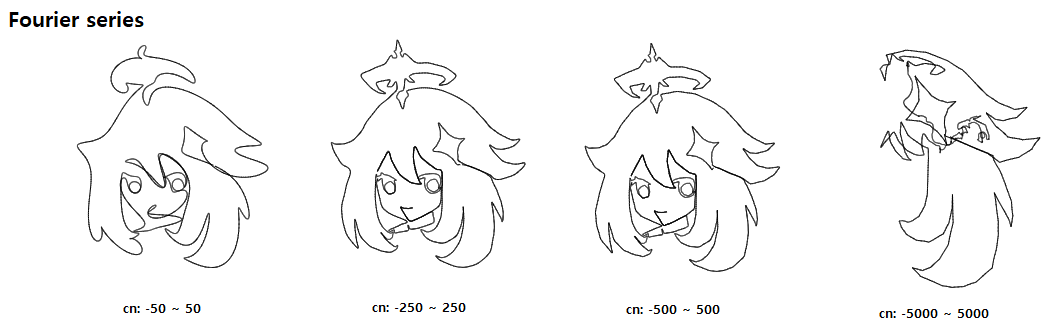
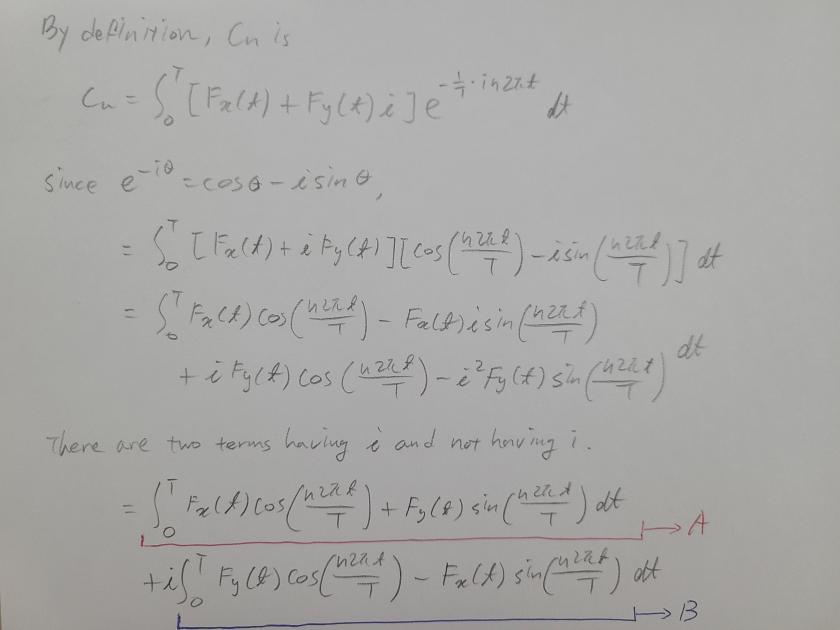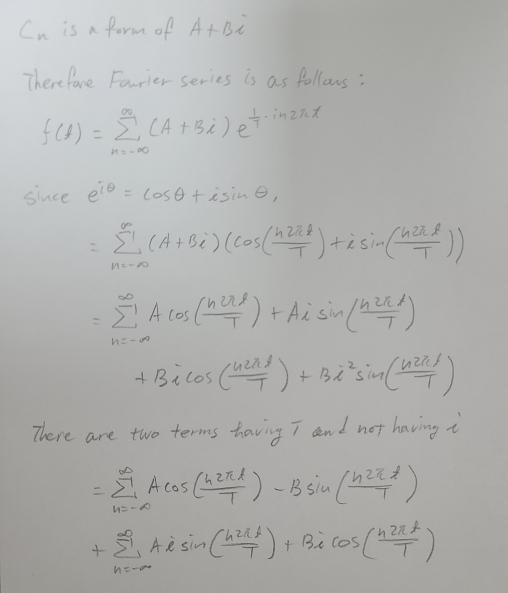I'm currently having difficulties at visualizing Fourier series. I tried the same thing about three times in order to find errors but in vain.
