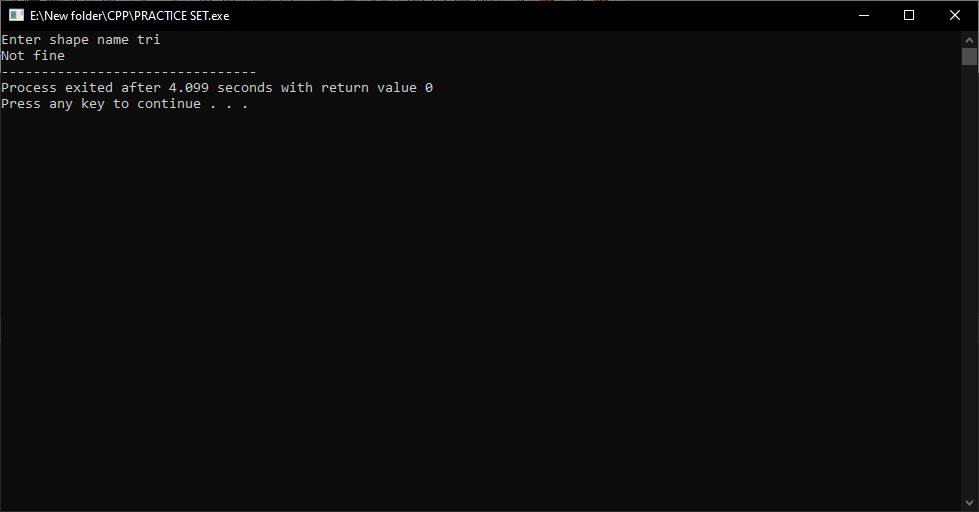
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char u[10];
cout<<"Enter shape name ";
cin>>u;
if(u=="tri")
{cout<<"everything is fine";}
else{cout<<"Not fine";}
return 0;
}
CodePudding user response:
You are comparing a Char with a String. You might want to rewrite it to this
int main(){
string u;
cout<<"Enter shape name ";
cin>>u;
if(u=="tri")
{cout<<"everything is fine";}
else{cout<<"Not fine";}
return 0;}
CodePudding user response:
The problem is that you're comparing two pointers instead of comparing two strings as explained below.
When your wrote:
if(u=="tri") //here both u and "tri" decay to pointers
{
}
In the above statement, u has type char[10] and it decays to a char* while the string literal "tri" has type const char[4] and it decays to a const char*, due to type decay. This means that you're comparing two pointers instead of comparing the contents of the two strings.
To avoid this problem you should use std::string as shown below:
int main()
{
std::string u; //used std::string
cout<<"Enter shape name ";
cin>>u;
if(u=="tri")
{
cout<<"everything is fine";
}
else
{
cout<<"Not fine";
}
}
