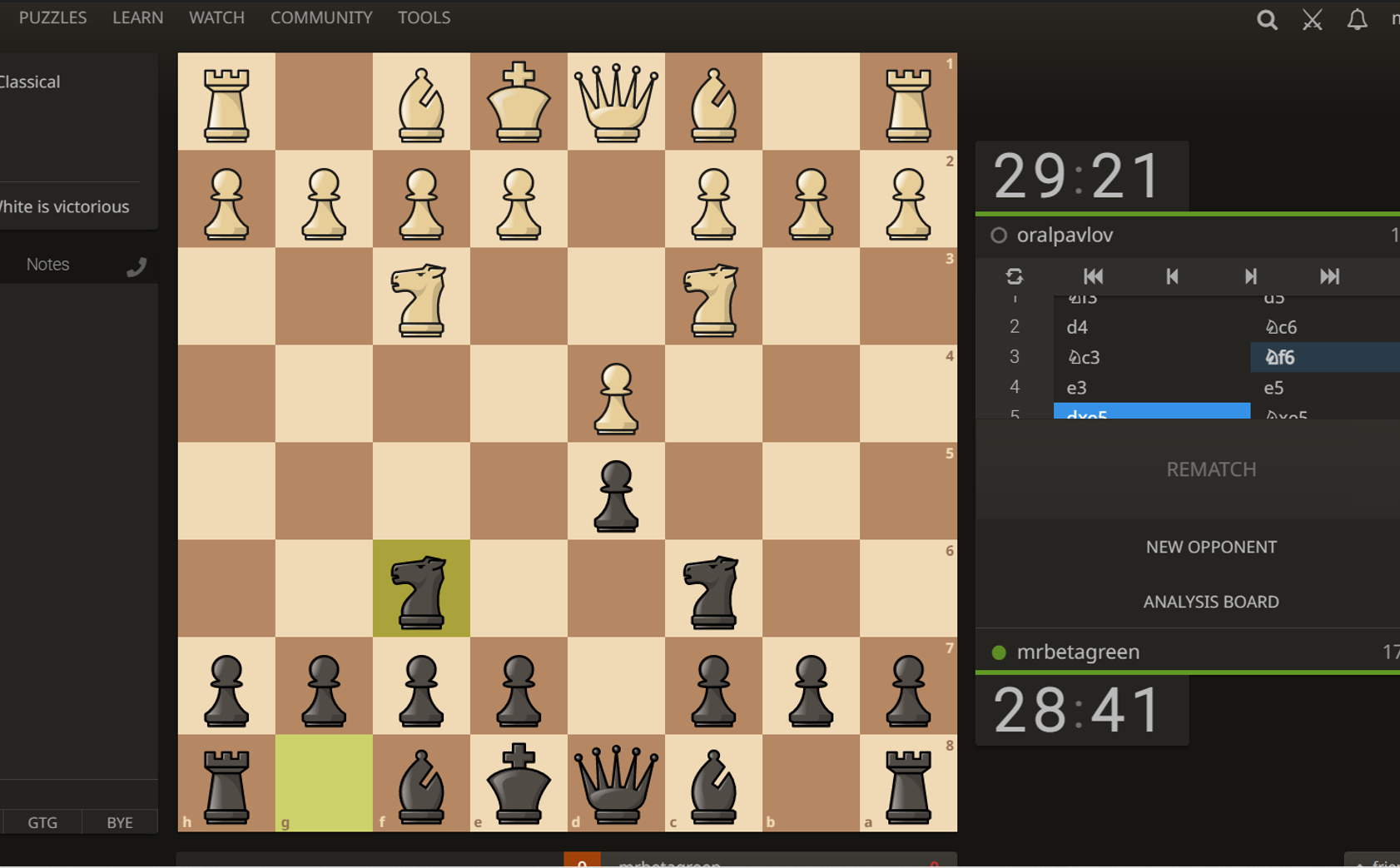
I wanted to detect contours of chess board black squares from the following image.