Now I even don't know what is wrong with my code or understanding of Fourier series.
What I'm trying to make is a thing like shown in the following Youtube video: 
(2) parameter
So now I would like to draw more complicated thing in a parametric way. Please let me show the process I've walked.
① From svg path, get coordinates. For example,
// svg path
const d = 'M 0 0 L 20 30 L 10 20 ... ... ... Z';
↓
↓ convert with some processing...
↓
const cx = [0, 20, 10, ...]; // function Fx(t)
const cy = [0, 30, 20, ...]; // function Fy(t)
② Get Fourier coefficients from Fx(t), Fy(t), respectively. After that, I can get approximated coordinates by calculating Fourier series respectively by using the coefficients I got. For example,
Let's say I have a0_x, an_x, bn_x, a0_y, an_y, bn_y.
Then, Fx(t) = a0_x an_x[1] * cos(1wt) bn_x[1] * cos(1wt)
an_x[2] * cos(2wt) bn_x[2] * cos(2wt) ...;
Fy(t) = a0_y an_y[1] * cos(1wt) bn_y[1] * cos(1wt)
an_y[2] * cos(2wt) bn_y[2] * cos(2wt) ...;
Therefore a set of points (Fx(t), Fy(t)) is an approximated path!
This is all! Only thing left is just drawing!
Meanwhile, I processed the data in the following way:
const d = [svg path data];
const split = d.split(/[, ]/);
const points = get_points(split);
const normalized = normalize(points);
const populated = populate(normalized, 8);
const cx = populated.x; // Fx(t)
const cy = populated.y; // Fy(t)
/**
* This function does the below job.
* populate([0,3,6], 2) => output 0 12 3 45 6
* populate([0,4,8], 3) => output 0 123 4 567 8
*/
function populate(data, n) {
if (data.x.length <= 1) throw new Error('NotEnoughData');
if (n < 1) throw new Error('InvalidNValue');
const arr_x = new Array(data.x.length (data.x.length - 1) * n);
const arr_y = new Array(data.y.length (data.y.length - 1) * n);
for (let i = 0; i < data.x.length; i ) {
arr_x[i * (n 1)] = data.x[i];
arr_y[i * (n 1)] = data.y[i];
}
for (let i = 0; i <= arr_x.length - n - 1 - 1; i = (n 1)) {
const x_interpolation = (arr_x[i n 1] - arr_x[i]) / (n 1);
const y_interpolation = (arr_y[i n 1] - arr_y[i]) / (n 1);
for (let j = 1; j <= n; j ) {
arr_x[i j] = arr_x[i] x_interpolation * j;
arr_y[i j] = arr_y[i] y_interpolation * j;
}
}
return { x: arr_x, y: arr_y };
}
// This function makes all values are in range of [-1, 1].
// I just did it... because I don't want to deal with big numbers (and not want numbers having different magnitude depending on data).
