I'm trying to sort this array by the last name, and if two last names are the same, I want to sort it by the first name:
String[][] phoneBook = {
/* name, number */
{"Sophia Thorarensen", "06508641036"},
{"Emma Blöndal", "06504228512"},
{"Olivia Thorarensen", "06501126965"},
{"Ava Hansen", "06762858077"}
};
What it should look like:
String[][] sortedPhoneBook = {
/* name, number */
{"Emma Blöndal", "06504228512"},
{"Ava Hansen", "06762858077"},
{"Olivia Thorarensen", "06501126965"},
{"Sophia Thorarensen", "06508641036"}
};
CodePudding user response:
This was a good exercise to try.
The idea is you need to use the sort method and then implement a custom Comparator based on your needs.
Here is one way I managed to do this according to the useful links provided by OH GOD SPIDERS.
I also think the sort happens in place so I did not create a new variable. I just printed out the contents of the old phoneBook at the end to show they are in the order we want.
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class SortStrings {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[][] phoneBook = {
/* name, number */
{ "Sophia Thorarensen", "06508641036" }, { "Emma Blöndal", "06504228512" },
{ "Olivia Thorarensen", "06501126965" }, { "Ava Hansen", "06762858077" } };
Arrays.sort(phoneBook, new Comparator<String[]>() {
public int compare(String[] a, String[] b) {
//get first names and last names of what we want to compare.
String first_name_a = a[0].split(" ")[0];
String first_name_b = b[0].split(" ")[0];
String last_name_a = a[0].split(" ")[1];
String last_name_b = b[0].split(" ")[1];
//if the last names are the same, sort by first name
if (last_name_a.compareTo(last_name_b) == 0) {
return first_name_a.compareTo(first_name_b);
}
return last_name_a.compareTo(last_name_b);
}
});
Arrays.stream(phoneBook)
.forEach(elem -> {
Arrays.stream(elem)
.forEach(System.out::println);
});
}
}
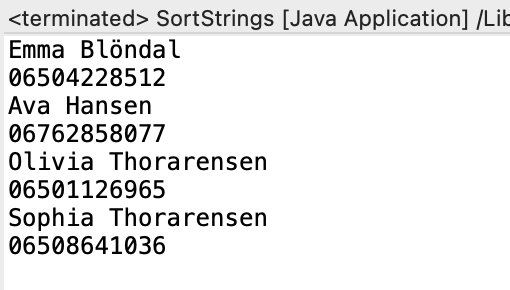
Output:
CodePudding user response:
In general, it is better to build a Comparator instance. To write a clean code, you should split your comparator into two parts: sort by the first name, sort by the last name.
The final comparator should be built based on simple ones using thenComparing().
public static void sort(String[][] phoneBook) {
final Comparator<String[]> sortByFirstName = (one, two) -> {
String lastName1 = one[0].substring(0, one[0].indexOf(' ')).trim();
String lastName2 = two[0].substring(0, two[0].indexOf(' ')).trim();
return lastName1.compareTo(lastName2);
};
final Comparator<String[]> sortByLastName = (one, two) -> {
String lastName1 = one[0].substring(one[0].lastIndexOf(' ')).trim();
String lastName2 = two[0].substring(two[0].lastIndexOf(' ')).trim();
return lastName1.compareTo(lastName2);
};
final Comparator<String[]> sortByLastNameAndFirstName =
sortByLastName.thenComparing(sortByFirstName);
Arrays.sort(phoneBook, sortByLastNameAndFirstName);
}