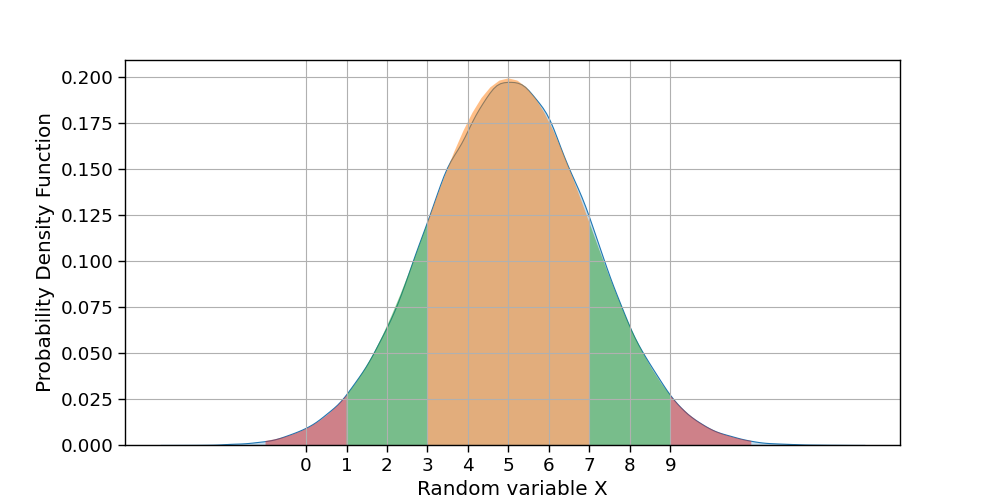
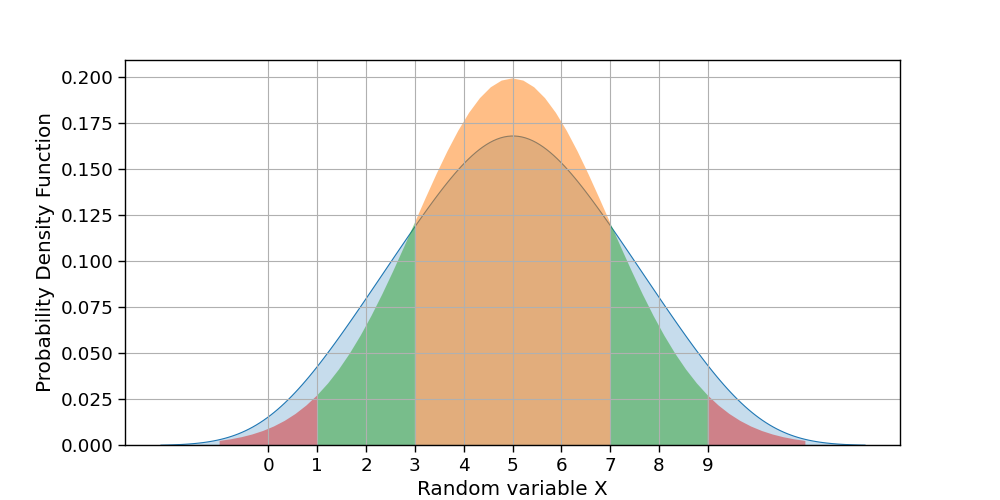
Recently I started learning Probability and Statistics for Datascience. I am trying to plot Standard Deviation for the below distribution X, like 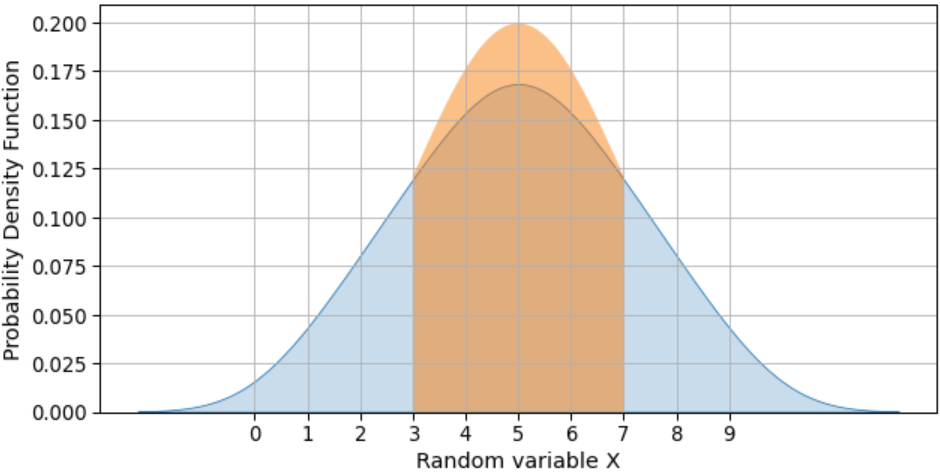
Questions:
- What is wrong in the code plotting 1 std from mean?
- I am not able to understand why there is a small peak above the
kdeplot? - How to plot 1-std, 2-std and 3-std?
CodePudding user response:
Nothing wrong in your code: mean is
5and std2, so you are shading an area between5 - 2 = 3and5 2 = 7.There is a small peak in the
kdeplot because it is a representation of the data distribution you give withXand, actually,Xis not a normal distribution. You can check this by using a true normal distribution:mean = 5 std = 2 X = np.random.randn(10000) X = (X - X.mean())/X.std()*std meanYou can plot other standard devaitions with a for loop over
i.x1is the left side,x2is the center part (then set tonp.nan) and finallyx3is the right side of the distribution. Then you have to set tonp.nanareas to exclude (which correspond tox2):N = 10 for i in [1, 2, 3]: x1 = np.linspace(mean - i*std, mean - (i - 1)*std, N) x2 = np.linspace(mean - (i - 1)*std, mean (i - 1)*std, N) x3 = np.linspace(mean (i - 1)*std, mean i*std, N) x = np.concatenate((x1, x2, x3)) x = np.where((mean - (i - 1)*std < x) & (x < mean (i - 1)*std), np.nan, x) y = norm.pdf(x, mean, std) ax.fill_between(x, y, alpha=0.5)
Complete Code
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import norm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
# Line width: Maximum 130 characters in the output, post which it will continue in next line.
np.set_printoptions(linewidth=130)
sns.set_context("paper", font_scale=1.5)
# Distribution
X = [1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9]
mean = np.mean(X)
var = np.var(X)
std = np.std(X)
print("Mean:", mean)
print("Variance:", var)
print("Standard Deviation:", std)
"""
Mean: 5.0
Variance: 4.0
Standard Deviation: 2.0
"""
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
ax = sns.kdeplot(X, shade=True)
N = 10
for i in [1, 2, 3]:
x1 = np.linspace(mean - i*std, mean - (i - 1)*std, N)
x2 = np.linspace(mean - (i - 1)*std, mean (i - 1)*std, N)
x3 = np.linspace(mean (i - 1)*std, mean i*std, N)
x = np.concatenate((x1, x2, x3))
x = np.where((mean - (i - 1)*std < x) & (x < mean (i - 1)*std), np.nan, x)
y = norm.pdf(x, mean, std)
ax.fill_between(x, y, alpha=0.5)
plt.xlabel("Random variable X")
plt.ylabel("Probability Density Function")
plt.xticks(ticks=range(0, 10))
plt.grid()
plt.show()