function normalize(obj) {
const _x = [];
const _y = [];
const biggest_x = Math.max(...obj.x);
const smallest_x = Math.min(...obj.x);
const final_x = Math.max(Math.abs(biggest_x), Math.abs(smallest_x));
const biggest_y = Math.max(...obj.y);
const smallest_y = Math.min(...obj.y);
const final_y = Math.max(Math.abs(biggest_y), Math.abs(smallest_y));
for (let i = 0; i < obj.x.length; i ) {
_x[i] = obj.x[i] / final_x;
_y[i] = obj.y[i] / final_y;
}
return { x: _x, y: _y };
}
// returns Fx(t) and Fy(t) from svg path data
function get_points(arr) {
const x = [];
const y = [];
let i = 0;
while (i < arr.length) {
const path_command = arr[i];
if (path_command === "M") {
x.push(Number(arr[i 1]));
y.push(Number(arr[i 2]));
i = 3;
} else if (path_command === 'm') {
if (i === 0) {
x.push(Number(arr[i 1]));
y.push(Number(arr[i 2]));
i = 3;
} else {
x.push(x.at(-1) Number(arr[i 1]));
y.push(y.at(-1) Number(arr[i 2]));
i = 3;
}
} else if (path_command === 'L') {
x.push(Number(arr[i 1]));
y.push(Number(arr[i 2]));
i = 3;
} else if (path_command === 'l') {
x.push(x.at(-1) Number(arr[i 1]));
y.push(y.at(-1) Number(arr[i 2]));
i = 3;
} else if (path_command === 'H') {
x.push(Number(arr[i 1]));
y.push(y.at(-1));
i = 2;
} else if (path_command === 'h') {
x.push(x.at(-1) Number(arr[i 1]));
y.push(y.at(-1));
i = 2;
} else if (path_command === 'V') {
x.push(x.at(-1));
y.push(Number(arr[i 1]));
i = 2;
} else if (path_command === 'v') {
x.push(x.at(-1));
y.push(y.at(-1) Number(arr[i 1]));
i = 2;
} else if (path_command === 'Z' || path_command === 'z') {
i ;
console.log('reached to z/Z, getting points done');
} else if (path_command === 'C' || path_command === 'c' || path_command === 'S' || path_command === 's' || path_command === 'Q' || path_command === 'q' || path_command === 'T' || path_command === 't' || path_command === 'A' || path_command === 'a') {
throw new Error('unsupported path command, getting points aborted');
} else {
x.push(x.at(-1) Number(arr[i]));
y.push(y.at(-1) Number(arr[i 1]));
i = 2;
}
}
return { x, y };
}
Meanwhile, in order to calculate Fourier coefficients, I used numerical integration. This is the code.
/**
* This function calculates Riemann sum (area approximation using rectangles).
* @param {Number} div division number (= number of rectangles to be used)
* @param {Array | Function} subject subject of integration
* @param {Number} start where to start integration
* @param {Number} end where to end integration
* @param {Number} nth this parameter will be passed to 'subject'
* @param {Function} paramFn this parameter will be passed to 'subject'
* @returns {Number} numerical-integrated value
*/
function numerical_integration(div, subject, start, end, nth = null, paramFn = null) {
if (div < 1) throw new Error(`invalid div; it can't be 0 or 0.x`);
let sum = 0;
const STEP = 1 / div;
const isSubjectArray = Array.isArray(subject);
if (isSubjectArray) {
for (let t = start; t < end; t ) {
for (let u = 0; u < div; u ) {
sum = subject[t 1] * STEP;
}
}
} else {
for (let t = start; t < end; t ) {
for (let u = 0; u < div; u ) {
const period = end - start;
const isParamFnArray = Array.isArray(paramFn);
if (isParamFnArray) sum = subject((t 1), period, nth, paramFn) * STEP;
else sum = subject(((t STEP) STEP * u), period, nth, paramFn) * STEP;
}
}
}
return sum;
// console.log(numerical_integration(10, (x) => x ** 3, 0, 2));
}
The approximation is near. For (x) => x, division 10, from 0 to 2, the approximation is 2.1 while actual answer is 2. For (x) => x ** 2, division 10, from 0 to 2, the approximation is 2.87, while actual answer is 2.67. For (x) => x ** 3, division 10, from 0 to 2, the approximation is 4.41, while actual answer is 4.