The following code is detecting only few black squares successfully, how can we increase the accuracy?
import cv2
import numpy as np
imPath = r" " # <----- image path
def imageResize(orgImage, resizeFact):
dim = (int(orgImage.shape[1]*resizeFact),
int(orgImage.shape[0]*resizeFact)) # w, h
return cv2.resize(orgImage, dim, cv2.INTER_AREA)
img = imageResize(cv2.imread(imPath), 0.5)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
thresh = cv2.inRange(gray, 135, 155) # to pick only black squares
# find contours
cnts = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[0] if len(cnts) == 2 else cnts[1]
cntImg = img.copy()
minArea, maxArea = 3000, 3500
valid_cnts = []
for c in cnts:
area = cv2.contourArea(c)
if area > minArea and area < maxArea:
valid_cnts.append(c)
# draw centers for troubleshooting
M = cv2.moments(c)
cX = int(M["m10"] / M["m00"])
cY = int(M["m01"] / M["m00"])
cv2.circle(cntImg, (cX, cY), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)
cv2.drawContours(cntImg, valid_cnts, -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('org', img)
cv2.imshow('threshold', thresh)
cv2.imshow('contour', cntImg)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
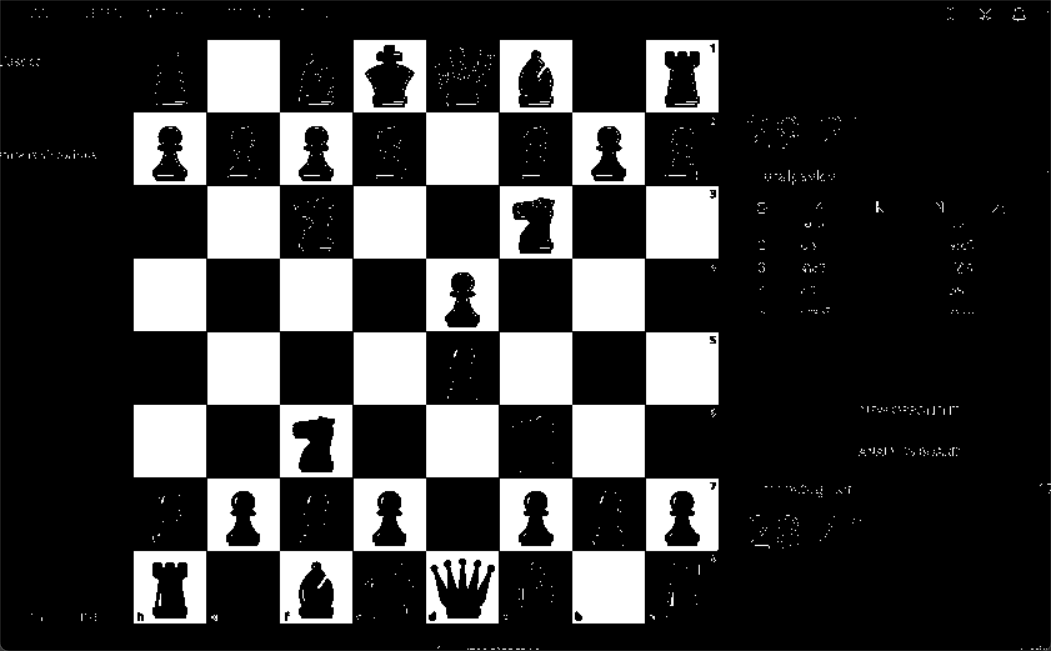
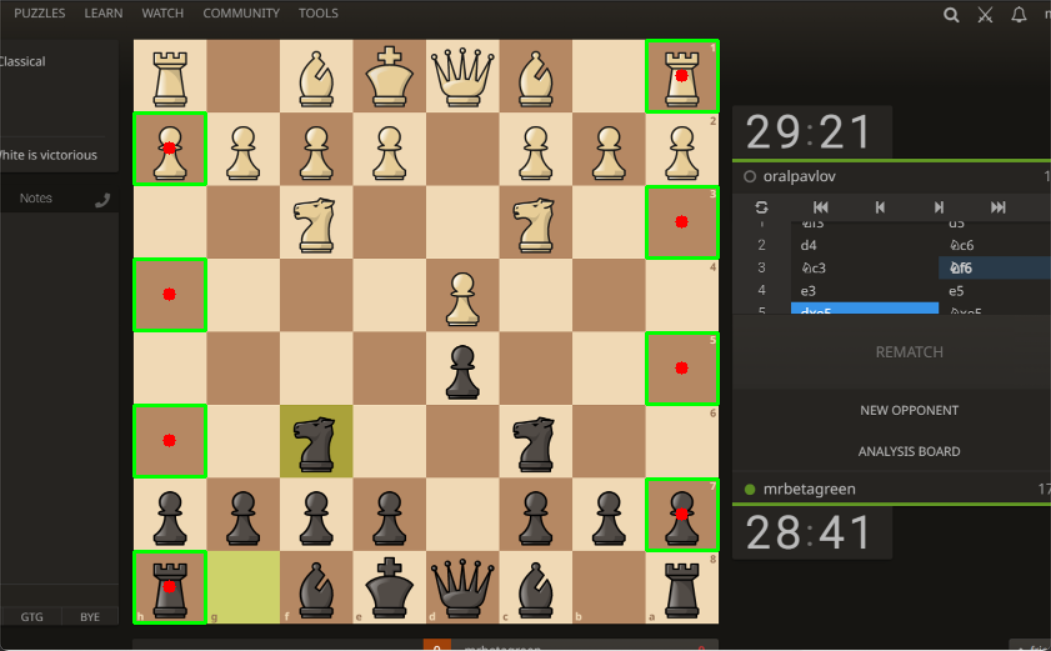
Gives threshold and contour -
[0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 3.0, 7.0, 7.5, 9.5, 3248.5, 3249.0, 6498.0] are the unique cnts areas. Typical areas for desired black squares are 3248.5, 3249.0, here's a quick snippet for getting unique cnts areas -
cntAreas = [cv2.contourArea(x) for x in cnts]
print(sorted(set(cntAreas)))
Highly appreciate any help!!
CodePudding user response:
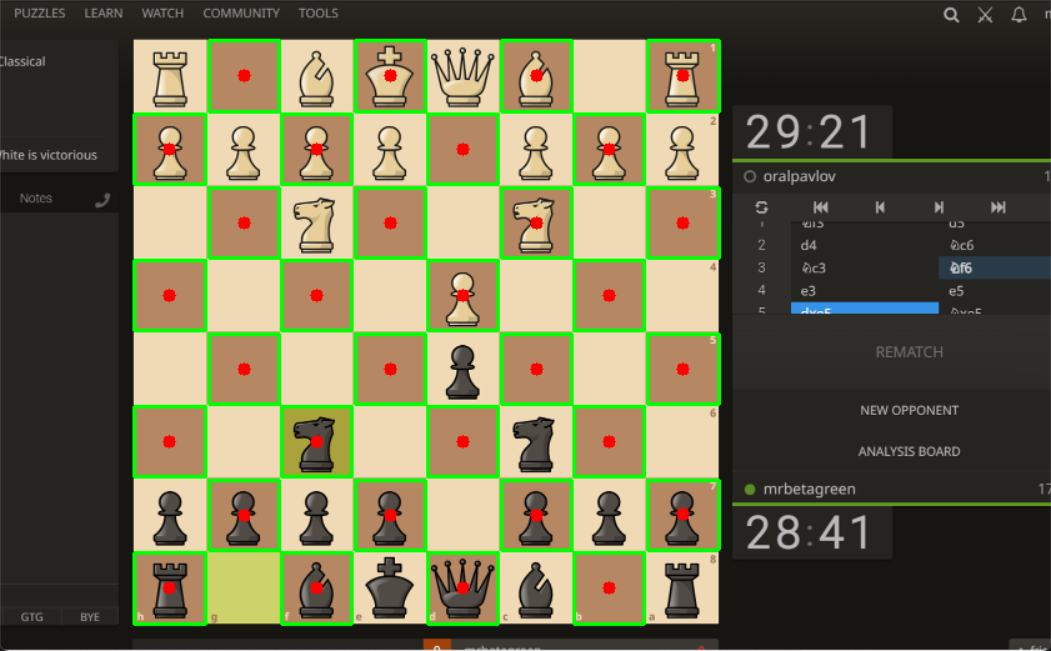
The problem was due to gaps in canny edges which was initiated from noise in the grayscale image. By using dilate morph operation, the noise is reduced and now giving well connected canny edges to make closed contours.
Full code -
import cv2
import numpy as np
imPath = r" " # <----- image path
def imageResize(orgImage, resizeFact):
dim = (int(orgImage.shape[1]*resizeFact),
int(orgImage.shape[0]*resizeFact)) # w, h
return cv2.resize(orgImage, dim, cv2.INTER_AREA)
img = imageResize(cv2.imread(imPath), 0.5)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (2, 2)) # <-----
morphed = cv2.dilate(gray, kernel, iterations=1)
thresh = cv2.inRange(morphed, 135, 155) # to pick only black squares
# find canny edge
edged_wide = cv2.Canny(thresh, 10, 200, apertureSize=3)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# find Contours
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(
thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE stores all coords unlike SIMPLE, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL
cntImg = img.copy()
minArea, maxArea = 2000, 4000
valid_cnts = []
for c in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(c)
if area > minArea and area < maxArea:
valid_cnts.append(c)
# draw centers
M = cv2.moments(c)
cX = int(M["m10"] / M["m00"])
cY = int(M["m01"] / M["m00"])
cv2.circle(cntImg, (cX, cY), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)
cv2.drawContours(cntImg, valid_cnts, -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('threshold', thresh)
cv2.imshow('morphed', morphed)
cv2.imshow('canny edge', edged_wide)
cv2.imshow('contour', cntImg)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()