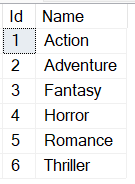I am building a Book List application. It has the following models:
- Book (int Id, string Title, string Type, int MinimumAge) [Id=Key, Title=Required, Type=Required, MinimumAge=Required]
- Genre (int Id, string Name) [Master table]
- BookGenre (int BookId, int GenreId) [Keyless Entity]
- CreateViewModel (Book Book, IEnumerable Genres)
Right now I am working on the CREATE operation.
CONTROLLER code (BookController.cs)
The Create() POST methods of this Controller is incomplete.
using BookList.Data;
using BookList.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace BookList.Controllers
{
public class BookController : Controller
{
private readonly ApplicationDbContext db;
public BookController(ApplicationDbContext db)
{
this.db = db;
}
// READ (Get)
public IActionResult Index()
{
IEnumerable<Book> bookList = db.Books;
return View(bookList);
}
// CREATE (Get)
public IActionResult Create()
{
// Create custom view model
CreateViewModel model = new CreateViewModel();
model.Book = new Book();
model.Genre = new Genre();
return View(model);
}
// CREATE (Post)
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public IActionResult Create(CreateViewModel obj)
{
// Write your code here
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
}
}
VIEW Code (Create.cshtml):
@model CreateViewModel
<div >
<div >
<div >
<h2 >Add a New Book</h2>
<hr />
</div>
<form asp-action="Create">
<div asp-validation-summary="All" ></div>
@* Title *@
<div >
<label asp-for="Book.Title"></label><br />
<input asp-for="Book.Title" />
<span asp-validation-for="Book.Title" ></span>
</div>
@* Genre *@
<div >
<label>Genre</label><br/>
<div>
@foreach(var genre in Model.Genres)
{
<label [email protected]>@genre.Name</label>
<input type="checkbox" [email protected] [email protected] />
}
</div>
</div>
@* Type(Fiction/Non-Fiction) *@
<div >
<label asp-for="Book.Type"></label><br />
<div>
Fiction <input type="radio" asp-for="Book.Type" value="Fiction" />
Non-Fiction <input type="radio" asp-for="Book.Type" value="Non-Fiction"/>
</div>
<span asp-validation-for="Book.Type" ></span>
</div>
@* Minimum Age(dropdown) *@
<div >
<label asp-for="Book.MinimumAge" ></label>
<select asp-for="Book.MinimumAge" >
<option value=8>8</option>
<option value=12>12</option>
<option value=16>16</option>
<option value=18>18</option>
</select>
<span asp-validation-for="Book.MinimumAge" ></span>
</div>
<div >
<input type="submit" value="Add" />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
@*Cient-side validation scripts*@
@section Scripts {
<partial name="_ValidationScriptsPartial" />
}
Let's say the user enters the following details and clicks Create:
Title="XYZ", Genres="Action,Adventure", Type="Fiction", Minimum Age=12
Then, I want (auto-id, "XYZ","Fiction",12) to go into the Book table. And, (auto-id,1) and (auto-id,2) to go into the BookGenre table.
For your reference, the Genre master table contains the following details. And BookGenre table is a Keyless entity.
CodePudding user response:
You need firstly know that model binding system bind data by name attribute.
From the view design I can see your CreateViewModel contains IEnumerable<Genre> Genres, so the frontend should add name like:Genres[index].PropertyName. But then you will find a problem that if you want to choose discontinuous checkbox, you will receive only continuous value and miss the discontinuous ones.
So suggest you also create a property List<string> GenresList and add name="GenresList" in your frontend.
Here is a whole working demo:
Model:
public class Book
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public int MininumAge { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Type { get; set; }
public ICollection<Genre>? Genres { get; set; }
}
public class Genre
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public ICollection<Book>? Books { get; set; }
}
public class CreateViewModel
{
public Book Book { get; set; }
public List<Genre>? Genres { get; set; }
public List<string> GenresList { get; set; }
}
View:
@model CreateViewModel
<div >
<div >
<div >
<h2 >Add a New Book</h2>
<hr />
</div>
<form asp-action="Create">
<div asp-validation-summary="All" ></div>
@* Title *@
<div >
<label asp-for="Book.Title"></label><br />
<input asp-for="Book.Title" />
<span asp-validation-for="Book.Title" ></span>
</div>
@* Genre *@
<div >
<label>Genre</label><br/>
<div>
@foreach(var genre in Model.Genres)
{
<label [email protected]>@genre.Name</label> @* add name here*@
<input type="checkbox" [email protected] [email protected] name="GenresList"/>
}
</div>
</div>
@* Type(Fiction/Non-Fiction) *@
<div >
<label asp-for="Book.Type"></label><br />
<div>
Fiction <input type="radio" asp-for="Book.Type" value="Fiction" />
Non-Fiction <input type="radio" asp-for="Book.Type" value="Non-Fiction"/>
</div>
<span asp-validation-for="Book.Type" ></span>
</div>
@* Minimum Age(dropdown) *@
<div >
<label asp-for="Book.MininumAge" ></label>
<select asp-for="Book.MininumAge" >
<option value=8>8</option>
<option value=12>12</option>
<option value=16>16</option>
<option value=18>18</option>
</select>
<span asp-validation-for="Book.MininumAge" ></span>
</div>
<div >
<input type="submit" value="Add" />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
@{await Html.RenderPartialAsync("_ValidationScriptsPartial");}
}
Controller:
public class BooksController : Controller
{
private readonly MvcProj6_0Context _context;
public BooksController(MvcProj6_0Context context)
{
_context = context;
}
// GET: Books/Create
public IActionResult Create()
{
CreateViewModel model = new CreateViewModel();
model.Book = new Book();
model.Genres = _context.Genre.ToList();
return View(model);
}
// POST: Books/Create
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActionResult> Create(CreateViewModel obj)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
var genres = new List<Genre>();
foreach (var item in obj.GenresList)
{
genres.Add(_context.Genre.Where(a => a.Name == item).First());
}
obj.Book.Genres = genres;
_context.Add(obj.Book);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
return View(obj);
}
}
Note:
In .NET 6, it includes the <Nullable>enable</Nullable> element in the project file which makes the property non-nullable. The non-nullable property must be required, otherwise the ModelState will be invalid. You can use ? or initialize the property in the model design to skip the required validation.