And I found a0, an, bn by the following: (※ You can find Fourier coefficients formulas in 
The below is the canvas drawing code:
const $cvs = document.createElement('canvas');
const cctx = $cvs.getContext('2d');
$cvs.setAttribute('width', 1000);
$cvs.setAttribute('height', 800);
$cvs.setAttribute('style', 'border: 1px solid black;');
document.body.appendChild($cvs);
window.requestAnimationFrame(draw_tick);
// offset
const xoo = { x: 200, y: 600 }; // x oscillator offset
const yoo = { x: 600, y: 200 }; // y ~
// path
const path = [];
// drawing function
let deg = 0;
function draw_tick() {
const rAF = window.requestAnimationFrame(draw_tick);
// initialize
cctx.clearRect(0, 0, 1000, 800);
// y oscillator
const py = { x: 0, y: 0 };
// a0
// a0 circle
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.arc(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y, Math.abs(ya0), 0, 2 * Math.PI);
cctx.stroke();
// a0 line
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y);
py.x = ya0 * Math.cos(0 * deg * Math.PI / 180);
py.y = ya0 * Math.sin(0 * deg * Math.PI / 180);
cctx.lineTo(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y);
cctx.stroke();
// an
for (let i = 0; i < yan.length; i ) {
const radius = yan[i];
// an circles
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.arc(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y, Math.abs(radius), 0, 2 * Math.PI);
cctx.stroke();
// an lines
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y);
py.x = radius * Math.cos((i 1) * deg * Math.PI / 180);
py.y = radius * Math.sin((i 1) * deg * Math.PI / 180);
cctx.lineTo(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y);
cctx.stroke();
}
// bn
for (let i = 0; i < ybn.length; i ) {
const radius = ybn[i];
// bn circles
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.arc(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y, Math.abs(radius), 0, 2 * Math.PI);
cctx.stroke();
// bn lines
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y);
py.x = radius * Math.cos((i 1) * deg * Math.PI / 180);
py.y = radius * Math.sin((i 1) * deg * Math.PI / 180);
cctx.lineTo(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y);
cctx.stroke();
}
// x oscillator
const px = { x: 0, y: 0 };
// a0
// a0 circle
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.arc(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y, Math.abs(xa0), 0, 2 * Math.PI);
cctx.stroke();
// a0 line
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y);
py.x = xa0 * Math.cos(0 * deg * Math.PI / 180);
py.y = xa0 * Math.sin(0 * deg * Math.PI / 180);
cctx.lineTo(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y);
cctx.stroke();
// an
for (let i = 0; i < xan.length; i ) {
const radius = xan[i];
// an circles
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.arc(xoo.x px.x, xoo.y px.y, Math.abs(radius), 0, 2 * Math.PI);
cctx.stroke();
// an lines
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(xoo.x px.x, xoo.y px.y);
px.x = radius * Math.cos((i 1) * deg * Math.PI / 180);
px.y = radius * Math.sin((i 1) * deg * Math.PI / 180);
cctx.lineTo(xoo.x px.x, xoo.y px.y);
cctx.stroke();
}
// bn
for (let i = 0; i < xbn.length; i ) {
const radius = xbn[i];
// bn circles
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.arc(xoo.x px.x, xoo.y px.y, Math.abs(radius), 0, 2 * Math.PI);
cctx.stroke();
// bn lines
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(xoo.x px.x, xoo.y px.y);
px.x = radius * Math.cos((i 1) * deg * Math.PI / 180);
px.y = radius * Math.sin((i 1) * deg * Math.PI / 180);
cctx.lineTo(xoo.x px.x, xoo.y px.y);
cctx.stroke();
}
// y oscillator line
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.moveTo(yoo.x py.x, yoo.y py.y);
cctx.lineTo(xoo.x px.x, yoo.y py.y);
cctx.stroke();
// x oscillator line
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.moveTo(xoo.x px.x, xoo.y px.y);
cctx.lineTo(xoo.x px.x, yoo.y py.y);
cctx.stroke();
// path
path.push({ x: px.x, y: py.y });
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(200 path[0].x, 200 path[0].y);
for (let i = 0; i < path.length; i ) {
cctx.lineTo(200 path[i].x, 200 path[i].y);
}
cctx.stroke();
// degree update
if (deg === 359) {
window.cancelAnimationFrame(rAF);
} else {
deg ;
}
}
So! I decided to be logical. First, I checked whether the converted path data is correct by drawing it at canvas. The below is the canvas code and the data.
let count = 0;
function draw_tick2() {
const rAF = window.requestAnimationFrame(draw_tick2);
const s = 100; // scale up
// initialize
cctx.clearRect(0, 0, 1000, 800);
cctx.beginPath();
// 200 has no meaning I just added it to move the path.
for (let i = 0; i < count; i ) {
if (i === 0) cctx.moveTo(200 s * cx[i], 200 s * cy[i]);
else cctx.lineTo(200 s * cx[i], 200 s * cy[i]);
}
cctx.stroke();
if (count < cx.length - 1) {
count ;
} else {
window.cancelAnimationFrame(rAF);
}
}
const paimon = 'm 0,0 -2.38235,-2.87867 -1.58823,-1.29045 -1.9853,-0.893384 -3.17647,-0.39706 1.58824,-1.98529 1.09191,-2.08456 v -2.38235 l -0.79412,-2.87868 1.88603,2.18383 1.6875,1.88602 1.78677,0.99265 1.78676,0.39706 1.78676,-0.19853 -1.6875,1.58824 -0.69485,1.68749 -0.0993,2.084564 0.39706,2.18383 9.62867,3.87132 2.77941,1.9853 4.66544,-1.09192 3.07721,-1.88603 1.9853,-2.58088 -3.97059,0.49633 -3.375,-0.79412 -2.87868,-2.58088 -2.08456,-3.077214 2.38235,1.48897 2.08456,0.19853 3.57353,-0.89338 2.58089,-2.48162 -3.07721,0.39706 -3.87132,-1.88603 -2.97794,-2.08456 -2.48162,-2.87868 -3.87133,-4.06985 -4.06985,-2.68015 -5.95588,-2.58088 -5.85662,-0.79412 -5.45956,0.99265 0.59559,1.6875 -0.99265,1.09191 -0.79412,3.47427 -1.29044,-2.97794 -0.89338,-1.19118 0.79412,-1.48897 1.6875,-0.79412 0.39706,-3.772057 1.48897,1.290441 1.78676,0.09926 -2.08456,-1.985293 1.78677,-0.893382 4.36765,-0.19853 4.86397,0.992648 1.19117,1.091912 -2.38235,1.985301 3.17647,-0.49633 2.87868,-2.680149 -3.57353,-2.580881 -5.45956,-1.488972 h -4.46691 l -3.6728,-3.176471 -0.79412,1.389706 -0.79411,-1.488969 0.69485,-0.595588 -1.58824,-3.871325 -0.39706,3.672795 -0.69485,0.297794 0.89338,1.091911 v 1.091912 h -1.19113 l -0.59559,-0.992648 -1.98529,2.878677 -4.06986,1.588236 -4.26838,1.985293 3.27574,3.871329 2.87867,1.88603 2.58088,0.29779 -2.58088,-1.58823 -0.89338,-2.084566 4.86397,-0.992645 -1.19118,2.382351 h 1.58824 l 1.48897,-1.88603 0.29779,2.77942 -2.38235,2.38235 -3.57353,2.87868 -3.97059,4.86397 -2.08456,3.67279 -2.58088,2.58088 -2.68015,1.09192 -3.17647,0.0993 -1.3897,-0.69485 1.09191,3.17647 2.18382,3.573534 3.375,2.38235 -1.78676,5.85662 -1.38971,6.05514 0.39706,4.36765 1.38971,4.66544 3.87132,4.46691 -0.79412,-3.57352 -0.49632,-4.06986 v -2.48162 l 1.78676,5.85662 3.07721,3.17647 3.07721,1.29044 3.37499,0.79412 2.28309,-0.89338 0.69486,-1.48897 -1.19118,0.49632 -2.48162,-1.98529 -2.28309,-2.87868 2.28309,2.48162 h 0.99265 l 0.69485,-0.49632 0.2978,-1.19118 0.0993,-0.79412 -0.89339,0.59559 -1.58823,-0.99265 -1.29044,-1.3897 -1.19118,-2.38236 -0.89338,-4.86397 -0.0993,-4.56617 0.29779,-4.96324 0.39706,0.89338 1.19118,-0.44669 0.0496,-0.89338 1.09191,0.69485 1.48897,0.2978 1.53861,0.89338 0.99264,0.64522 h -0.79411 l 0.49632,2.43199 -0.44669,1.58823 -1.78676,0.39706 -1.24081,-1.24081 -0.24817,-1.43934 0.84375,-0.94301 1.19118,-0.49633 1.14154,0.94302 0.24816,1.14154 -0.0993,1.48897 -1.83639,0.64523 -1.58824,-1.53861 -0.44669,-1.48897 -0.24816,-2.18382 -1.43934,0.99264 0.0496,-0.99264 -0.44669,1.78676 0.69485,3.12684 1.09192,4.26838 1.78676,1.78677 6.89889,3.02757 -2.53124,0.99265 -3.17647,1.3897 -0.79412,0.39706 0.59559,0.39706 1.34007,-0.69485 0.0496,1.19117 1.98529,-0.39705 2.68015,-0.44669 -0.2978,-1.93567 0.79412,1.58824 2.82905,-0.44669 4.06985,-1.34008 1.04229,-0.59559 -0.2978,-1.78676 -0.34743,-1.73713 -4.9136,2.48162 -2.58088,0.94301 -3.17648,-4.81434 1.53861,0.49633 1.3897,0.0496 1.43935,-0.24816 -1.34008,0.24816 h -1.58824 l -1.41452,-0.54596 3.12684,4.78953 2.63052,-0.89339 4.86397,-2.4568 2.65533,-2.08456 0.39706,-5.90625 -0.84375,1.5386 -1.14155,0.54596 -1.5386,0.19853 -1.29044,-0.89338 -0.59559,-1.09191 -0.24816,-1.73714 0.24816,-1.3897 -2.08456,0.54595 -0.29779,-0.34742 0.34743,-0.49633 0.64522,-0.39706 1.5386,-0.39705 2.18382,-0.19853 1.24081,0.0993 1.14154,0.54596 0.4467,1.43934 -0.19853,1.63786 -0.59559,1.29044 -1.24081,0.89339 -1.43934,-0.39706 -0.99264,-1.09191 -0.0496,-1.19118 0.79412,-0.89338 0.89338,-0.44669 1.19118,-0.0496 0.64522,1.04228 0.34742,0.79412 -0.14889,1.14155 0.99265,-0.4467 0.29779,-1.34007 -0.19853,-4.06985 -1.93566,-0.44669 -2.53125,-1.6875 -2.23346,-1.88603 -2.23345,-4.069864 -0.44669,3.920964 0.64522,4.21875 1.5386,3.92096 0.74448,0.44669 h -1.73713 l -2.18383,-0.54596 -3.12684,-2.08456 -1.58823,-2.28309 -1.14154,-2.08456 -1.29044,-3.871324 -1.38971,2.481624 -1.48897,2.63051 -0.94302,1.9853 3.8217,-6.948534 1.29044,3.672794 2.33272,3.92096 2.9283,2.13419 0.49633,0.44669 2.28309,0.49632 h 1.63787 l -0.69485,-0.69485 -0.84375,-1.93566 -1.34008,-5.80698 0.44669,-3.970594 2.33273,4.069854 4.56617,3.47426 2.08456,0.59559 0.19853,2.82905 -0.0496,3.97058 -0.0993,6.00552 -0.54595,3.02757 -1.58824,2.77941 -1.5386,0.89339 -1.19118,0.24816 -1.48897,-0.69485 -0.69485,-0.1489 0.69485,1.24081 1.43934,1.6875 2.68015,1.19117 3.17647,0.2978 3.77206,-2.23346 1.3897,-2.77941 0.89339,-3.82169 0.0496,-3.375 0.14889,6.25368 -1.14154,5.11213 -2.08456,3.27573 -2.08456,1.6875 -1.88603,0.59559 -2.28308,-0.79412 1.78676,1.6875 4.9136,1.88603 2.43199,0.2978 2.68015,-0.39706 2.72977,-1.09191 3.62317,-3.27574 0.89338,-3.97059 0.49632,-3.57353 -0.0993,-2.87867 -0.39706,-3.17647 -0.49632,-3.07721 1.98529,3.47427 1.19117,2.18382 0.39706,1.29044 0.39706,-2.28309 -0.39706,-3.0772 -1.29044,-3.77206 -1.29044,-2.87868 -1.6875,-3.27573 -10.125,-4.16912 z';
This is ★Paimon chan★. Thus it is proved that there are no flaws at the data, since all the data is plotted correctly.
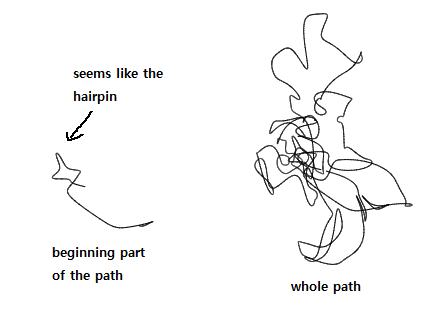
Next, I plotted the approximated (Fx(t), Fy(t)) points so that I can check whether there is a problem. And It turned out that there was a problem. But I don't understand what is the problem. At the same time this path is interesting; The beginning part of the path seems like the hairpin.
This is the drawing code:
function approxFn(t) {
let x = xa0;
let y = ya0;
for (let i = 0; i < xan.length; i ) {
x = xan[i] * Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * i * t / cx.length);
x = xbn[i] * Math.sin(2 * Math.PI * i * t / cx.length);
y = yan[i] * Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * i * t / cx.length);
y = ybn[i] * Math.sin(2 * Math.PI * i * t / cx.length);
}
return { x, y };
}
function draw_tick3() {
const rAF = window.requestAnimationFrame(draw_tick3);
const s = 5;
// initialize
cctx.clearRect(0, 0, 1000, 800);
cctx.beginPath();
for (let t = 0; t < count; t ) {
if (count === 0) cctx.moveTo(200 s * approxFn(t).x, 200 s * approxFn(t).y);
else cctx.lineTo(200 s * approxFn(t).x, 200 s * approxFn(t).y);
}
cctx.stroke();
if (count < cx.length - 1) {
count ;
} else {
window.cancelAnimationFrame(rAF);
}
}
The above is all the code in my js file. In where I made a mistake? It's a mystery! I know this question is exceptionally seriously long question. But please help me! I want to realize Paimon chan! ㅠwㅠ
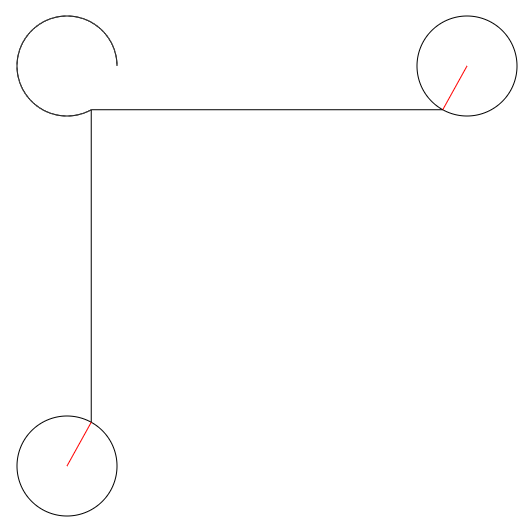
※ (This section is irrelevant with the question) Meanwhile I made a success to draw the path in a complex number plane. If you're interested, please see my work... I would like to add circle things to this but I have no idea what is 'radius' in this case.
// You can see that I used real part for x and imaginary part for y.
for (let i = 0; i <= count; i ) {
if (i === 0) {
cctx.moveTo(coords[i].real * scaler paimonPosition, coords[i].imag * scaler paimonPosition);
} else {
cctx.lineTo(coords[i].real * scaler paimonPosition, coords[i].imag * scaler paimonPosition);
}
}
And this is the result. But what makes me confused is a case of cn = -5000 ~ 5000. As far as I understand, more cn, more accurate as original wave. But why it crashes when cn is so big?
Anyways, thank you very much for reading this long question!
CodePudding user response: