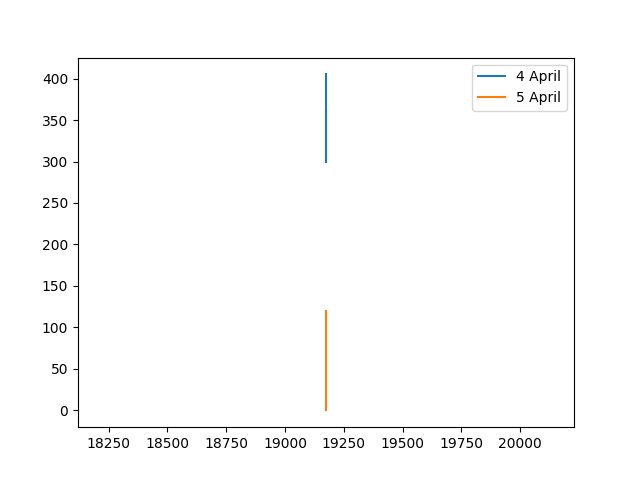
I'm trying to plot multiple plots on the same figure using python. The graph should be linear, the x coordinates represent the time of the day, and the y coordinates match the values. Each plot matches a different date.
The data is stored inside a dictionary. The keys represent the dates, and the values hold 2 lists: the first matches the x coordinates, and the second matches the y coordinates. For example:
dict_data = {"4 April": [[datetime(1900, 1, 1, 22, 59), datetime(1900, 1, 1, 23, 1), datetime(1900, 1, 1, 23, 8), datetime(1900, 1, 1, 23, 50)], [405, 320, 300, 360]], "5 April": [[datetime(1900, 1, 1, 8, 10), datetime(1900, 1, 1, 9, 40), datetime(1900, 1, 1, 11, 8), datetime(1900, 1, 1, 11, 10)], [120, 20, 10, 0]]}
I found apost on stack overflow Plotting time in Python with Matplotlib. It was'nt helpful because the x-axis on the graph they created is in "datetime" type, while I use "datetime.time"datetime". (I don't want the x-axis to show the dates). Also, the graph they created is a scatter plot, while I need it to be linear.
This is what I tried:
def multiple_plots(dict_data):
"""
Method to plot multiple times in one figure.
It receives a dictionary with the representation of the data in the csv file.
Every key in the dictionary represent a different date that will have its own plot ont the graph.
"""
for date, coordinates in dict_data.items():
time_coordinates = coordinates[0]
# converting the x coordinates in the type datetime.time to int
x_coordinates = matplotlib.dates.date2num(time_coordinates)
val_coordinates = coordinates[1]
plt.plot(list(map(int, x_coordinates)), list(map(int, val_coordinates)), label=date)
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
CodePudding user response:
This should just work without any fuss:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import datetime
dict_data = {"4 April": [[datetime.datetime(1900, 1, 1, 22, 59), datetime.datetime(1900, 1, 1, 23, 1), datetime.datetime(1900, 1, 1, 23, 8), datetime.datetime(1900, 1, 1, 23, 50)], [405, 320, 300, 360]], "5 April": [[datetime.datetime(1900, 1, 1, 8, 10), datetime.datetime(1900, 1, 1, 9, 40), datetime.datetime(1900, 1, 1, 11, 8), datetime.datetime(1900, 1, 1, 11, 10)], [120, 20, 10, 0]]}
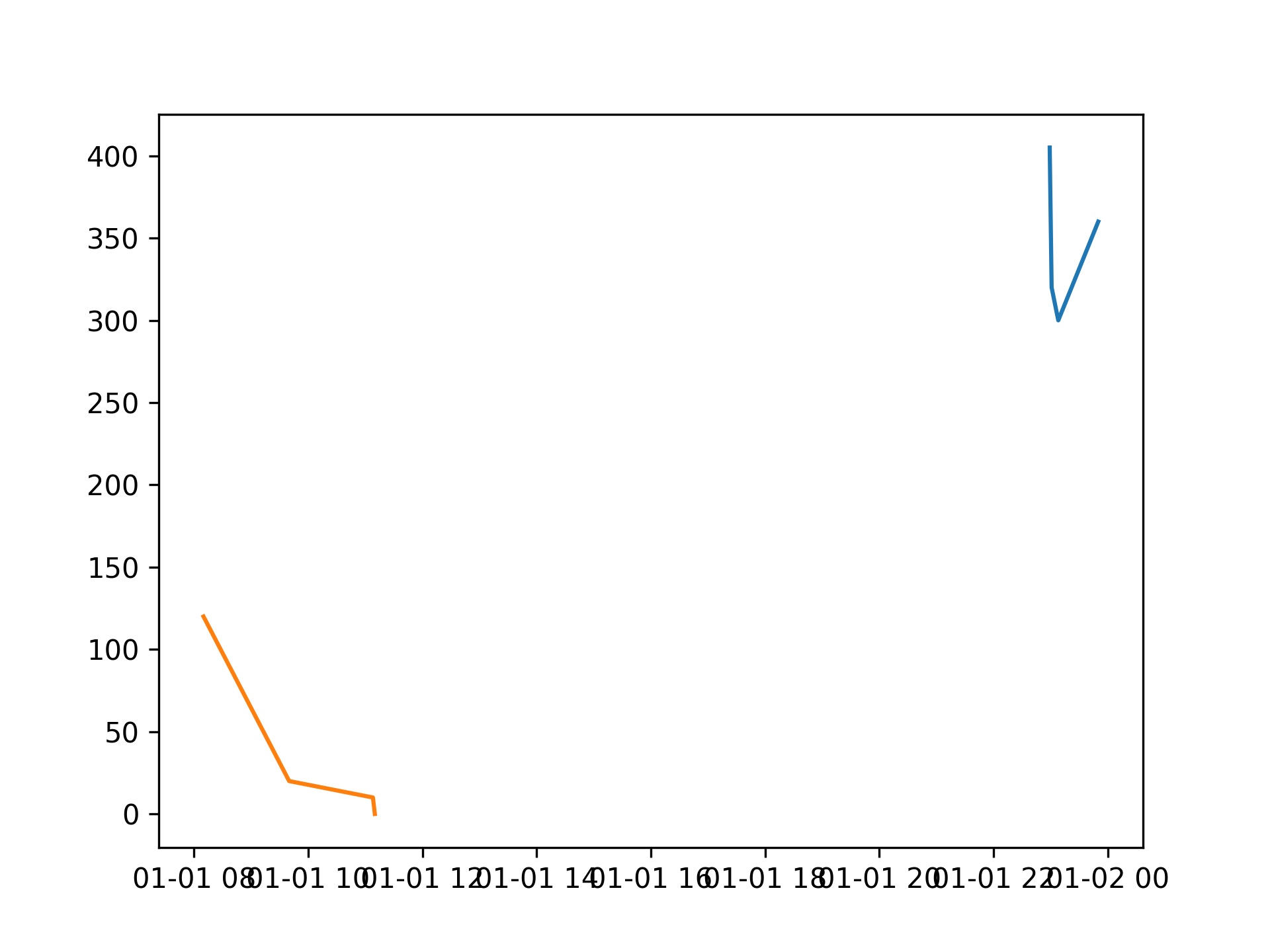
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
for k in dict_data:
ax.plot(dict_data[k][0], dict_data[k][1])
plt.show()
Obviously that looks a little cramped, but if you use concise converter:
plt.rcParams['date.converter'] = 'concise'
CodePudding user response:
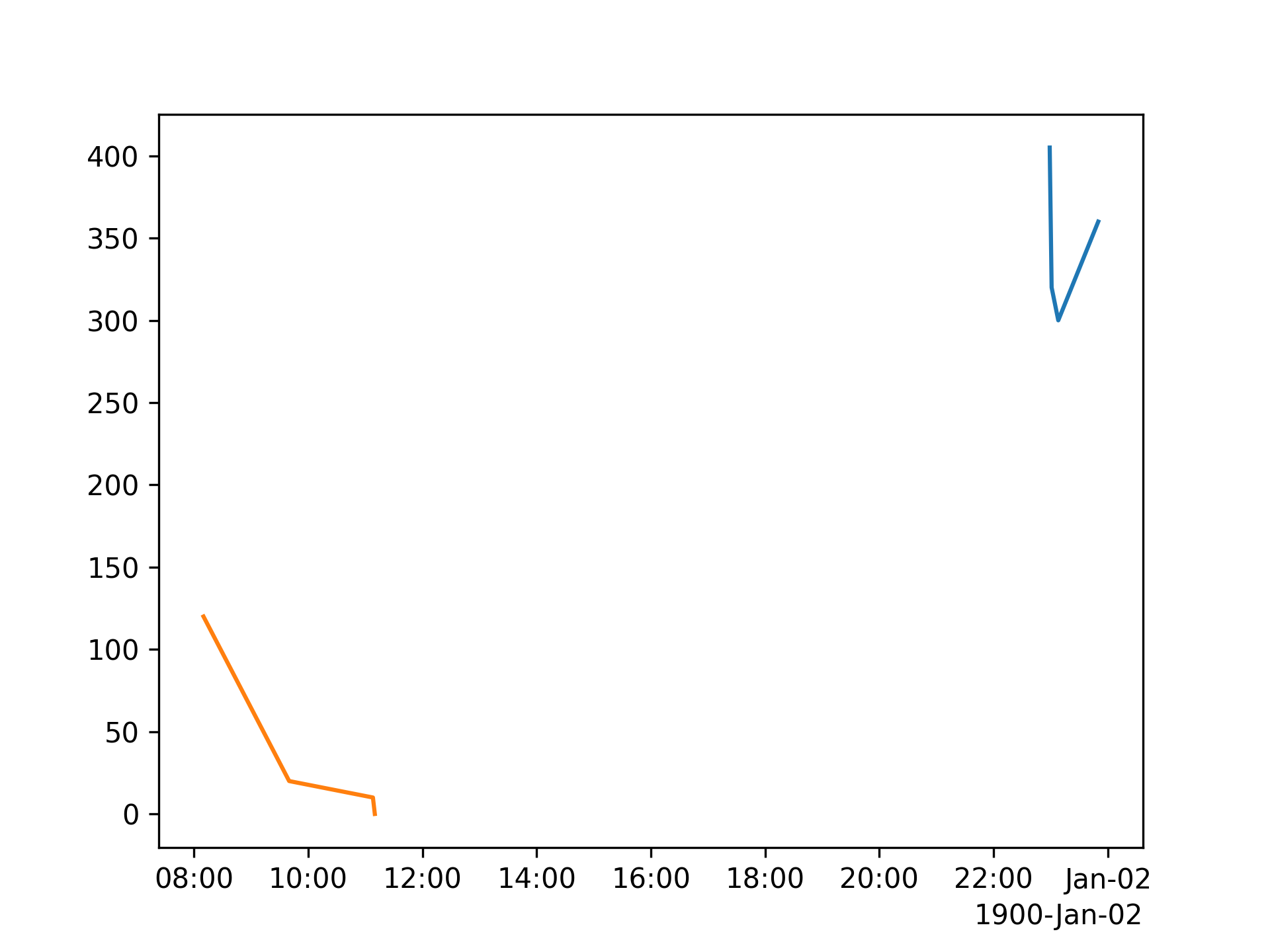
Edit based on edit in question
The code, using plot_date and line type '-'.
import matplotlib
import numpy as np
from datetime import datetime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
dict_data = {"4 April": [[np.datetime64("2022-07-01T22:59:00"), np.datetime64("2022-07-01T23:01:00"), np.datetime64("2022-07-01T23:08:00"), np.datetime64("2022-07-01T23:50:00")], [405, 320, 300, 360]], "5 April": [[np.datetime64("2022-07-01T08:10:00"), np.datetime64("2022-07-01T09:40:00"), np.datetime64("2022-07-01T11:08:00"), np.datetime64("2022-07-01T11:10:00")], [120, 20, 10, 0]]}
# dict_data = {"4 April": [[datetime(2022, 7, 1, 22, 59), datetime(2022, 7, 1, 23, 1), datetime(2022, 7, 1, 23, 8), datetime(2022, 7, 1, 23, 50)], [405, 320, 300, 360]], "5 April": [[datetime(2022, 7, 1, 8, 10), datetime(2022, 7, 1, 9, 40), datetime(2022, 7, 1, 11, 8), datetime(2022, 7, 1, 11, 10)], [120, 20, 10, 0]]}
def multiple_plots(dict_data):
"""
Method to plot multiple times in one figure.
It receives a dictionary with the representation of the data in the csv file.
Every key in the dictionary represent a different date that will have its own plot ont the graph.
"""
for date, coordinates in dict_data.items():
time_coordinates = coordinates[0]
# converting the x coordinates in the type np.datetime64 t2022-07-01To int
x_coordinates = matplotlib.dates.date2num(time_coordinates)
val_coordinates = coordinates[1]
plt.plot_date(list(map(int, x_coordinates)), list(map(int, val_coordinates)), '-', label=date)
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
multiple_plots(dict_data)
Final Output:
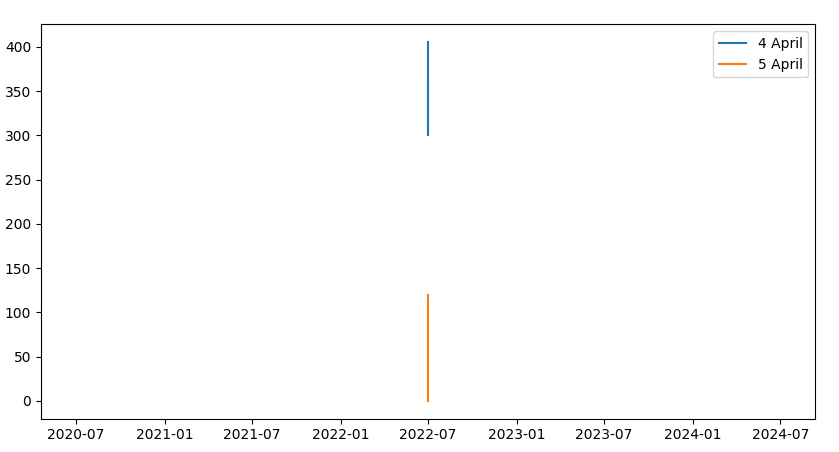
The date2num function requires the year, month and date in addition to time. So, two simple fixes are:
- Sending in year, month and time
dict_data = {"4 April": [[datetime(2022, 7, 1, 22, 59), datetime(2022, 7, 1, 23, 1), datetime(2022, 7, 1, 23, 8), datetime(2022, 7, 1, 23, 50)], [405, 320, 300, 360]], "5 April": [[datetime(2022, 7, 1, 8, 10), datetime(2022, 7, 1, 9, 40), datetime(2022, 7, 1, 11, 8), datetime(2022, 7, 1, 11, 10)], [120, 20, 10, 0]]}
- Sending in
np.datetime64type
dict_data = {"4 April": [[np.datetime64("2022-07-01T22:59:00"), np.datetime64("2022-07-01T23:01:00"), np.datetime64("2022-07-01T23:08:00"), np.datetime64("2022-07-01T23:50:00")], [405, 320, 300, 360]], "5 April": [[np.datetime64("2022-07-01T08:10:00"), np.datetime64("2022-07-01T09:40:00"), np.datetime64("2022-07-01T11:08:00"), np.datetime64("2022-07-01T11:10:00")], [120, 20, 10, 0]]}
They both work. The final plot is: